Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent malignancies globally, with significant morbidity and mortality. The identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status has revolutionized breast cancer management, enabling targeted therapies that have improved outcomes for many patients. Traditionally, HER2 status was classified as either overexpressed (HER2-positive) or not overexpressed (HER2-negative). However, recent advancements have introduced a new category: HER2-low. This classification, defined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) scores of 1+ or 2+ without gene amplification, represents a significant shift in diagnostic and therapeutic paradigms.
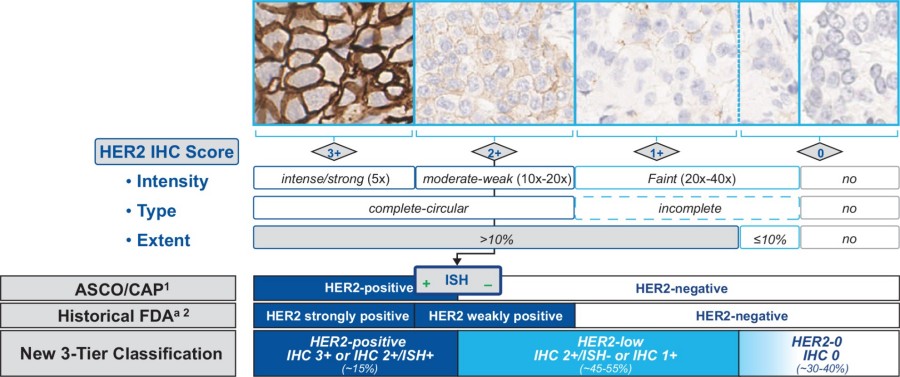 Fig.1 Comparison of the HER2 Staining Classification Scheme According to FDA and ASCO/CAP 2018 with the New HER2-low Scoring System (versus HER2-0 and HER2-positive). (Rüschoff J., et al., 2025)
Fig.1 Comparison of the HER2 Staining Classification Scheme According to FDA and ASCO/CAP 2018 with the New HER2-low Scoring System (versus HER2-0 and HER2-positive). (Rüschoff J., et al., 2025)
The Clinical Significance of HER2-Low Status
The introduction of HER2-low status is driven by the development of novel therapies such as trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), an antibody-drug conjugate that targets HER2 with a potent cytotoxic agent. Clinical trials have demonstrated that T-DXd is effective in patients with metastatic breast cancer who exhibit low levels of HER2 expression, even in the absence of gene amplification. This has expanded the pool of patients potentially eligible for targeted HER2 therapies, emphasizing the need for accurate and reliable diagnostic methods to identify HER2-low status.
Diagnostic Challenges in HER2-Low Detection
Accurate diagnosis of HER2-low breast cancer is fraught with challenges. Traditional IHC assays, such as the Ventana PATHWAY 4B5 and Dako HercepTest, have been widely used for HER2 status determination. However, these assays were initially designed to distinguish between HER2-positive and HER2-negative tumors. The nuances of low HER2 expression levels (IHC 1+ or 2+ without amplification) require a higher degree of precision and consistency.
Pathologists often face difficulties in interpreting IHC results, particularly when staining intensity is faint or when membrane staining is incomplete. Studies have shown that interobserver variability can be significant, with disagreement rates as high as 20%-30% in some cases. This variability is primarily attributed to subjective interpretation of staining patterns and intensity, as well as challenges in distinguishing between specific and nonspecific staining.
The Role of Immunohistochemistry in HER2-Low Diagnosis
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) remains the cornerstone of HER2 status determination. The Ventana PATHWAY 4B5 and Dako HercepTest assays are the two most commonly used IHC methods in clinical practice. Both assays have been validated for their ability to detect HER2 overexpression and gene amplification. However, their performance in detecting low levels of HER2 expression (IHC 1+ or 2+ without amplification) requires careful evaluation.
The Ventana PATHWAY 4B5 assay utilizes a monoclonal antibody that targets the extracellular domain of HER2. This assay has demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity for detecting HER2 overexpression. In contrast, the Dako HercepTest uses a polyclonal antibody and has been widely used for many years. Both assays have their strengths and limitations, and their performance can vary depending on the specific staining patterns and interpretation criteria used.
The Impact of Training on Diagnostic Accuracy
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of training in improving diagnostic accuracy for HER2-low status. A global study involving 77 pathologists from 14 countries demonstrated that a 4-hour training program significantly enhanced the ability of pathologists to accurately identify HER2-low cases. The training focused on the use of the magnification rule for intensity scoring and the identification of challenging staining patterns. This intervention led to a substantial improvement in both positive and negative percentage agreements, reducing the rate of underscoring and overscoring.
The training program emphasized the importance of high magnification (up to 40x) for accurate intensity scoring, as well as the need to distinguish between specific membrane staining and nonspecific cytoplasmic or basal membrane-like staining. These practical guidelines helped pathologists achieve a more consistent and reliable interpretation of IHC results.
The Future of HER2-Low Diagnostics: Technological Advancements
While IHC remains the primary method for HER2 status determination, technological advancements offer promising avenues for improving diagnostic accuracy. Digital image analysis (DIA) has emerged as a valuable tool for standardizing and quantifying IHC results. By providing objective and reproducible measurements of staining intensity and extent, DIA can reduce interobserver variability and enhance diagnostic precision.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms into DIA platforms holds the potential to further streamline the diagnostic process. AI can be trained to recognize specific staining patterns and intensity levels, providing pathologists with a second opinion and reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation. This combination of advanced imaging techniques and AI-driven analysis represents a significant step forward in the quest for precision diagnostics.
Standardization and Quality Control in HER2-Low Testing
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of HER2-low testing requires rigorous standardization and quality control measures. The use of validated IHC assays, adherence to established scoring criteria, and the implementation of on-slide controls are essential components of a robust diagnostic workflow. Additionally, regular proficiency testing and participation in quality assurance programs can help maintain high standards of diagnostic accuracy.
The College of American Pathologists (CAP) and other professional organizations have developed guidelines and recommendations for HER2 testing, emphasizing the importance of standardized protocols and continuous education for pathologists. These guidelines provide a framework for laboratories to ensure the consistency and reliability of their diagnostic results.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The diagnosis of HER2-low breast cancer represents a significant advancement in the field of oncology, expanding treatment options for patients who previously had limited therapeutic choices. However, the accurate identification of HER2-low status requires meticulous attention to detail and the application of standardized diagnostic protocols. Through targeted training programs, the adoption of advanced imaging technologies, and adherence to quality control measures, pathologists can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of HER2-low diagnostics.
As the field of breast cancer diagnostics continues to evolve, the integration of innovative technologies and evidence-based practices will be crucial in ensuring that patients receive the most accurate and effective care. The quest for precision in HER2-low diagnosis is not only a scientific pursuit but also a commitment to improving patient outcomes and advancing the fight against breast cancer.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Rüschoff, Josef, et al. "Global study on the accuracy of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-low diagnosis in breast cancer." Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 149.5 (2025): 431-438.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
Trending Products



 Fig.1 Comparison of the HER2 Staining Classification Scheme According to FDA and ASCO/CAP 2018 with the New HER2-low Scoring System (versus HER2-0 and HER2-positive). (Rüschoff J., et al., 2025)
Fig.1 Comparison of the HER2 Staining Classification Scheme According to FDA and ASCO/CAP 2018 with the New HER2-low Scoring System (versus HER2-0 and HER2-positive). (Rüschoff J., et al., 2025)