- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- The Power of MALDI-TOF MS: Revolutionizing Microbial Identification in Hospitals
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has emerged as a transformative technology in the field of clinical microbiology. This advanced diagnostic tool offers rapid, accurate, and cost-effective identification of microorganisms, significantly enhancing the ability to manage infections in healthcare settings. By analyzing the unique protein profiles of bacteria and fungi, MALDI-TOF MS provides a comprehensive overview of the microbial landscape, enabling clinicians to implement targeted treatments and infection control measures more effectively.
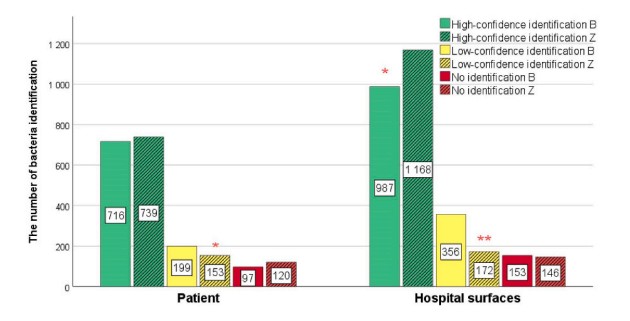 Fig.1 Comparative analysis of microorganism identification using BRUKER (B) and ZYBIO (Z) systems. (Czeszewska-Rosiak G., et al., 2025)
Fig.1 Comparative analysis of microorganism identification using BRUKER (B) and ZYBIO (Z) systems. (Czeszewska-Rosiak G., et al., 2025)
Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) pose a significant threat to patient safety, particularly in vulnerable populations such as oncology patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The rapid identification of pathogens is crucial for initiating appropriate antimicrobial therapy and reducing morbidity and mortality. Traditional methods, such as Gram staining and biochemical tests, often lack the sensitivity and speed required for timely diagnosis. Molecular techniques like PCR offer high sensitivity but are limited in their ability to provide a complete microbial profile. MALDI-TOF MS bridges this gap by offering rapid, accurate identification of a broad range of microorganisms, thereby enhancing patient outcomes.
MALDI-TOF MS operates by ionizing proteins from microbial colonies using a laser. The ionized proteins are then analyzed based on their time-of-flight, which is converted into a mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). This spectral profile is compared against a reference database to identify the microorganism. The technology's ability to analyze ribosomal proteins provides a highly specific and sensitive identification method. Since its introduction in the 1970s, MALDI-TOF MS has become a cornerstone of clinical microbiology, displacing traditional biochemical methods in many laboratories.

Recent studies have compared the performance of different MALDI-TOF MS systems, such as BRUKER and ZYBIO. Both systems demonstrated high accuracy and consistency in identifying microorganisms at the genus and species levels. However, discrepancies were noted in the identification of certain genera, including Brevibacterium, Streptococcus, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, and Neisseria. These differences can be attributed to variations in reference spectra generation and database composition. For instance, the BRUKER system may struggle with identifying certain Bacillus species, while the ZYBIO system might group closely related Neisseria species into broader categories. These findings highlight the importance of selecting the appropriate system based on the specific needs of the clinical laboratory.

A comprehensive study conducted at the Maria Skłodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology in Poland analyzed 189 samples from both patient and environmental sources. The study identified 96 species from patient samples and 124 species from hospital surfaces, highlighting the diverse microbial landscape within healthcare environments. The most commonly identified microorganisms included Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus salivarius, and Micrococcus luteus. The presence of these microorganisms underscores the potential for cross-contamination between patients and their surroundings, emphasizing the need for stringent infection control measures.

The ability to rapidly identify pathogens using MALDI-TOF MS allows for the implementation of targeted infection control strategies. By identifying potential sources of infection, healthcare providers can take proactive measures to reduce the risk of transmission. For example, the identification of Staphylococcus aureus on hospital surfaces can prompt enhanced cleaning protocols and patient isolation measures. Additionally, the technology's speed and accuracy enable faster initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy, reducing the time patients spend on broad-spectrum antibiotics and minimizing the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
Despite its advantages, MALDI-TOF MS faces challenges in accurately identifying certain microorganisms. For instance, the identification of Streptococcus and Neisseria species can be problematic due to their high genetic similarity and the limitations of reference databases. To address these challenges, ongoing enhancements in database expansion and the integration of external spectral databases are essential. Additionally, the use of MALDI-TOF MS in combination with other diagnostic tools, such as PCR and next-generation sequencing, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the microbial landscape.
MALDI-TOF MS has revolutionized microbial identification in hospitals by offering rapid, accurate, and cost-effective solutions. The technology's ability to analyze a broad range of microorganisms provides valuable insights into the microbial landscape, enabling targeted infection control measures and improved patient outcomes. As the field continues to evolve, the integration of advanced technologies and the expansion of reference databases will further enhance the diagnostic capabilities of MALDI-TOF MS, ensuring its continued relevance in the fight against hospital-acquired infections.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00203
Rotavirus Antigen Group A and Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00206
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00207
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00211
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00212
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. IP-00189
Influenza A Rapid Assay Kit

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00200
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00201
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00202
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00208
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00209
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit(Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00210
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
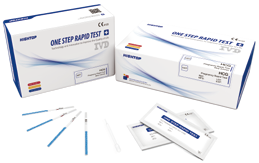
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0001
hCG Pregnancy Test Strip
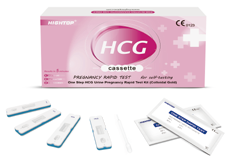
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0002
hCG Pregnancy Test Cassette
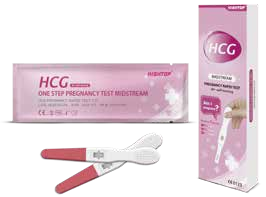
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0003
hCG Pregnancy Test Midstream

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0001
Cocaine (COC) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0002
Marijuana (THC) Rapid Test Kit
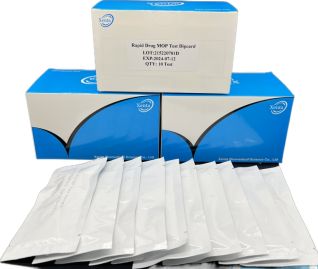
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0003
Morphine (MOP300) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0004
Methamphetamine (MET) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0005
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine ecstasy (MDMA) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0006
Amphetamine (AMP) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0007
Barbiturates (BAR) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0008
Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0009
Methadone (MTD) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0011
Opiate (OPI) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0002
Multi-Drug Test L-Cup, (5-16 Para)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0005
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) with Fentanyl
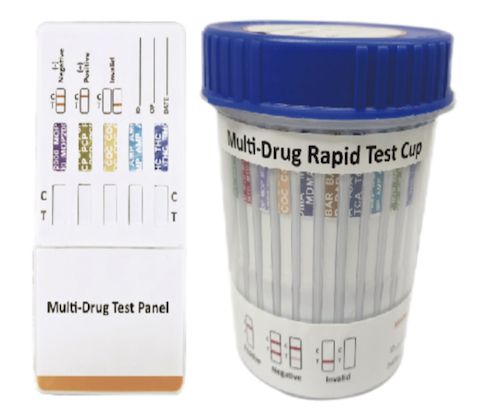
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0006
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) without Fentanyl
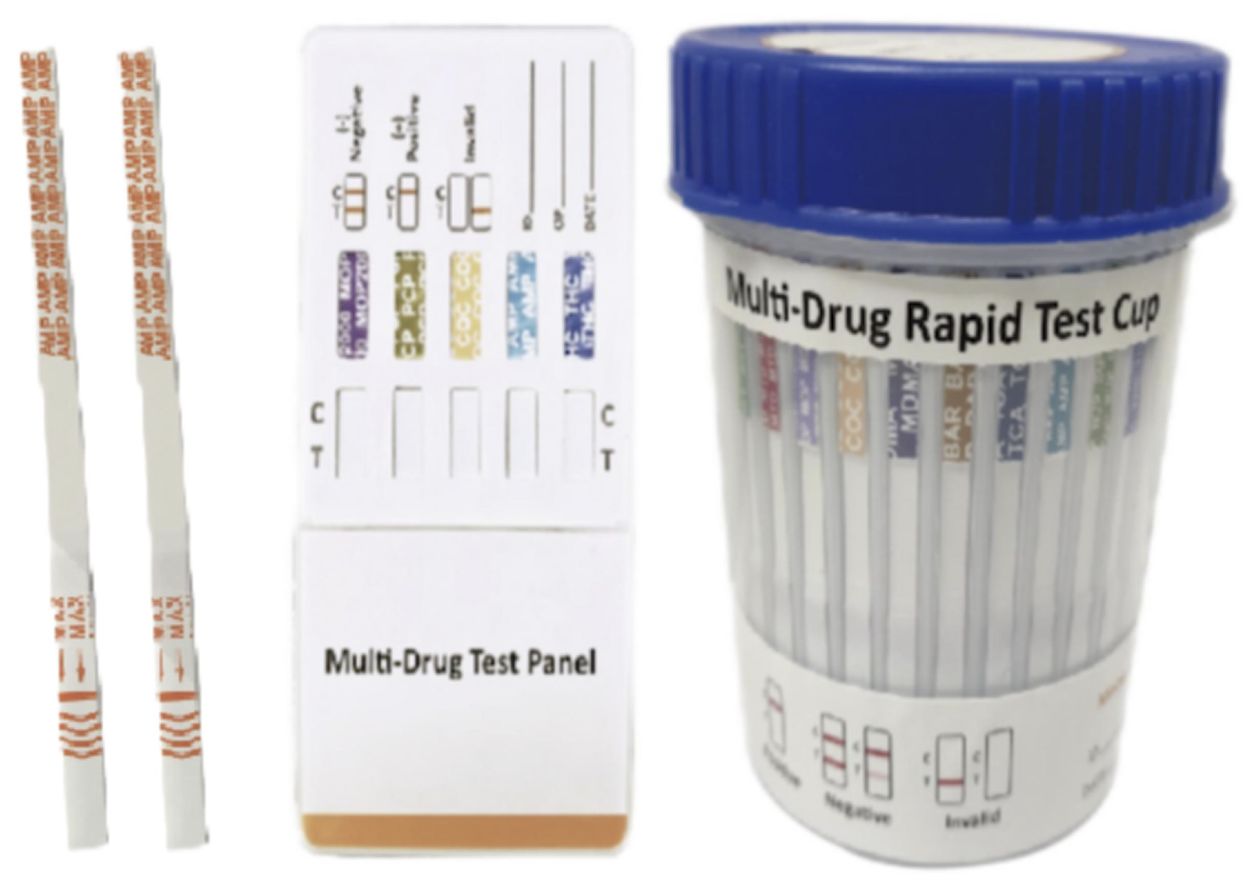
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0007
Multi-Drug 2~14 Drugs Rapid Test (Dipstick & Dipcard & Cup)
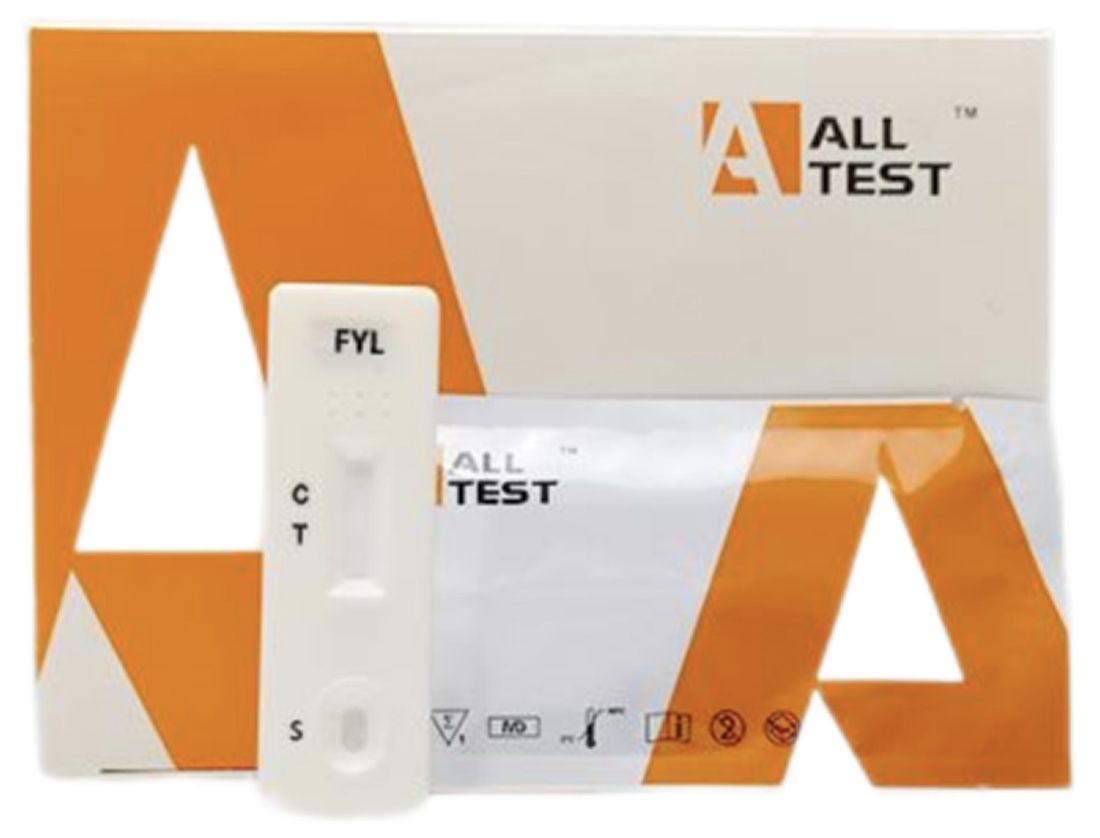
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0008
Fentanyl (FYL) Rapid Test (For Prescription Use)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0009
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (CLIA Waived)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0010
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (Home Use)
|
There is no product in your cart. |