- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Autoimmune Diseases
- A Comprehensive Overview of Diagnostic Methods for Sjögren's Syndrome
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Sjögren's syndrome is a complex and often underdiagnosed systemic autoimmune disease. Accurate diagnosis presents significant clinical challenges due to the high degree of symptom overlap with other conditions and the lack of a single confirmatory test. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of Sjögren's syndrome diagnosis and details a multifaceted approach, including advanced serological testing, objective functional assays, and morphological analysis. Read on to explore the specific criteria, cutting-edge biomarkers, and detailed testing methods that form the cornerstone of an effective diagnostic strategy.
Sjögren's syndrome is a chronic systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by the body's immune system mistakenly attacking its own moisture-producing glands, primarily the salivary and lacrimal glands. This leads to the hallmark symptoms of dry eyes (xerophthalmia) and dry mouth (xerostomia). However, the disease often extends beyond glandular involvement, potentially affecting various organs and causing debilitating fatigue, joint pain, and complications in the skin, lungs, kidneys, and nervous system. Diagnosis is complex and requires a multifaceted approach, integrating clinical evaluation of symptoms with objective testing.
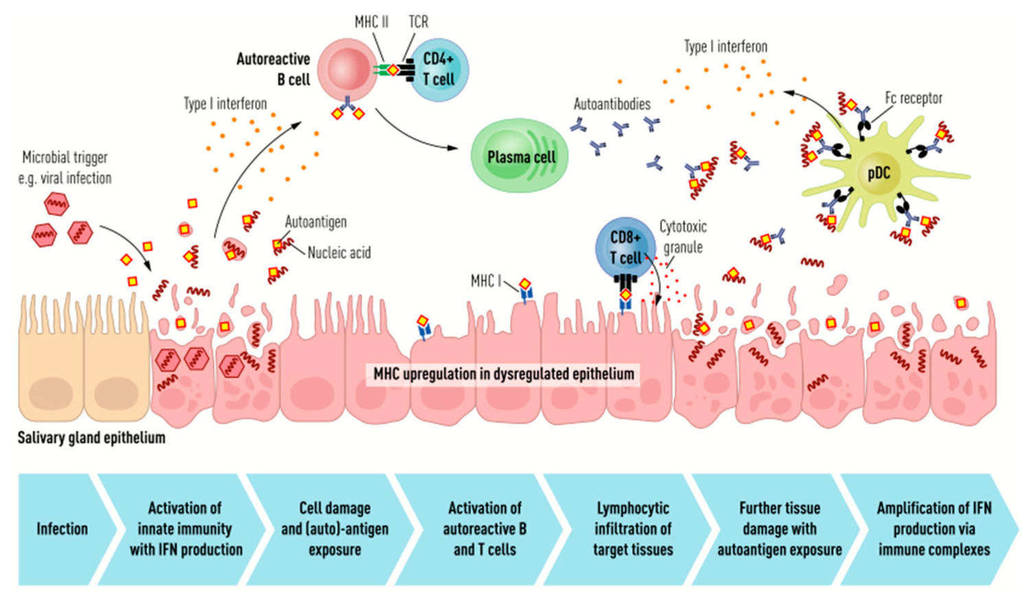 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the pathogenetic mechanisms at the basis of Sjögren's syndrome. (Kelly A L, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the pathogenetic mechanisms at the basis of Sjögren's syndrome. (Kelly A L, et al., 2022)
Serological testing forms the cornerstone of the objective diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome. While clinical symptoms provide the initial suspicion, it is the detection of specific autoantibodies in the blood that delivers crucial, measurable evidence of the underlying autoimmune dysfunction. These tests are indispensable for differentiating Sjögren's from other conditions with overlapping symptoms and are integral to formal classification criteria. The most significant serological markers include:
Anti-SSA (Ro) and Anti-SSB (La) Antibodies
These are the most specific autoantibodies associated with Sjögren's syndrome. The presence of anti-SSA/Ro is a powerful predictor and is a key component in modern diagnostic criteria. Anti-SSB/La is often found alongside anti-SSA/Ro, and their combined presence further strengthens the serological profile. It is important to note that a subset of patients ("seronegative") will not have these antibodies, necessitating further diagnostic investigation.
Antinuclear Antibody (ANA)
A positive ANA test is a common, highly sensitive screening tool for autoimmunity and is frequently seen in Sjögren's patients. However, it is not specific to Sjögren's, as it is positive in many other autoimmune diseases. Therefore, it is often used as an initial test to justify more specific antibody profiling.
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
This antibody is commonly detected in Sjögren's syndrome, even in patients without rheumatoid arthritis. Its presence adds supporting evidence to the autoimmune picture.

