If you are interested in products and services related to the research phase in this field, please contact for further inquiries.
The field of rehabilitation has seen significant advancements with the advent of robotic exoskeletons, and the Nukawa exoskeleton system stands out as a pioneering development in this domain. Designed to provide dynamic support and precise control for lower limb rehabilitation, the Nukawa system integrates cutting-edge technology with ergonomic design principles, offering a tailored solution for patients with mobility impairments. This article delves into the intricacies of the Nukawa exoskeleton, exploring its design, functionality, safety features, and potential impact on rehabilitation practices.
Introduction to the Nukawa Exoskeleton System
The Nukawa exoskeleton system is a state-of-the-art rehabilitation device developed by researchers at the Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana in Medellín, Colombia. This innovative system aims to enhance the rehabilitation process for patients with lower limb injuries and mobility impairments by providing dynamic support and precise control through robotics and surface electromyography. Unlike traditional orthopedic devices, which often fail to consider individual anthropometric and ergonomic factors, the Nukawa system is designed to adapt to a wide range of body shapes and sizes, ensuring optimal comfort and functionality for each patient.
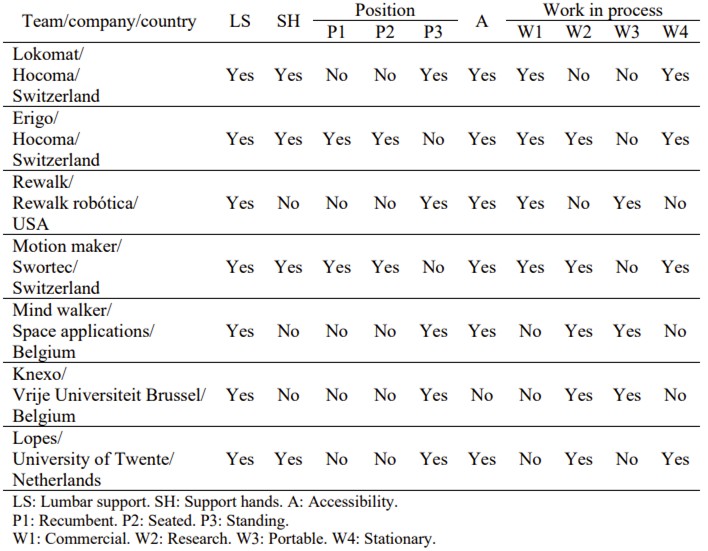 Fig.1 Summary of fixation systems for rehabilitation devices. (Páramo-Velásquez C. A., et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Summary of fixation systems for rehabilitation devices. (Páramo-Velásquez C. A., et al., 2019)
The Need for Advanced Rehabilitation Solutions
Traditional rehabilitation methods often rely on manual assistance from therapists, which can be time-consuming and inconsistent. Moreover, generic orthopedic devices may not adequately support patients with varying body shapes and sizes, leading to discomfort and potential complications. The Nukawa exoskeleton addresses these limitations by offering a customizable and dynamic support system that enhances the rehabilitation process. By leveraging robotic technology and surface electromyography, the Nukawa system can precisely control and monitor the rehabilitation exercises, providing valuable data to therapists and improving patient outcomes.
Design Methodology and Innovation
The development of the Nukawa exoskeleton followed a rigorous methodology, combining top-down design principles with network design and brainstorming techniques. This approach ensured that the final product met the diverse needs of patients and healthcare providers. The design process began with a comprehensive survey of requirements, focusing on key elements such as lumbar support, hand support, fixation mode, grip, and suspension.
Anthropometric and Ergonomic Considerations
Anthropometric analysis, which involves studying the physical dimensions and characteristics of the human body, was crucial in designing the Nukawa exoskeleton. By considering factors such as height, weight, and limb length, the researchers were able to create a modular orthosis system that adapts to individual patients, ensuring optimal comfort and functionality. Ergonomic considerations were equally important, as the exoskeleton needed to be intuitive and easy to use. The design team focused on creating a user-friendly interface that minimizes the risk of injury and muscle fatigue.
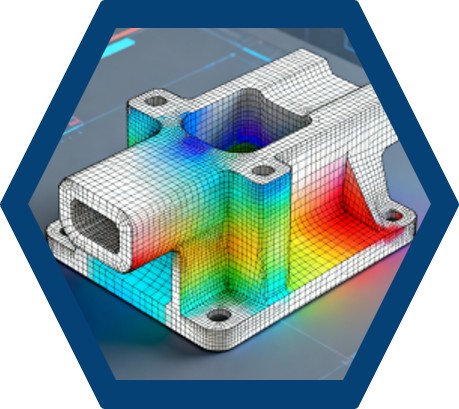
Virtual Prototyping and Finite Element Analysis
Once the initial design requirements were established, the team used computer-aided design (CAD) software to create virtual three-dimensional models of the exoskeleton. This allowed them to visualize and refine the design before moving on to physical prototyping. The CAD models were then analyzed using finite element software, which evaluated the structural integrity and resistance of the components. Finite element analysis is a powerful tool that simulates how a design will perform under various conditions. By subjecting the virtual models to different loads and stresses, the researchers could identify potential weaknesses and make necessary adjustments.
