In the era of breakthrough spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) therapies, timely and accurate diagnosis is critical to optimize outcomes. This resource synthesizes the latest international guidelines, covering gold-standard genetic testing (SMN1/SMN2 analysis), newborn screening protocols, and multidisciplinary care pathways - providing clinicians, labs, and IVD distributors with actionable strategies to bridge the gap between evidence-based standards and clinical practice.
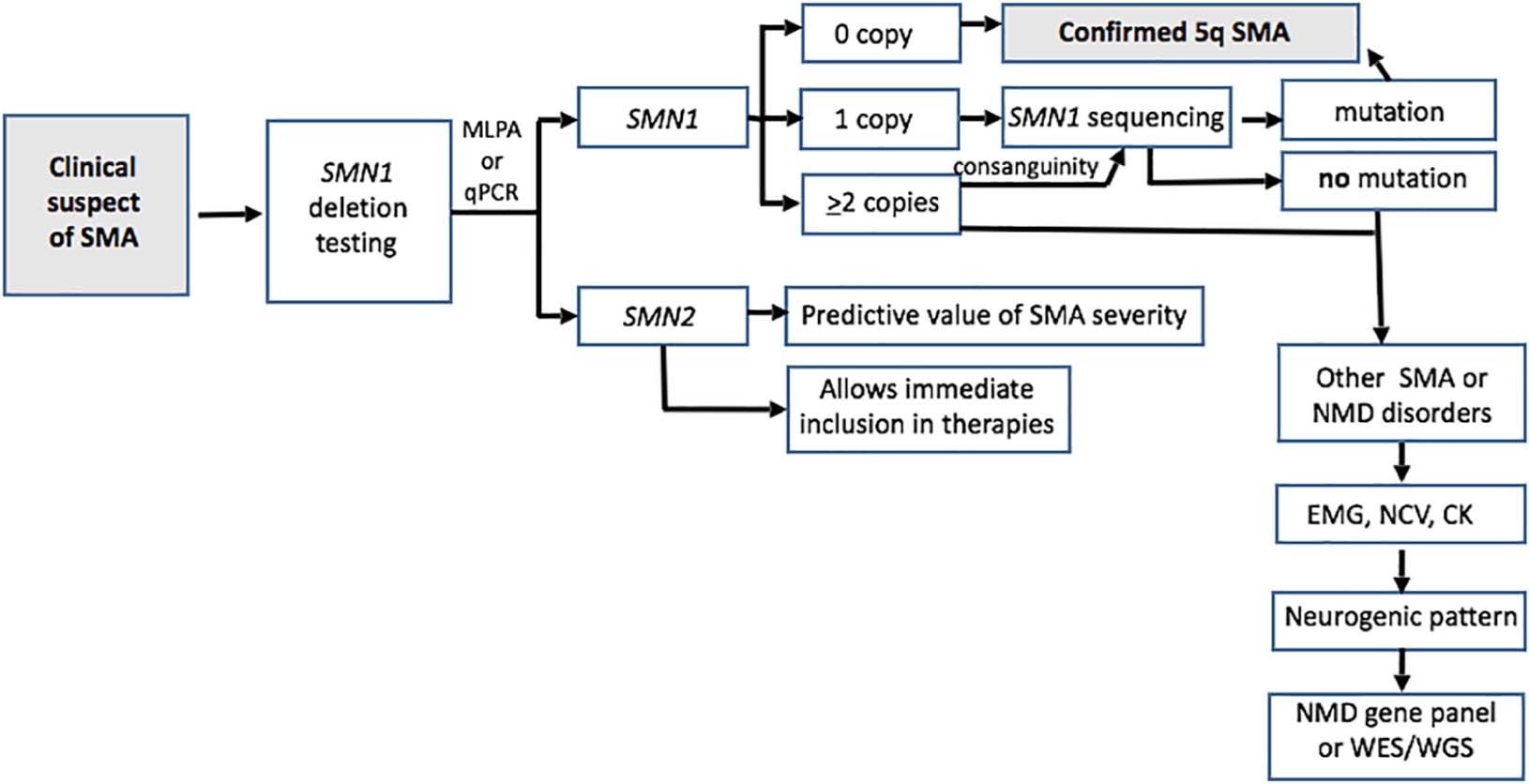 Fig.1 Diagnostic algorithm for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mercuri E, et al., 2018)
Fig.1 Diagnostic algorithm for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mercuri E, et al., 2018)
Overview of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a progressive neuromuscular disorder caused by biallelic mutations in the SMN1 gene, leading to degeneration of alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord. The disease severity primarily depends on residual SMN2 copy number, which produces limited functional SMN protein. Early diagnosis is critical, as disease-modifying therapies can significantly improve outcomes when administered pre-symptomatically or early in disease progression.
