- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- Wearable Point-of-Care Devices Enabled by Smart Technologies for Early Disease Diagnosis and Biomarker Exploration
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Modern diagnostics hinge on the timely identification of disease-specific biomarkers—molecular signatures including proteins, nucleic acids, and metabolites that provide a window into the patient's physiological state. Biomarker identification is central to early disease detection, therapeutic monitoring, and prognosis. With the growing adoption of in vitro diagnostics (IVDs), the integration of biosensing technologies into wearable and point-of-care (POC) platforms has become a focal innovation in precision medicine.
Biomarkers like prostate-specific antigen (PSA), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and C-reactive protein (CRP) are now detectable using compact systems. Electrochemical and optical detection methods—commonly used in ELISA, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), or lateral flow assays (LFA)—are being miniaturized for seamless incorporation into wearable sensors. The integration of microfluidic platforms with advanced biosensors ensures not only high sensitivity but also multiplexed detection capacity at the patient's side.
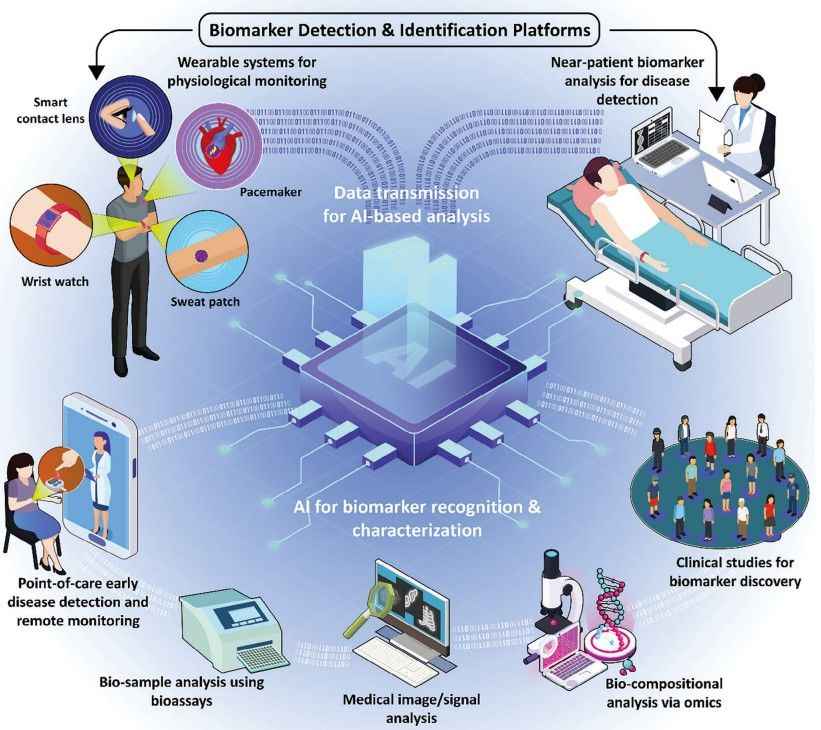 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the biomarker detection and identification platforms. (Haghayegh F., et al., 2024)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the biomarker detection and identification platforms. (Haghayegh F., et al., 2024)
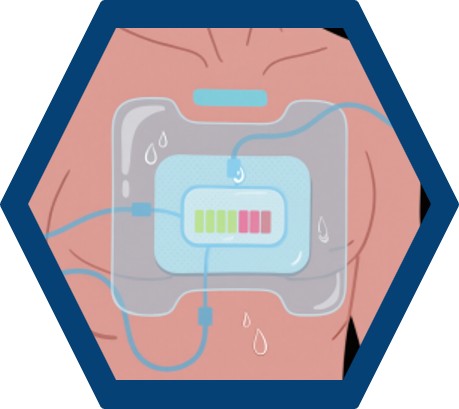
Skin-Attached Platforms for Sweat, ISF, and Temperature Biomarkers
Wearable sensors have emerged as intelligent devices capable of continuously tracking physiological and biochemical indicators. Platforms such as microneedle patches, epidermal electrochemical sensors, and hydrogel-based sweat patches enable continuous assessment of sweat analytes like cortisol, glucose, and lactate.
Devices such as MicroSweat and Gx Patch utilize colorimetric and electrochemical transduction to measure analytes like chloride and CRP from sweat. Embedded wireless systems transmit real-time data to smartphones for user monitoring and clinician review. Additionally, wearable microneedles allow for interstitial fluid (ISF) sampling, enabling analyte detection with minimal invasiveness and high temporal resolution.

Ocular and Oral Wearables for Tear and Saliva Diagnostics
Smart contact lenses embedded with fluorescent or electrochemical sensors have shown efficacy in monitoring intraocular pressure and detecting glucose and salt concentrations in tear fluid. These ocular biosensors offer non-invasive access to critical metabolic data for conditions like glaucoma and diabetes.
Oral wearable devices—for instance, saliva-based biosensors integrated into dental appliances—allow for the detection of stress hormones and metabolic by-products. These platforms enable continuous sampling and analysis of salivary analytes, including α-amylase, uric acid, and antibodies.
Microfluidic integration into POC devices enables the miniaturization of complex laboratory functions. Technologies such as capillary-driven channels, valve-controlled chambers, and droplet microreactors allow manipulation of microscale fluid volumes for sample preparation, separation, and reaction.
Advanced systems demonstrated include:
These platforms can manage multiplexed detection with precise reagent control and reduced cross-contamination. They are critical for transitioning complex diagnostic workflows into wearable or portable devices that maintain analytical rigor.
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) have transformed the landscape of diagnostic analytics. Algorithms now process biosensor data, medical imaging, and clinical signals—such as ECG, EEG, and EMG—to identify disease-specific anomalies with higher accuracy than traditional methods.
For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are employed to detect atrial fibrillation from PPG signals captured by smartwatches. In neurology, DL models have enabled seizure prediction through wearable EEG signal analysis. Explainable AI is increasingly being embedded in wearable platforms to ensure medical interpretability and clinical trust.

Artificial intelligence enables real-time interpretation of colorimetric, SERS, and fluorescent bioassays. Smartphone-based applications, using ML models such as support vector machines (SVMs) and random forests, interpret spectral data to quantify biomarker concentrations with high precision.
Examples include:
These integrations significantly reduce interpretation errors and allow for automated triage and decision-making.
The acceleration of AI and wearable diagnostics necessitates alignment with regulatory frameworks. Devices like the Abbott i-STAT TBI test and the Butterfly iQ ultrasound probe exemplify successful pathways through FDA approval. The FDA is now adapting its Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) framework to encompass dynamic AI systems, requiring continuous performance monitoring and post-market evaluation.
The European Union is enacting the Artificial Intelligence Act, with direct implications for AI-powered medical devices. Manufacturers are now required to demonstrate algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and performance generalizability across populations.
Translational Examples and Clinical Use Cases
Several wearable diagnostics have successfully moved from academic prototypes to commercial deployment:
These cases demonstrate the convergence of advanced sensing, bioinformatics, and real-time computation in deployable diagnostic products.
The integration of omics datasets—proteomics, metabolomics, genomics, and transcriptomics—is critical for robust biomarker discovery. ML techniques like principal component analysis (PCA), random forests, and autoencoders allow reduction of data dimensionality and highlight clinically relevant biomolecular patterns.
Examples of applications:
These findings illustrate the potential of integrated AI-omics platforms for early, accurate disease stratification.
| Device Type | Biofluid Sampled | Target Biomarkers | Detection Method | Clinical Application |
| Smart Contact Lens | Tears | Glucose, IOP | Fluorescence, Electrochemical | Diabetes, Glaucoma |
| Epidermal Sweat Patch | Sweat | Cortisol, CRP, Lactate | Colorimetric, Amperometric | Stress, Sepsis, Metabolic Status |
| Microneedle ISF Sensor | ISF | Glucose, Sodium | EGT, Potentiometric | Diabetes, Hyponatremia |
| Smart Diaper | Urine | Glucose, Uric Acid | Electrochemical | Renal Disease, Neonatal Health |
| Breath VOC Analyzer | Breath | VOCs (e.g., aldehydes) | SERS | COVID-19, Oral Cancer |
The convergence of wearable diagnostics, AI algorithms, and cloud computing paves the way for predictive and personalized healthcare. Through real-time data streaming and longitudinal monitoring, these platforms are transitioning from reactive diagnostics to proactive health maintenance.
Emerging capabilities include:
The fusion of wearable technology, intelligent diagnostics, and biomarker-driven medicine is catalyzing a transformation in healthcare delivery. This paradigm shift—from centralized labs to distributed, patient-centric platforms—will redefine how diseases are detected, managed, and prevented. With robust regulatory pathways, continued AI innovation, and interdisciplinary collaboration, the vision of personalized, real-time diagnostics is now a practical, scalable reality.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00203
Rotavirus Antigen Group A and Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00206
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00207
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00211
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00212
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. IP-00189
Influenza A Rapid Assay Kit

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00200
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00201
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00202
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00208
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00209
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit(Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00210
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0001
hCG Pregnancy Test Strip
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0002
hCG Pregnancy Test Cassette
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0003
hCG Pregnancy Test Midstream

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0001
Cocaine (COC) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0002
Marijuana (THC) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0003
Morphine (MOP300) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0004
Methamphetamine (MET) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0005
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine ecstasy (MDMA) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0006
Amphetamine (AMP) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0007
Barbiturates (BAR) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0008
Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0009
Methadone (MTD) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0011
Opiate (OPI) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0002
Multi-Drug Test L-Cup, (5-16 Para)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0005
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) with Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0006
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) without Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0007
Multi-Drug 2~14 Drugs Rapid Test (Dipstick & Dipcard & Cup)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0008
Fentanyl (FYL) Rapid Test (For Prescription Use)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0009
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (CLIA Waived)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0010
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (Home Use)
|
There is no product in your cart. |