Polyclonal Hypergammaglobulinemia
This is not a specific test for a single antibody but rather a general finding of elevated immunoglobulins (antibodies) in the blood. It reflects the widespread B-cell hyperactivity and immune system dysregulation characteristic of the disease.
While serological testing reveals the autoimmune cause of Sjögren's syndrome, functional and morphological tests are essential for objectively measuring the glandular damage and its physiological impact. These tests provide tangible, quantifiable evidence of exocrine gland dysfunction, which is a critical requirement for formal diagnosis according to current classification criteria (e.g., ACR/EULAR). They are crucial for assessing the severity of disease and for confirming diagnosis in patients who are seronegative.
Functional tests quantitatively measure the output of exocrine glands to objectively assess impairment. The most common examples include the Schirmer's test, which measures tear production by placing filter paper under the eyelid, and sialometry, which evaluates saliva flow rates either in an unstimulated or stimulated state. These tests provide critical, numerical data on gland function, helping to confirm sicca symptoms and quantify disease severity beyond subjective patient reports.

Salivary gland ultrasonography is a key non-invasive method that reveals characteristic abnormalities like parenchymal inhomogeneity and hypoechoic areas, while the minor salivary gland biopsy (lip biopsy) remains the histological gold standard, directly showing focal lymphocytic infiltration and providing a focus score for diagnosis. These tests offer tangible evidence of glandular injury, especially valuable in seronegative cases.

Ocular surface staining evaluates damage to the eye caused by dryness, rather than measuring tear production directly. Using dyes such as Lissamine Green or Rose Bengal, this test stains devitalized cells on the corneal and conjunctival surfaces. The resulting staining pattern is scored to objectively grade the severity of keratoconjunctivitis sicca, providing a visual confirmation of dry eye disease that complements functional tear measurements.
The journey to a definitive Sjögren's syndrome diagnosis is often a process of exclusion, as its core symptoms of fatigue, pain, and dryness are highly non-specific and overlap with numerous other conditions. Furthermore, a significant number of patients present with negative results for the classic biomarkers, anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La, creating a diagnostic dilemma. This makes a structured approach to differential diagnosis and the pursuit of novel biomarkers critical for advancing clinical practice.
Differential Diagnosis
Key disorders to rule out include systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), IgG4-related disease, sarcoidosis, fibromyalgia, and side effects of medications, as well as viral infections like hepatitis C and HIV. This process relies on a combination of detailed clinical evaluation, targeted serological testing (e.g., anti-CCP for RA, anti-dsDNA for SLE), and sometimes histological or radiological findings.
Evolving Biomarkers
Research is focused on novel autoantibodies (e.g., anti-SP1, anti-CA6, anti-PSP), which may appear earlier or in different disease subsets, as well as molecular markers such as BAFF cytokine levels, salivary proteomic profiles, and characteristic salivary gland ultrasonography patterns. These emerging tools hold promise for improving diagnostic sensitivity, enabling earlier detection, identifying clinical subtypes.
In summary, the diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome relies on a multifaceted approach that integrates clinical evaluation, serological testing, functional assessments, and morphological analysis. This comprehensive strategy is essential to accurately identify the disease, distinguish it from overlapping conditions, and address the unique challenges of seronegative cases. As research continues to advance, the emergence of novel biomarkers and refined diagnostic technologies promises to further enhance early detection, improve diagnostic precision, and ultimately support more personalized and effective management strategies for patients.
Alta DiagnoTech provides a comprehensive IVD solution for Sjögren's syndrome, including autoantibody assays (anti-SSA/Ro, anti-SSB/La, ANA), functional test kits, and emerging biomarker panels. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
| Cat.No | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| EK-YJL-0350 | Rat Rheumatoid Factor (RF) ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EK-YJL-1458 | Human Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Antibody (IgM) ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EK-YJL-3616 | Human Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Antibody (IgG) ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EK-YJL-1467 | Human Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Antibody (IgA) ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| MK-QCY-0011 | Antinuclear Antibody Spectrum Test Kit (Microarray Chip Method) | Add To Cart |
| EC-008 | Murine IL-1 alpha ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EC-0011 | Murine IL-12 ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EC-007 | Human IL-22 ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EC-0057 | Human CD213a2 ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EC-0048 | Human CD117 ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| CA-00182 | EBV VCA IgG rapid assay kit | Add To Cart |
| EC-0079 | Human IL-8 ELISA kit | Add To Cart |
| IP-00177 | Cryptococcus antigen rapid assay kit | Add To Cart |
| EC-0074 | Human IL-17F ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| CA-00153 | Chagas rapid assay kit | Add To Cart |
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |