- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- Tailored Biofunctional Enzyme Mimics for Catalytic Therapy and Diagnostic Applications
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
In the realm of medical diagnostics and therapeutics, the quest for innovative, efficient, and cost-effective solutions is unending. Traditional enzymes have long been the cornerstone of biochemical assays and treatments, yet their limitations—ranging from instability to high production costs—have spurred scientists to seek alternatives. Enter biofunctional enzyme-mimics (BF/Enz-Ms), synthetic nanomaterials engineered to replicate the catalytic prowess of natural enzymes. These cutting-edge entities are reshaping the landscape of in vitro diagnostics (IVD) and medicine, offering unprecedented precision, stability, and versatility.
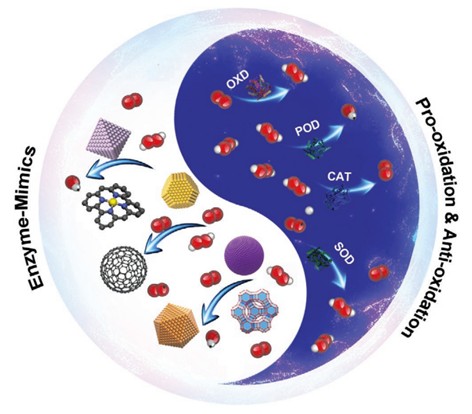 Fig.1 Illustration of the species of Enz-Ms (or nanozymes in many nanomedicine systems) and their biocatalytic mechanisms for prooxidation and antioxidation. (Tang Q., et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Illustration of the species of Enz-Ms (or nanozymes in many nanomedicine systems) and their biocatalytic mechanisms for prooxidation and antioxidation. (Tang Q., et al., 2021)

Colorimetric assays are a cornerstone of IVD, providing rapid and cost-effective detection of biomarkers. BF/Enz-Ms, particularly those with peroxidase-like activity, have emerged as powerful tools in this domain. For example, iron porphyrin-based COFs have been utilized to detect glucose and H₂O₂ with high sensitivity. The catalytic activity of these enzyme-mimics leads to a color change in the presence of the target analyte, which can be easily quantified using a spectrophotometer.
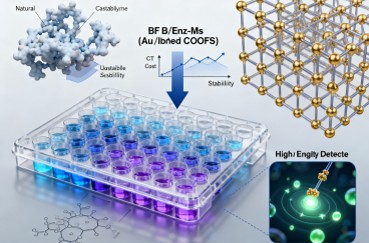
Immunoassays, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), are widely used for the detection of proteins, antibodies, and other biomolecules. BF/Enz-Ms offer several advantages over natural enzymes in this context, including enhanced stability and cost-effectiveness. For instance, Au-doped COFs have been employed in ELISAs to detect allergens with high specificity and sensitivity. The ability to customize the catalytic properties of BF/Enz-Ms allows for the development of highly sensitive and selective immunoassays.

Biosensors are devices that combine biological recognition elements with physicochemical transducers to detect specific analytes. BF/Enz-Ms play a pivotal role in the development of next-generation biosensors. Their high catalytic efficiency and stability make them ideal candidates for use in electrochemical, optical, and piezoelectric biosensors. For example, MOF-based biosensors have been developed to detect glucose and other biomarkers with remarkable accuracy.

Cancer Therapy
Cancer remains one of the most formidable challenges in medicine. BF/Enz-Ms are being explored as potent anticancer agents, either alone or in combination with other therapies. For instance, MOF-based nanoparticles loaded with chemotherapy drugs and photosensitizers can achieve synergistic antitumor effects. Upon near-infrared (NIR) light irradiation, these nanoparticles generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), inducing apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues.
Antibacterial Treatment
The rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has necessitated the development of novel antibacterial strategies. BF/Enz-Ms offer a promising solution in this regard. For example, MoS₂-based hydrogels with peroxidase-like activity can generate ROS to kill bacteria effectively. Similarly, metal-polyphenol networks (MPNs) loaded with antibiotics and platinum prodrugs can achieve enhanced antibacterial effects through a cascade reaction.

Wound Healing
Wound healing is a complex process that can be significantly impaired in conditions such as diabetes. BF/Enz-Ms are showing promise in promoting wound healing by modulating the local microenvironment. For instance, hydrogels loaded with MnO₂ nanoparticles can alleviate oxidative stress in diabetic wounds, enhancing cellular viability and accelerating the healing process. Similarly, cerium oxide (CeO₂)-based nanoparticles can scavenge ROS, protecting cells from oxidative damage and facilitating tissue regeneration.
Despite the remarkable progress made in the field of BF/Enz-Ms, several challenges remain to be addressed. One of the primary concerns is the biocompatibility and long-term toxicity of these nanomaterials in vivo. While many BF/Enz-Ms have shown promising results in preclinical studies, their safety and efficacy need to be validated in clinical trials.
Another challenge lies in the scalable production of BF/Enz-Ms with consistent quality and performance. Current synthesis methods often involve complex and time-consuming procedures, limiting their widespread adoption. Therefore, there is a pressing need for the development of simple, efficient, and scalable manufacturing processes.
Looking ahead, the future of BF/Enz-Ms is bright, with numerous opportunities for innovation and discovery. As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries of enzyme-mimetic catalysis and explore new materials and functionalization strategies, we can expect to see a new generation of BF/Enz-Ms with enhanced performance and expanded applications.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
| Cat.No | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| IEC-HMM-0020 | Carboxypeptidase B | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0023 | Glutathione S-transferase | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0038 | Ribonuclease Inhibitor, Human Placenta | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0039 | M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase, RNase H Plus | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0037 | pfu DNA Polymerase | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0031 | Malatedehydrogenase, MDH | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0040 | M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase, RNase H Minus | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0005 | Pyruvate Kinase, PK | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0001 | AcyI-CoA Oxidase, ACO | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0035 | Proteinase K Liquid (20 mg/mL) | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0030 | Adenosine Deaminase | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0004 | Glutamate dehydrogenase, GLDH | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0015 | S-adenosylmethionine Synthetase | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0045 | Uracil-DNA Glycosylase (UNG), Heat-labile | Add To Cart |
| IEC-HMM-0021 | Trypsin from Porcine, Recombinant | Add To Cart |
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |