Hematology laboratories serve as the indispensable backbone of modern diagnostic medicine, playing a pivotal role in delivering critical, actionable information about blood and its cellular and non-cellular components—from red and white blood cells to platelets, plasma, and coagulation factors. This vital data directly guides clinicians in making accurate diagnoses, formulating targeted treatment plans, monitoring disease progression, and evaluating the effectiveness of therapies across a wide range of conditions, including anemia, leukemia, coagulation disorders, and infections. Despite the rapid advancement of diagnostic technologies, such as automated hematology analyzers and digital microscopy, as well as the implementation of stringent quality control (QC) protocols and industry standards designed to ensure precision, preanalytical errors continue to pose a persistent and often underrecognized challenge in hematology testing workflows.
These preanalytical errors, which occur during the phases preceding the actual laboratory testing of blood samples, encompass a broad spectrum of mistakes—from specimen collection and labeling to transportation, handling, and storage. Unlike analytical errors (which arise during testing itself) or postanalytical errors (which occur during result reporting), preanalytical errors are often hidden from direct laboratory oversight, making them harder to detect and address. Even minor discrepancies in these pre-test phases can significantly compromise the accuracy and reliability of hematology test results, leading to far-reaching consequences: misdiagnosis of critical conditions, inappropriate or delayed treatment interventions, unnecessary additional testing, increased patient morbidity and mortality risks, and a substantial rise in overall healthcare costs for both healthcare facilities and patients.
Against this backdrop, this article delves into the hidden challenges posed by preanalytical errors in hematology laboratories, shedding light on their diverse types, prevalence rates across different clinical settings, the multifaceted impacts on patient care and healthcare systems, and evidence-based strategies to effectively mitigate their occurrence. By addressing these often-overlooked errors, hematology laboratories can further enhance the quality of their diagnostic services, reinforce trust with clinicians, and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
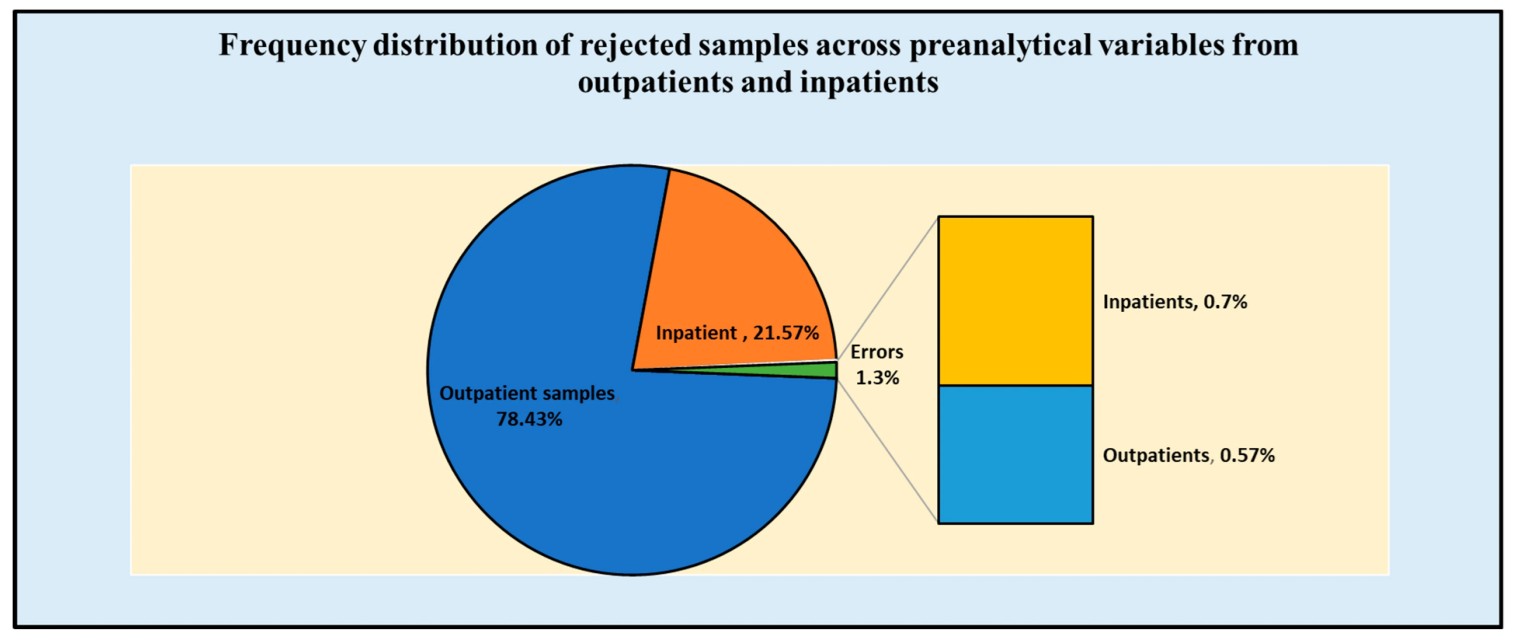 Fig.1 Frequency distribution of rejected samples across preanalytical variables from outpatients and inpatients. (Iqbal M. S., et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Frequency distribution of rejected samples across preanalytical variables from outpatients and inpatients. (Iqbal M. S., et al., 2023)
The Significance of Preanalytical Phase in Hematology
- Defining the Preanalytical Phase
The preanalytical phase is a critical and often underappreciated component of the diagnostic process in hematology, encompassing all activities and steps that occur from the exact moment a healthcare provider requests a hematology test until the collected sample is properly prepared and ready for analytical testing in the laboratory. This phase is not limited to a single step but rather a sequential series of essential actions, including accurate patient identification (a cornerstone to prevent sample mix-ups), proper sample collection (using appropriate needles, tubes, and techniques), careful post-collection handling (such as gentle mixing to avoid hemolysis), timely transportation to the laboratory (maintaining optimal temperature and conditions), and proper short-term or long-term storage when necessary. Although the majority of these activities are performed by healthcare professionals outside the laboratory—such as nurses, phlebotomists, or even primary care providers—rather than by laboratory personnel who have direct control over the analytical process, they play an irreplaceable role in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and validity of the final hematology test results. Errors that occur during the preanalytical phase, no matter how minor they may seem, can introduce significant variability and inaccuracy into the test data, potentially compromising the entire diagnostic workflow, leading to misinterpretation by clinicians, and undermining the quality of patient care.
- The Impact on Patient Care
Accurate and timely hematology test results are indispensable for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating a wide range of medical conditions, including various types of anemia (such as iron-deficiency anemia, megaloblastic anemia), acute and chronic infections (like bacterial sepsis, viral infections), bleeding and clotting disorders (e.g., hemophilia, thrombocytosis), and hematological malignancies (such as leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma). These test results—including complete blood count (CBC), peripheral blood smears, coagulation profiles, and hematocrit levels—provide critical, actionable information that guides clinical decision-making, helps healthcare providers select the most appropriate treatment plans, and assesses the effectiveness of ongoing therapies for patients. However, preanalytical errors, which are among the most common sources of laboratory errors in hematology, can have profound and far-reaching consequences for patient care, often leading to false-positive or false-negative test results that distort the clinical picture.
Such inaccuracies can trigger a cascade of adverse outcomes, including unnecessary delays in diagnosing life-threatening conditions, inappropriate or unnecessary treatments that expose patients to avoidable risks, or missed opportunities for timely intervention that could improve patient outcomes or even save lives. For instance, an insufficient or improperly collected blood sample (e.g., a sample that is too small, contaminated, or subjected to excessive shaking leading to hemolysis) might result in an incorrect complete blood count (CBC), leading to a misdiagnosis of anemia—either failing to detect a true case of anemia or falsely indicating anemia in a healthy patient. In the case of a true iron-deficiency anemia, a false-negative result could delay the initiation of necessary treatments, such as oral or intravenous iron supplementation, allowing the condition to worsen over time; this can lead to more severe health complications, including fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, reduced immune function, and even heart problems in severe cases.
Conversely, a false-positive result for anemia might lead to unnecessary medical interventions, such as prolonged iron supplementation (which can cause iron overload and damage to organs like the liver and heart) or further invasive diagnostic procedures (such as bone marrow biopsies), all of which cause undue physical and emotional stress to the patient, increase healthcare costs, and divert resources from other critical needs. Similarly, in the context of acute or chronic infections, an inaccurate CBC—such as a falsely low white blood cell count or abnormal differential count—could result in the inappropriate use of antibiotics (e.g., prescribing antibiotics for a viral infection that does not respond to them, or failing to prescribe antibiotics for a severe bacterial infection). This not only fails to treat the patient effectively but also contributes to the growing global problem of antimicrobial resistance, which reduces the effectiveness of existing antibiotics and makes future infections harder to treat. In more severe cases, such errors could lead to untreated sepsis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate, targeted antimicrobial therapy to prevent organ failure and death.
Types and Frequencies of Preanalytical Errors
- Common Preanalytical Errors
Insufficient Sample Volume
One of the most frequent preanalytical errors encountered in clinical settings is the collection of an insufficient blood sample. This issue can arise due to various factors, including improper venipuncture technique, small vein size, or premature withdrawal of the needle. Insufficient samples can lead to inaccurate test results, particularly for tests that require precise blood-to-anticoagulant ratios, such as coagulation studies. In these cases, inadequate sample volume can result in unreliable measurements, potentially delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Clotted Samples
Clotting of blood samples is another common preanalytical issue, often resulting from inadequate mixing of the sample with anticoagulant or delays in processing. When blood clots, it forms a solid mass that makes the sample unsuitable for analysis. This necessitates recollection of the sample, causing delays in diagnosis and increasing the burden on both healthcare providers and patients. Proper mixing and timely processing are essential to prevent clotting and ensure the integrity of the sample.
Hemolyzed Samples
Hemolysis, the rupture of red blood cells, is a significant preanalytical error that can occur due to rough handling of the sample, improper needle size, or prolonged storage before processing. Hemolyzed samples release cellular contents into the plasma, which can interfere with various hematological tests, leading to inaccurate results. This interference can affect the measurement of critical parameters such as hemoglobin levels and enzyme activities, potentially misleading clinical decisions. Proper handling and timely processing are crucial to minimize hemolysis and ensure accurate test results.
Incorrect Labeling and Identification
Errors in patient identification and sample labeling can have severe consequences, including misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment. These critical errors often stem from human factors, such as fatigue, distraction, or lack of training. Incorrect labeling can lead to the wrong patient receiving test results, causing unnecessary anxiety and potentially harmful interventions. Ensuring accurate patient identification and sample labeling is essential to maintain the reliability and safety of diagnostic processes. Implementing standardized protocols and double-checking procedures can help mitigate these risks and ensure that each sample is correctly associated with the appropriate patient.
- Frequency of Preanalytical Errors
Studies have shown that preanalytical errors account for a significant proportion of total laboratory errors. In a retrospective analysis of 67,892 hematology samples, 1.3% were discarded due to preanalytical errors, with insufficient sample volume and clotted samples being the most common. Similar frequencies have been reported in other studies, highlighting the widespread nature of this issue.
Factors Contributing to Preanalytical Errors
- Human Factors
Lack of Training
Inadequate training of phlebotomists and laboratory personnel in proper sample collection and handling techniques is a significant contributor to preanalytical errors. Continuous education and certification programs can help mitigate this risk.
Fatigue and Distraction
High workload and long hours can lead to fatigue and distraction among laboratory staff, increasing the likelihood of errors. Implementing ergonomic practices and providing regular breaks can help alleviate these issues.
- Process and Systemic Issues
Inadequate Standardization
Lack of standardized procedures for sample collection, handling, and transportation can introduce variability and errors. Developing and enforcing standardized protocols can help ensure consistency and accuracy.
Poor Communication
Effective communication between laboratory personnel, healthcare providers, and patients is crucial for minimizing preanalytical errors. Miscommunication can lead to incorrect sample collection, handling, or testing. Implementing clear communication channels and protocols can help mitigate this risk.