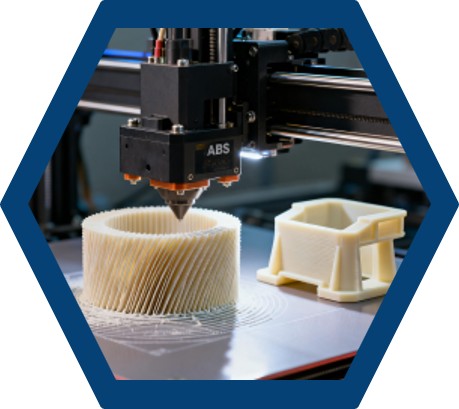
Additive Manufacturing and Material Selection
The advent of additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has transformed the way engineers approach prototyping. For the Nukawa exoskeleton, 3D printing offered a cost-effective and efficient way to produce physical models of the design. The team selected acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) as the primary material, known for its strength and durability. Using an Ultimaker 2+ 3D printer, the researchers were able to quickly iterate and refine the design, making adjustments based on real-world testing.
Functional Verification and Safety Measures
With the prototype in hand, the next step was to verify its functionality and safety. This involved rigorous testing and validation, ensuring that the exoskeleton met all relevant standards and requirements. The team developed a comprehensive protocol for functional verification, incorporating feedback from physiotherapists, doctors, and bioengineers.
- Safety Systems and Protocols
Safety is paramount in any medical device, and the Nukawa exoskeleton is no exception. The team implemented a range of safety features to protect both the patient and the equipment. One such feature is the emergency stop system, which allows both the patient and medical personnel to halt the device in case of an emergency. The system uses commercial controllers and inductive sensors to detect dangerous positions and stop the machine within two seconds.
In addition to the emergency stop system, the exoskeleton incorporates mechanical and electrical stops at each joint to prevent excessive movement. These stops reduce the risk of injury by limiting the range of motion within safe parameters. The team also designed protective casings for the moving parts, ensuring that patients and therapists are not exposed to potential hazards.
- Ergonomic and Semiotic Design
The Nukawa exoskeleton is not just a functional device; it is also designed with the user experience in mind. The ergonomic design ensures that the device is comfortable and easy to use, with adjustable supports and fixation systems that adapt to individual patients. The semiotic design, which focuses on the visual and tactile aspects of the device, further enhances usability. The team developed a semiotic proposal to guide the design of the exoskeleton, incorporating color schemes and visual cues to indicate the direction of movement and the location of key components.
Practical Applications and Future Directions
The Nukawa exoskeleton has the potential to revolutionize lower limb rehabilitation, offering a dynamic and customizable solution for patients with a range of mobility impairments. By integrating robotic technology with ergonomic design principles, the device provides a level of support and precision that traditional orthopedic devices cannot match.
Potential Impact on Rehabilitation
The introduction of the Nukawa exoskeleton could have a significant impact on the field of rehabilitation. By providing dynamic support and precise control, the device can enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation exercises, leading to faster recovery times and improved patient outcomes. The modular design also allows for customization, ensuring that each patient receives the support they need.
Moreover, the Nukawa system can be used in various settings, from hospitals and rehabilitation centers to home-based care. Its portability and ease of use make it a versatile tool for therapists and patients alike, offering a flexible solution for lower limb rehabilitation.
Future Developments and Research
While the Nukawa exoskeleton represents a significant advancement in rehabilitation technology, there is still room for improvement. Future research will focus on refining the design and incorporating additional features, such as surface electromyography, to further enhance the device's capabilities. This technology will allow for real-time monitoring of muscle activity, providing valuable feedback to therapists and ensuring that the correct muscle groups are being activated during rehabilitation exercises.
Additionally, the team plans to conduct clinical trials to test the efficacy of the Nukawa system on patients with various mobility impairments. These trials will provide valuable data on the device's performance and help identify any areas for improvement. The ultimate goal is to make the Nukawa exoskeleton widely available, improving access to high-quality rehabilitation services for individuals in need.
Conclusion: A New Era in Rehabilitation Technology
The Nukawa lower limb rehabilitation device marks a new era in the field of biomedical engineering and rehabilitation. By combining advanced robotics with ergonomic design principles, the device offers a dynamic and customizable solution for patients with mobility impairments. The rigorous design process, incorporating virtual prototyping, finite element analysis, and functional verification, ensures that the Nukawa exoskeleton is both safe and effective.
As research and development continue, the potential applications of the Nukawa system are vast. From enhancing the rehabilitation process to improving patient outcomes, this innovative device has the power to transform lives. The future of rehabilitation is bright, and the Nukawa exoskeleton is leading the way.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Páramo-Velásquez, C. A., et al. "System for supporting and fixing body segment for nukawa lower limb rehabilitation device." Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Vol. 1418. No. 1. IOP Publishing, 2019.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
Lower Limb Fixation Series



 Fig.1 Summary of fixation systems for rehabilitation devices. (Páramo-Velásquez C. A., et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Summary of fixation systems for rehabilitation devices. (Páramo-Velásquez C. A., et al., 2019)