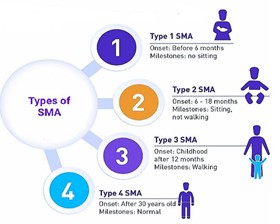 Fig.2 Common types of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mahendra Dwivedi, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 Common types of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mahendra Dwivedi, et al., 2023)
Key Insights of International SMA Diagnostic Guidelines
Current international guidelines emphasize standardized approaches for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) diagnosis and management to optimize outcomes in the era of disease-modifying therapies. These protocols focus on four critical pillars:
Genetic Testing as the Gold Standard
First-line testing requires SMN1 deletion analysis (detecting 95% of cases), with SMN2 copy number assessment for prognosis. Next-generation sequencing identifies rare variants in deletion-negative patients.
Carrier Screening & Prenatal Testing
ACMG recommends universal carrier screening. Prenatal options include CVS/amniocentesis, while emerging cfDNA techniques show promise for non-invasive SMN1 analysis in clinical trials.
Newborn Screening (NBS) Recommendations
Population-based NBS enables pre-symptomatic treatment, with data showing 91% of screened infants achieve independent sitting. Successful programs now operate in 35+ U.S. states and multiple EU countries.
Multidisciplinary Care Pathways
Comprehensive care requires neuromuscular specialists coordinating respiratory, nutritional and supportive therapies, with electromyography (EMG) for atypical presentations.
Gold-Standard Testing Methods for SMA Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) relies on quantitative genetic analysis to detect SMN1 deletions, assess SMN2 copy numbers, and identify rare variants. The following gold-standard methods are endorsed by international guidelines for comprehensive SMA testing:
- Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA)
MLPA is the most widely validated method for SMA diagnosis, enabling simultaneous quantification of SMN1 and SMN2 exon-level deletions/duplications. It detects homozygous SMN1 deletions (exon 7/8) with >99% accuracy and provides critical SMN2 copy number data for prognostic stratification. MLPA is considered the first-line test in most diagnostic pipelines.
qPCR offers a rapid, cost-effective alternative for initial SMN1 deletion screening. While it lacks the precision of MLPA for SMN2 copy analysis, it is useful in resource-limited settings or urgent clinical scenarios. Its limitations include inability to detect point mutations or small intragenic variants.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
NGS is reserved for atypical or deletion-negative cases, identifying subtle SMN1 mutations (e.g., missense variants, splice-site mutations). It also facilitates concurrent analysis of other neuromuscular genes in differential diagnoses. Though more expensive, NGS is invaluable for cases with strong clinical suspicion but negative deletion testing.
Emerging Challenges and Future Directions in SMA Diagnosis
While current diagnostic methods have transformed SMA management, several challenges persist alongside promising technological advancements. This section highlights key gaps and innovations shaping the future of SMA testing.
Current Diagnostic Challenges
Despite standardized genetic testing, SMA diagnosis faces hurdles including phenotypic overlap with other neuromuscular disorders, limited prognostic precision of SMN2 copy numbers, and unequal global access to testing—where 60% of low-income countries lack newborn screening programs.
Innovations on the Horizon
Promising advances such as long-read sequencing for SMN1/2 structural variants, blood-based neurofilament light chain biomarkers, and AI-powered phenotype-genotype correlation tools are addressing these gaps. Recent pilot studies demonstrate these innovations can reduce diagnostic delays by 30% in atypical cases.
From the establishment of genetic testing standards to the global promotion of newborn screening, significant progress has been made in the field of SMA diagnosis. However, challenges remain in achieving equitable access and optimizing precision medicine approaches. As a leading genetic diagnostic solutions provider, Alta DiagnoTech offers guideline-compliant IVD products to support every step of SMA diagnosis. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Mercuri E, Finkel R S, Muntoni F, et al. Diagnosis and management of spinal muscular atrophy: Part 1: Recommendations for diagnosis, rehabilitation, orthopedic and nutritional care[J]. Neuromuscular disorders, 2018, 28(2): 103-115.
- Mahendra Dwivedi, et al. A review on spinal muscular atrophy: An inherited neuromuscular disease[J]. International Journal of Comprehensive and Advanced Pharmacology, 2023.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.



 Fig.1 Diagnostic algorithm for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mercuri E, et al., 2018)
Fig.1 Diagnostic algorithm for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mercuri E, et al., 2018)
 Fig.2 Common types of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mahendra Dwivedi, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 Common types of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). (Mahendra Dwivedi, et al., 2023)