Strategies for Mitigating Preanalytical Errors
- Standardization of Procedures
Developing and enforcing standardized protocols for sample collection, handling, and transportation is essential for minimizing preanalytical errors, which account for a significant portion of diagnostic inaccuracies in clinical settings. These protocols should be comprehensive, covering every critical aspect of the preanalytical phase—from the exact moment a sample is collected from the patient to its safe and timely arrival at the laboratory for analysis. This includes specifying the use of appropriate collection tubes (matched to the type of test being performed, such as serum, plasma, or whole blood tubes), ensuring proper and consistent mixing of samples with anticoagulants or preservatives to prevent clotting or degradation, and strictly adhering to recommended storage temperatures and transportation timelines. Standardized procedures also involve clear documentation of each step, from patient identification at collection to sample handoff at the lab, to ensure traceability. By establishing and enforcing these uniform guidelines, healthcare facilities can ensure consistency and reliability across all staff and shifts, reducing the variability that often leads to errors and inaccuracies in final test results.
- Training and Education
Continuous training and education programs for phlebotomists, nursing staff, and laboratory personnel are crucial for ensuring proficiency in sample collection and handling techniques, as human error is a leading cause of preanalytical mistakes. These programs should be tailored to the specific roles of each staff member, covering industry best practices, updates in diagnostic technology and equipment, and detailed protocols relevant to the preanalytical phase—such as proper venipuncture technique, sample labeling requirements, and how to handle difficult or special samples (e.g., pediatric, geriatric, or coagulation samples). Certification programs, offered by recognized clinical organizations, can provide formal validation of skills, while regular competency assessments (including hands-on demonstrations and written tests) can further enhance and reinforce knowledge. Ongoing education, such as monthly workshops or online modules, helps to keep staff updated on the latest developments in preanalytical care and reinforces the critical importance of adhering to standardized protocols to protect patient safety and ensure accurate diagnostic outcomes.
- Technology and Automation
Leveraging advanced technology and automation tools can significantly reduce human errors in the preanalytical phase, streamlining workflows and improving overall efficiency. Automated sample processing systems, for example, are designed to handle tasks such as sample mixing, centrifugation, and aliquoting with consistent precision, minimizing the risk of common issues like clotting, hemolysis, or incorrect sample volume. These systems also reduce the need for manual intervention, which not only cuts down on error but also speeds up the sample preparation process, allowing laboratories to process more samples in less time. Additionally, barcode scanning and electronic tracking systems integrate seamlessly with electronic health record (EHR) platforms, improving patient identification and sample traceability at every step. By scanning a patient's wristband and the corresponding sample tube, staff can eliminate the risk of mislabeling—a critical error that can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment. By automating these key preanalytical processes, healthcare providers can enhance the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of diagnostic testing, ultimately improving patient care.
- Quality Assurance Programs
Implementing robust quality assurance (QA) programs, including regular internal audits, external assessments, and feedback mechanisms, is essential for identifying areas for improvement and tracking progress in reducing preanalytical errors. Internal quality control (IQC) protocols involve daily checks of equipment (such as centrifuges and pipettes) and regular monitoring of preanalytical processes to ensure they meet established standards. External quality assurance (EQA) schemes, administered by independent accrediting bodies, provide benchmarks and comparison data against other laboratories, allowing facilities to measure their performance and identify gaps. Regular audits, conducted by a dedicated QA team, can help pinpoint potential issues in the preanalytical phase—such as inconsistent protocol adherence, equipment malfunctions, or staff training gaps—allowing for timely interventions and process improvements. Feedback mechanisms, such as regular staff meetings, performance reviews, and incident reporting systems, foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging staff to share challenges, suggest solutions, and learn from mistakes. Together, these QA measures ensure that preanalytical processes are consistently evaluated and optimized, maintaining high standards of accuracy and reliability in diagnostic testing.
Conclusion
Preanalytical errors in hematology laboratories represent a significant challenge, impacting patient care, healthcare costs, and patient satisfaction. Understanding the types, frequencies, and causes of these errors is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. By standardizing procedures, providing regular training, leveraging technology, and implementing quality assurance programs, laboratories can significantly reduce preanalytical errors and improve the overall quality of healthcare services. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, a commitment to continuous improvement and patient-centered care will be essential in addressing this hidden yet critical issue.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Iqbal, Mohammad Shahid, et al. "Preanalytical errors in a hematology laboratory: an experience from a tertiary care center." Diagnostics 13.4 (2023): 591.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
 Fig.1 Frequency distribution of rejected samples across preanalytical variables from outpatients and inpatients. (Iqbal M. S., et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Frequency distribution of rejected samples across preanalytical variables from outpatients and inpatients. (Iqbal M. S., et al., 2023)