- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- The Future of AI in Pathology Diagnostics with the EMPAIA Initiative
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into pathology diagnostics represents one of the most transformative advancements in medical technology. Pathology is a cornerstone of modern medicine, influencing patient diagnoses, treatment strategies, and outcomes. With the increasing demand for faster, more accurate, and cost-effective diagnostics, AI-driven solutions have emerged as an essential tool for pathologists. However, despite significant progress in AI technology, the widespread adoption of AI in clinical pathology remains slow due to various technical, regulatory, and logistical challenges. The EMPAIA initiative, a groundbreaking project designed to address these obstacles, aims to create a standardized, interoperable, and sustainable ecosystem for AI in pathology diagnostics. This article delves into the future of AI in pathology, exploring how the EMPAIA initiative is laying the groundwork for a seamless integration of AI tools in clinical settings.
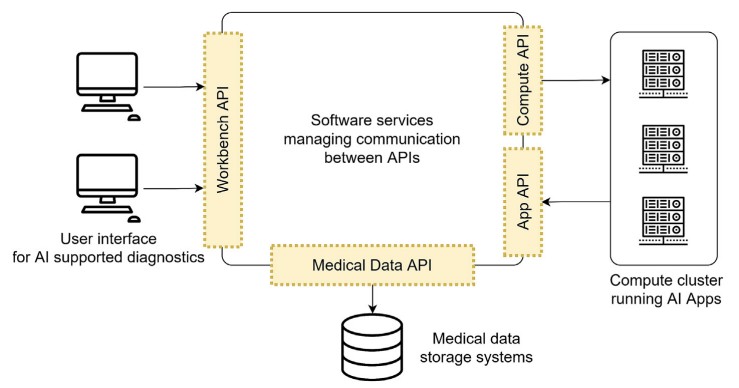 Fig.1 EMPAIA Platform architecture. (Zerbe N., et al., 2024)
Fig.1 EMPAIA Platform architecture. (Zerbe N., et al., 2024)

AI has made considerable strides in recent years, and its potential in healthcare is increasingly recognized. In pathology, AI promises to enhance diagnostic accuracy, reduce human error, and streamline workflows. By analyzing vast amounts of medical data, AI algorithms can uncover patterns and detect subtle changes in tissue that may not be immediately visible to the human eye. AI-powered image analysis, for example, enables the identification of cancerous cells, the assessment of tumor growth, and the evaluation of biopsies with precision and speed.
However, the transition from promising research results to routine clinical practice has been slow. One of the primary reasons for this delay is the lack of standardization across different pathology labs, imaging systems, and AI tools. Pathology departments often use proprietary technologies that are incompatible with one another, making it difficult for AI applications to integrate seamlessly. Without a standardized framework, AI vendors must create custom solutions for each lab's specific system, leading to significant delays and increased costs.
The EMPAIA initiative directly addresses this issue by focusing on creating an open, vendor-neutral standard for the integration of AI tools in pathology. Through a collaborative approach, EMPAIA aims to foster interoperability between AI applications and pathology software systems, ultimately enabling AI to be seamlessly incorporated into the diagnostic workflow.
The EMPAIA initiative was born out of the recognition that, in order to unlock the full potential of AI in pathology, several key challenges needed to be overcome. These challenges were multifaceted, involving technical, regulatory, and organizational hurdles that prevented the widespread adoption of AI solutions. The core objectives of EMPAIA revolve around four key pillars: standardization, AI integration, regulatory support, and knowledge sharing.

Standardization and Interoperability
One of the most pressing issues in digital pathology is the lack of standardized interfaces for AI tools. Pathology labs rely on diverse image management systems (IMS) and laboratory information systems (LIS) that store, manage, and transmit medical data. These systems, however, often operate in isolation, making it difficult to integrate AI applications across different platforms. EMPAIA aims to solve this problem by specifying open, vendor-neutral interfaces for the integration of AI apps in pathology.
By developing a standardized EMPAIA App Interface, the initiative has established a foundation for AI tools to communicate across various clinical systems without requiring complex custom integrations. This open interface enables AI vendors to focus on developing and refining their algorithms, while laboratories can adopt AI tools without the burden of integrating them with their existing systems.

AI Integration in Pathology Labs
To ensure that AI tools are usable in real-world clinical settings, EMPAIA emphasizes the importance of effective integration with the lab’s diagnostic workflow. The EMPAIA Platform is designed to facilitate this integration by providing a highly modular architecture. The platform includes all necessary components for AI applications, such as data management services, user interfaces, and compute infrastructure for running AI algorithms.
One of the standout features of the EMPAIA Platform is its virtual microscope viewer, which allows pathologists to interact with AI tools in a familiar environment. By enabling users to draw regions of interest (ROIs) and interact with diagnostic images, the platform bridges the gap between AI-driven analysis and human interpretation, making it easier for pathologists to adopt AI solutions into their daily work. This integration is crucial for ensuring that AI tools are not isolated but are embedded within the broader clinical system, thereby increasing their value and usability.

Supporting AI Developers and Vendors
The development and commercialization of AI tools for pathology come with a series of regulatory hurdles. AI solutions used for clinical diagnostics are subject to rigorous standards that vary by region, and the certification process can be complex and time-consuming. Recognizing this challenge, EMPAIA has provided significant support to AI vendors through its open-source reference implementations of the standardized interfaces and by offering regulatory guidance for product development.
In addition to facilitating the development of AI tools, EMPAIA offers a validation service that helps vendors assess the performance of their AI solutions using standardized datasets. This validation service ensures that AI applications meet the required performance standards and can be safely and effectively deployed in clinical settings.

Promoting Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration
EMPAIA’s success depends not only on technical solutions but also on the collaboration of various stakeholders, including pathologists, AI developers, regulatory bodies, and medical institutions. To foster knowledge exchange, EMPAIA has created the EMPAIA Academy, which offers educational resources and workshops to train both pathologists and AI developers. These workshops focus on the intersection of pathology and AI, ensuring that both sides understand the challenges and needs of each other.
By creating an open forum for discussion and sharing experiences, EMPAIA encourages collaboration across the digital pathology ecosystem. This collaborative approach ensures that AI tools are developed with the end-users in mind, enabling the creation of solutions that meet the practical needs of pathology labs while adhering to regulatory standards.
The integration of AI tools into clinical pathology workflows is complex, requiring not only the development of advanced algorithms but also the design of systems that facilitate their adoption in real-world settings. EMPAIA's work in this area has focused on building a platform that can seamlessly integrate AI tools into existing laboratory infrastructures. The EMPAIA Platform is a key technological advancement, offering modular components that can be customized and extended to meet the specific needs of different pathology labs.
The EMPAIA Platform is built on a modular architecture, which allows various components, such as AI applications, image management systems, and pathology workstations, to communicate with each other effectively. The platform's modular design enables labs to integrate only the components they need, providing flexibility and scalability. For example, the platform includes an AI App Interface that enables AI applications to communicate with other systems, as well as user workbench APIs that allow pathologists to interact with AI tools.
This approach to AI integration is crucial for ensuring that AI solutions can be implemented in diverse clinical environments, ranging from small private labs to large hospital networks.
As AI tools are integrated into pathology labs, ensuring the security and privacy of patient data is of utmost importance. EMPAIA's platform includes built-in features for data anonymization, which protect sensitive medical information while allowing AI applications to process the data. This data anonymization process ensures compliance with privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and facilitates the secure transfer of medical data across different systems.
One of EMPAIA's most significant achievements is its ability to integrate AI apps from multiple vendors into a single platform. By integrating 14 AI-based image analysis apps from eight different vendors, EMPAIA has demonstrated how diverse AI applications can work together using a unified interface. This approach fosters interoperability between different vendors and platforms, creating a more cohesive ecosystem for AI in pathology.
For AI tools to be fully embraced in clinical settings, it is essential that pathologists can understand and trust the results generated by these systems. Explainable AI (XAI) is a critical component of the EMPAIA platform, ensuring that AI applications provide transparent, interpretable results. The platform incorporates local explanations that help pathologists understand how AI algorithms arrive at specific diagnoses.
XAI is particularly important in pathology, as pathologists need to make informed decisions based on AI-generated results. By providing clear explanations of AI models and their outputs, EMPAIA helps build trust between pathologists and AI tools.

While the EMPAIA initiative has made significant strides in advancing the integration of AI into pathology, several challenges remain. One of the primary obstacles to broader AI adoption in pathology is the regulatory approval process. Obtaining approval for AI solutions in clinical diagnostics requires extensive testing and validation, and this process can be time-consuming and costly. However, EMPAIA's focus on creating standardized testing datasets and providing regulatory guidance has made it easier for vendors to navigate this complex process.
Another challenge is the digitization of pathology labs. Many labs still rely on traditional paper-based systems or legacy technologies, making the transition to digital pathology a costly and time-consuming endeavor. However, as digital pathology becomes more widespread, AI applications will become an increasingly essential tool for pathologists.
Finally, the issue of reimbursement remains a significant hurdle. AI solutions often require significant upfront investments, and the financial viability of AI-assisted pathology is still uncertain in many regions. Advocacy for policy changes and the development of cost-effective AI tools will be key to ensuring the sustainable adoption of AI in pathology.
The future of AI in pathology is bright, and the EMPAIA initiative is leading the way toward a more standardized, interoperable, and sustainable ecosystem for AI integration. By developing open interfaces, providing regulatory support, and fostering collaboration between stakeholders, EMPAIA is bridging the gap between AI research and clinical practice. As the platform continues to evolve, it will pave the way for AI-driven innovations that enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of pathology diagnostics worldwide.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00203
Rotavirus Antigen Group A and Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00206
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00207
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00211
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00212
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. IP-00189
Influenza A Rapid Assay Kit

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00200
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00201
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00202
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00208
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00209
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit(Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00210
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0001
hCG Pregnancy Test Strip
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0002
hCG Pregnancy Test Cassette
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0003
hCG Pregnancy Test Midstream

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0001
Cocaine (COC) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0002
Marijuana (THC) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0003
Morphine (MOP300) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0004
Methamphetamine (MET) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0005
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine ecstasy (MDMA) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0006
Amphetamine (AMP) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0007
Barbiturates (BAR) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0008
Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0009
Methadone (MTD) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0011
Opiate (OPI) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0002
Multi-Drug Test L-Cup, (5-16 Para)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0005
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) with Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0006
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) without Fentanyl
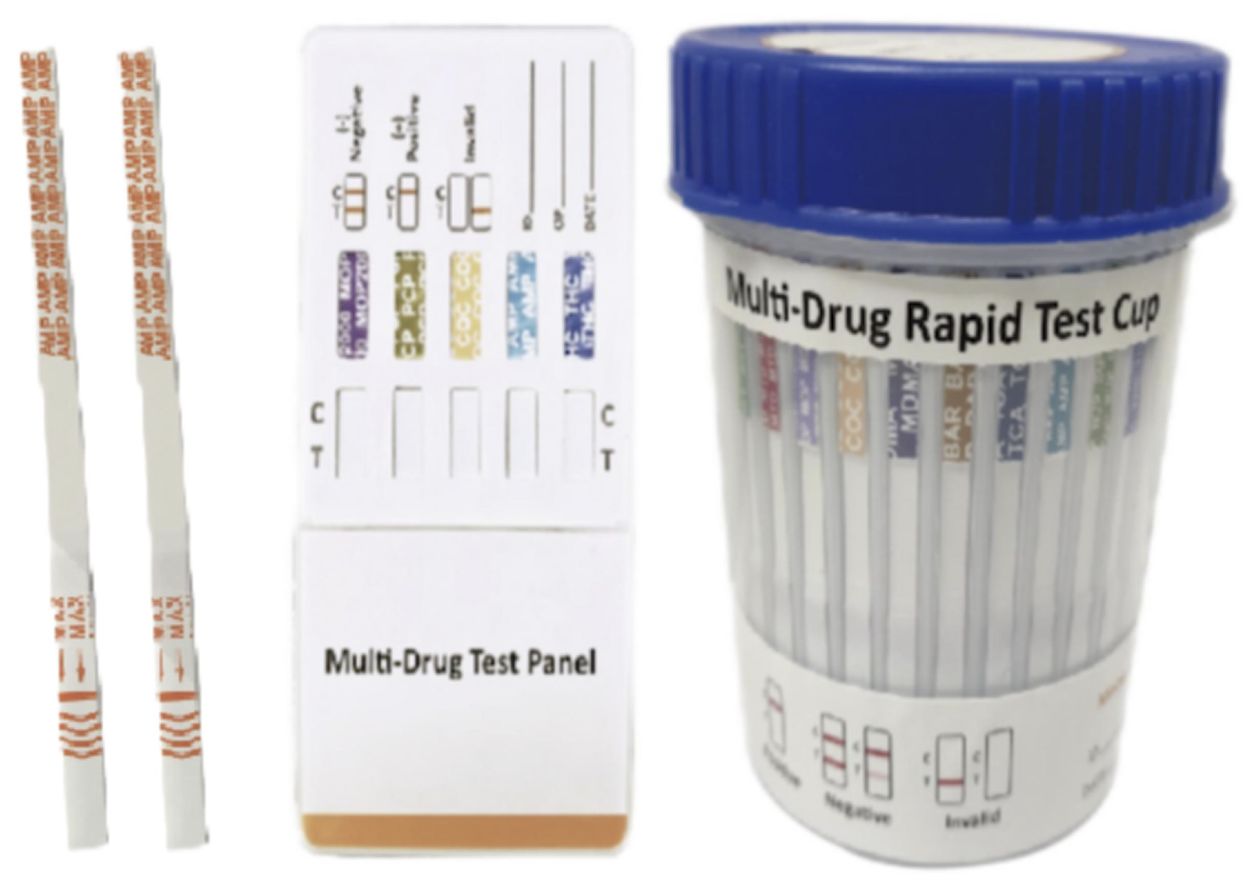
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0007
Multi-Drug 2~14 Drugs Rapid Test (Dipstick & Dipcard & Cup)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0008
Fentanyl (FYL) Rapid Test (For Prescription Use)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0009
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (CLIA Waived)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0010
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (Home Use)
|
There is no product in your cart. |