- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- The Future of Cervical Cancer Screening: Advanced IVD Strategies and Technologies
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Cervical cancer remains a significant global health challenge, yet it is uniquely preventable through advanced screening and early intervention. This comprehensive resource explores the future of cervical cancer screening, focusing on the transformative role of innovative IVD strategies and technologies. We will delve into primary HPV testing, advanced genotyping, triage biomarkers, and novel point-of-care solutions that are reshaping detection paradigms, enabling more precise risk stratification and personalized management approaches to ultimately reduce the global burden of this disease.
Cervical cancer represents a significant yet highly preventable global health challenge, primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV). While historically one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, the implementation of organized screening programs using Pap smears and the more recent introduction of HPV testing have dramatically reduced its incidence in developed regions. The disease typically develops slowly through precancerous stages, creating a crucial window for early detection and intervention. This established understanding of its viral etiology and predictable progression makes cervical cancer uniquely positioned for prevention through vaccination and highly effective early detection through advanced in vitro diagnostic approaches.
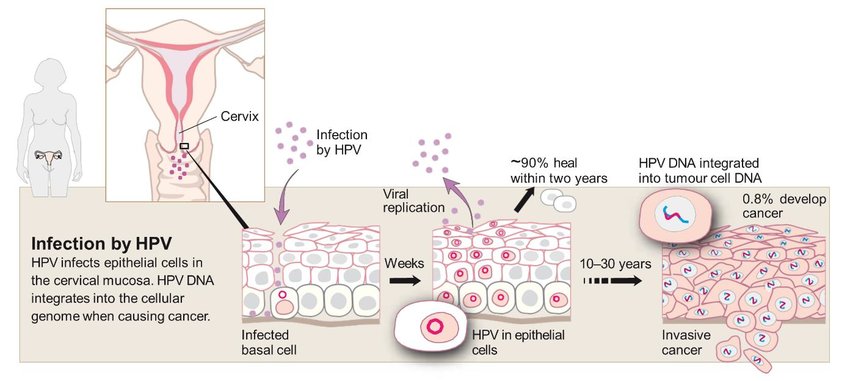 Fig.1 Cervical cancer pathogenesis. (Stark H, Živković A., 2018)
Fig.1 Cervical cancer pathogenesis. (Stark H, Živković A., 2018)
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is recognized as the necessary cause of cervical cancer, with persistent infection by high-risk HPV types responsible for over 99% of cases. HPV is a common DNA virus transmitted through sexual contact. While most infections are cleared by the immune system, persistent infection with high-risk types can lead to cancer development.

The landscape of cervical cancer prevention is being transformed by advanced in vitro diagnostic strategies that move beyond traditional methods to enable more effective, personalized risk assessment. These approaches leverage molecular technologies to detect the root cause of cervical cancer and intelligently triage women at greatest risk, optimizing clinical pathways and resource allocation.
Primary HPV Testing
This strategy establishes detection of high-risk HPV DNA as the initial screening step, replacing cytology-based Pap smears for women over a certain age. Recognized by WHO as the recommended screening method, it offers superior sensitivity for detecting precancerous lesions, allows for extended screening intervals due to its high negative predictive value, and facilitates the implementation of self-sampling to improve screening accessibility and coverage.
Genotyping for Risk Stratification
This approach involves identifying the specific high-risk HPV types present in a positive sample. It is clinically crucial because it differentiates the highest-risk infections—notably HPV 16 and 18, which are responsible for the majority of cervical cancers—from infections with other high-risk types. This stratification enables precise clinical management, typically directing women with HPV 16/18 positivity to immediate colposcopy, while other high-risk types may be managed with reflex cytology or other biomarkers.

Biomarkers for Triage and Precision Management
For women who test positive for high-risk HPV, specific biomarkers are used to identify those most likely to have or develop significant precancer, thereby reducing unnecessary follow-up procedures.
The advancement of cervical cancer screening is being propelled by a new generation of core in vitro diagnostic (IVD) technologies that enable highly sensitive, automated, and comprehensive testing. These innovative platforms are crucial for implementing advanced screening strategies efficiently and on a large scale, making precise and accessible prevention a reality.

These high-throughput, fully automated systems are the workhorses of modern HPV testing, utilizing technologies like real-time PCR to detect and genotype high-risk HPV DNA with exceptional sensitivity and reproducibility. By standardizing the testing process and minimizing manual intervention, they ensure reliable results for large-scale screening programs and enable efficient reflex testing to streamline clinical workflows.

Designed for simplicity and speed, these portable molecular systems deliver HPV test results in under an hour, facilitating a potential "test-and-treat" approach directly within a clinical visit. This technology is particularly transformative for low-resource and remote settings, as it eliminates the need for sophisticated laboratory infrastructure and reduces patient loss to follow-up, thereby expanding screening access to underserved populations.
These advanced tests integrate multiple analyses into a single platform, allowing for the simultaneous detection of HPV DNA, specific genotyping (especially for HPV 16/18), and measurement of complementary biomarkers such as DNA methylation. By providing a detailed molecular profile from one sample, they deliver a comprehensive risk assessment that supports more precise and individualized clinical management decisions.
Alta DiagnoTech provides a comprehensive portfolio of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions for cervical cancer screening and diagnosis, supporting healthcare providers with accurate, reliable, and efficient testing options. Our innovative products leverage advanced technologies to enable early detection, precise risk stratification, and improved patient management throughout the cervical cancer care continuum. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| HPV DNA Detection Kit | Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | Qualitative detection of high-risk HPV DNA in cervical samples for primary screening |
| HPV Genotyping Assay | DNA Microarray | Identification of specific high-risk HPV types (including 16/18) for risk stratification |
| Dual Stain Cytology Kit | Immunocytochemistry | Detection of p16/Ki-67 biomarkers in cervical cells for triage of HPV-positive cases |
| Rapid HPV Test Kit | Lateral Flow Immunoassay | Qualitative detection of high-risk HPV E6/E7 proteins |
| HPV Rapid Genotyping Card | Nucleic Acid Amplification | Identification of HPV 16/18 and other high-risk types |
| Methylation Analysis Panel | Quantitative Methylation-Specific PCR | Detection of host gene methylation markers for progression risk assessment |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |