- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- The Diagnostic Workflow for Neuroendocrine Tumors: From Clinical Suspicion to Molecular Profiling
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) represent a diverse group of neoplasms characterized by variable clinical behavior and complex diagnostic requirements. This resource provides a comprehensive guide to the modern diagnostic workflow for NETs, detailing the systematic pathway from initial clinical suspicion through biochemical testing, imaging localization, and histopathological confirmation to advanced molecular profiling. The following sections will explore the essential roles of biomarker assays, advanced imaging techniques, pathological evaluation, and genomic testing in achieving an accurate diagnosis and guiding personalized treatment strategies.
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms arising from neuroendocrine cells throughout the body, most commonly in the gastrointestinal tract and lungs. They exhibit a wide spectrum of clinical behavior, ranging from indolent to highly aggressive, and can be classified as functional (secreting hormones that cause distinct clinical syndromes) or non-functional. Diagnosis relies on a multimodal approach integrating biochemical marker analysis, advanced imaging, and histopathological evaluation to determine tumor grade, stage, and molecular characteristics for optimal management.
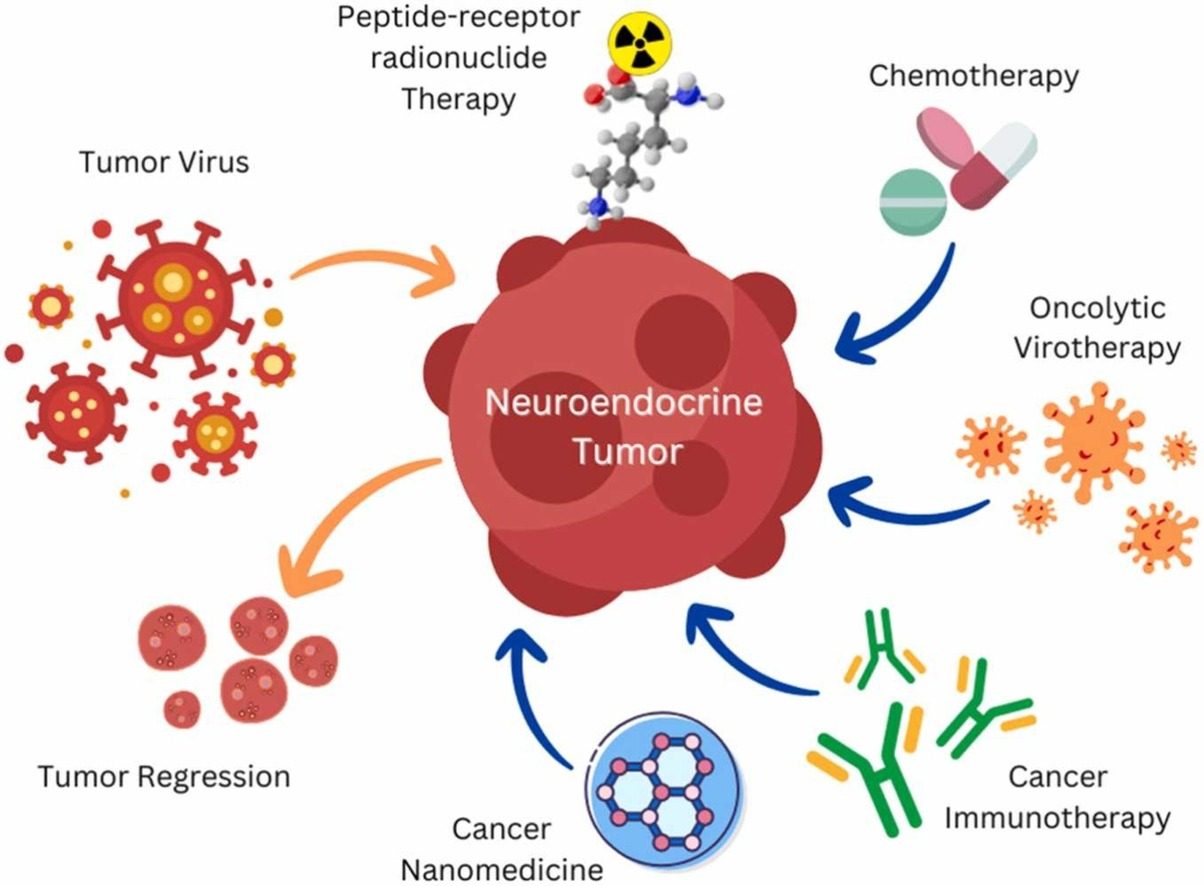 Fig.1 Virus-associated neuroendocrine cancers: pathogenesis and current therapeutics. (Banerjee J, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Virus-associated neuroendocrine cancers: pathogenesis and current therapeutics. (Banerjee J, et al., 2023)
The diagnostic journey for neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) begins with a high index of suspicion based on clinical presentation, which guides targeted biochemical testing. This initial phase is crucial for distinguishing NETs from more common conditions and determining the direction of further investigation.
Clinical Presentation
Biomarker Testing
Accurate localization and staging are critical following biochemical confirmation of neuroendocrine tumors, requiring a dual imaging approach that combines anatomical detail with functional molecular targeting to define disease extent and guide therapeutic decisions.
CT and MRI provide essential structural detail for tumor localization, characterization of primary lesions, and assessment of metastatic burden. These modalities offer excellent spatial resolution for evaluating relationships with adjacent organs and planning surgical interventions.

Gallium-68 DOTATATE PET/CT exploits somatostatin receptor overexpression for superior sensitivity in detecting primary and metastatic NETs. This technique enables precise staging and selection of patients for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy.
Histopathological confirmation forms the definitive diagnostic step for neuroendocrine tumors, transforming clinical and radiological suspicions into a precise diagnosis. This process relies on the successful integration of tissue acquisition, morphological analysis, and specialized staining techniques to establish tumor type, grade, and origin.

Molecular profiling represents the final, advanced tier in the diagnostic workflow for neuroendocrine tumors, moving beyond morphology to uncover the genetic underpinnings of the disease. This critical step involves comprehensive genomic analysis to identify specific mutations, alterations, and biomarkers that inform prognosis, predict treatment response, and reveal targets for personalized therapies, ultimately refining patient stratification and enabling precision oncology.
Alta DiagnoTech provides a comprehensive portfolio of IVD solutions for neuroendocrine tumors, delivering precise diagnostic tools spanning biochemical, histopathological, and molecular approaches. Our standardized assays enable accurate tumor detection, grading, and therapeutic targeting, supporting clinicians throughout the diagnostic and management pathway. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| Chromogranin A (CgA) Quantitative Assay | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) | Serum-based detection and monitoring of NETs |
| Urinary 5-HIAA Detection Kit | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Diagnosis and monitoring of carcinoid syndrome |
| Synaptophysin & Chromogranin A IHC Panel | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Confirmation of neuroendocrine differentiation |
| Ki-67 Proliferation Index Detection Kit | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Tumor grading according to WHO criteria |
| SSTR2 Immunohistochemistry Assay | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Prediction of somatostatin analog therapy response |
| NET Molecular Profiling Panel | Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | Comprehensive genomic analysis for targeted therapy |
| Somatostatin Receptor PET Imaging Companion Assay | In Situ Hybridization | Patient selection for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |