If you are interested in products and services related to the research phase in this field, please contact for further inquiries.
Intelligent human-machine synergy systems (IHMSS) represent a pivotal advancement in the integration of human physiology and artificial intelligence. These systems, encompassing rehabilitation equipment, active prostheses, and exoskeletons, are designed to enhance human mobility and functionality by interpreting and responding to human motion intentions. The key to the effectiveness of IHMSS lies in the accurate and timely decoding of these intentions, which is where surface electromyogram (sEMG) signals play a crucial role. sEMG signals, captured non-invasively from muscles, provide a rich dataset that can be analyzed to predict and facilitate human movements. This article delves into the significance of a comprehensive dataset for lower limb movement intent recognition, specifically focusing on the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology Lower Limb Motion Dataset (SIAT-LLMD).
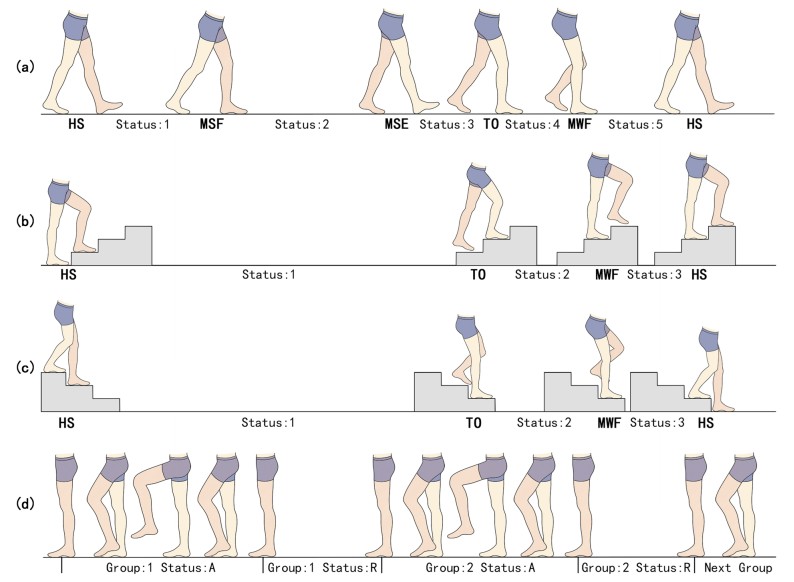 Fig.1 Description of the labels associated with the limb movements. (a) Shows the labels for WAK; (b) Shows the labels for UPS; (c) Present the labels for DNS; and (d) Represent the labels of other movements. (Wei W., et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Description of the labels associated with the limb movements. (a) Shows the labels for WAK; (b) Shows the labels for UPS; (c) Present the labels for DNS; and (d) Represent the labels of other movements. (Wei W., et al., 2023)
The Importance of Comprehensive Datasets in IHMSS Development
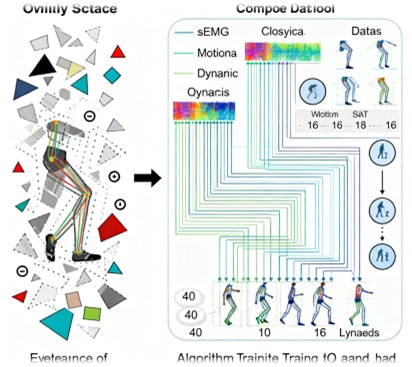
The development of robust IHMSS requires extensive and diverse datasets to train and validate algorithms that can accurately interpret human motion intentions. Existing datasets for lower limb movement characterization often fall short due to limitations in the types of movements captured and the lack of detailed gait phase labels. These limitations hinder the ability to conduct thorough investigations into gait phase characterization and to ensure fair comparisons between different machine learning algorithms. The SIAT-LLMD addresses these shortcomings by providing a comprehensive dataset that includes sEMG, kinematic, and kinetic data from 40 healthy subjects performing 16 different lower limb movements. This dataset not only includes detailed gait phase labels but also offers a diverse range of movements, making it a valuable resource for advancing research in lower limb movement intent recognition.
The SIAT-LLMD Dataset: A Detailed Overview
The SIAT-LLMD dataset is a meticulously curated collection of lower limb movement data designed to support the development of advanced algorithms and models for characterizing lower limb motion. The dataset comprises:
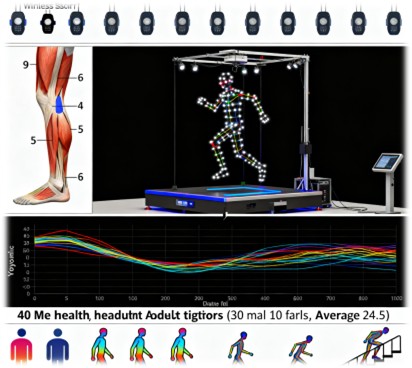
- sEMG Data: Captured using nine wireless sensors placed on the thigh and calf muscles of the left limb.
- Kinematic Data: Collected using a motion capture system with 41 reflective markers.
- Kinetic Data: Recorded using six-dimensional force platforms.
- Labels: Provided for movement classification and gait phase analysis.
The dataset was collected from 40 healthy adult subjects, including 30 males and 10 females, with an average age of 24.5 years. The subjects performed a variety of movements, including walking on level ground, climbing stairs, sitting down, standing up, and various discrete movements such as knee lifts and leg lifts. The inclusion of both continuous and discrete movements ensures that the dataset can support a wide range of research applications.
Experimental Setup and Data Collection Methodology
The data collection process for the SIAT-LLMD involved a sophisticated experimental setup to ensure high accuracy and reliability. The motion capture system used six cameras to track the 3D trajectories of the reflective markers placed on the subjects' bodies. The force platforms recorded ground reaction forces, and the sEMG acquisition system captured muscle activity signals. To ensure data synchronization, the experiment was carefully designed to align the sEMG signals with the motion capture and force platform data. The subjects were prepared by cleaning their skin to reduce electrode impedance and securing the sEMG sensors with double-sided tape. The experiment involved a series of movements, each performed multiple times to ensure data repeatability.
Data Processing and Analysis Techniques
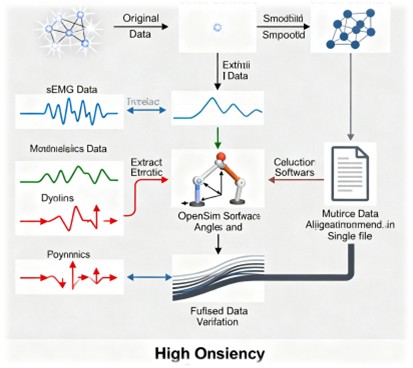
The collected data underwent several processing steps to ensure its usability for research purposes. These steps included:
- Markers Data Processing: Missing markers were fixed, and the data was smoothed using the Cortex Software.
- Data Extraction: The sEMG data, kinematic data, and kinetic data were extracted from the processed files.
- Kinematics and Kinetics Computation: The OpenSim software was used to calculate joint angles and torques from the extracted data.
- Data Alignment: The sEMG, kinematic, and kinetic datasets were aligned and combined into a single file for each subject and movement.
The dataset was validated for repeatability and synchronization. The results showed high consistency in the movement data, with average R-square values above 0.80 for most movements, indicating good data repeatability. The synchronization between the sEMG acquisition system and the motion capture system was verified, ensuring that the data from different sources aligned correctly.
Technical Validation and Results
The SIAT-LLMD dataset was subjected to rigorous technical validation to assess its accuracy and reliability. The validation process included:
- Repeatability Analysis: The consistency of the data was evaluated by calculating the coefficient of determination (R²) for each movement. The results showed high repeatability, with most R² values above 0.80.
- Synchronization Check: The synchronization between the sEMG acquisition system and the motion capture system was verified, ensuring that the data from different sources aligned correctly.
- Classification and Regression Analysis: The dataset was used to train and test machine learning models, including Support Vector Machines (SVM) and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) classifiers, as well as Gaussian Process Regression models. The classification accuracy for 12 movements was 90.74% using SVM and 85.06% using KNN. The regression models showed low Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) values, indicating accurate prediction of joint angles and torques.
Potential Applications and Future Work
The SIAT-LLMD dataset offers numerous applications in the field of human-machine synergy. It can be used to develop advanced algorithms for real-time movement intent recognition, improve the control systems of prosthetic limbs and exoskeletons, and enhance rehabilitation protocols for patients with mobility impairments. Future work may involve expanding the dataset to include a wider range of movements and subjects, exploring the use of deep learning techniques for more accurate predictions, and integrating the dataset with other modalities such as EEG and ECG to provide a more comprehensive understanding of human movement.
Conclusion
The SIAT-LLMD dataset represents a significant advancement in the field of intelligent human-machine synergy systems. By providing a comprehensive and well-documented dataset of lower limb movements, it enables researchers to develop more accurate and effective algorithms for movement intent recognition. The dataset's high repeatability and synchronization make it a reliable resource for advancing research and development in this exciting field. As technology continues to evolve, the SIAT-LLMD dataset will play a crucial role in shaping the future of human-machine interaction and mobility assistance.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Wei, Wenhao, et al. "Surface electromyogram, kinematic, and kinetic dataset of lower limb walking for movement intent recognition." Scientific Data 10.1 (2023): 358.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
Lower Limb Fixation Series



 Fig.1 Description of the labels associated with the limb movements. (a) Shows the labels for WAK; (b) Shows the labels for UPS; (c) Present the labels for DNS; and (d) Represent the labels of other movements. (Wei W., et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Description of the labels associated with the limb movements. (a) Shows the labels for WAK; (b) Shows the labels for UPS; (c) Present the labels for DNS; and (d) Represent the labels of other movements. (Wei W., et al., 2023)