The CV-Chip Platform: Transforming Drug Abuse Detection
Drug abuse is a pervasive public health issue affecting millions globally, causing significant morbidity, mortality, and economic burden. In the United States alone, millions of individuals aged 12 and older struggle with illicit drug use annually. Effective drug abuse detection is pivotal for clinical diagnosis, forensic investigations, and monitoring treatment efficacy. Traditional methods, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), while accurate, are constrained by their complexity, cost, and the need for specialized laboratory settings. The urgency for a sensitive, rapid, and accessible point-of-care (POC) solution has never been greater.
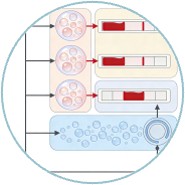
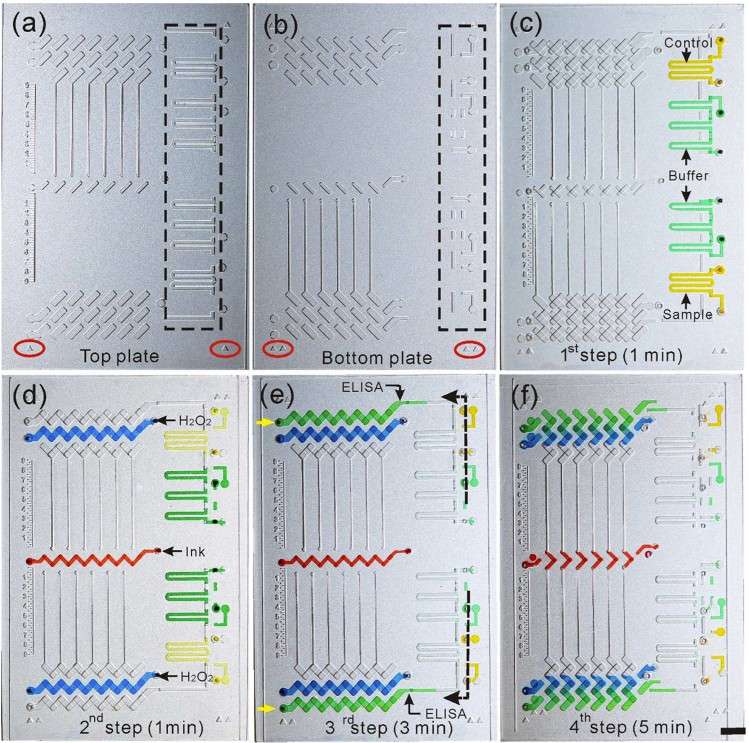 Fig.1 Working principle of the integrated CV-Chip. (Li Y., et al., 2017)
Fig.1 Working principle of the integrated CV-Chip. (Li Y., et al., 2017)
The Emergence of Microfluidics in POC Diagnostics
Microfluidics, a field dedicated to manipulating small volumes of fluids in microscale channels, has emerged as a transformative technology in POC diagnostics. Its potential for multiplexed and quantitative measurements, portability, low cost, and high throughput positions it as an ideal candidate for drug abuse detection. Over the past decade, significant efforts have been directed towards developing microfluidic devices tailored for this purpose.
Challenges with Current Drug Abuse Detection Platforms
Technical Limitations
Current platforms for drug abuse detection face several technical challenges that hinder their effectiveness and widespread adoption. One of the primary issues is the prevalence of non-quantitative results, which provide only a binary indication of drug presence without precise concentration levels. This lack of quantitative data limits the ability of healthcare providers to assess the severity of substance use or monitor treatment progress accurately.
Inaccuracy is another significant concern, as false positives and false negatives can lead to incorrect diagnoses and inappropriate treatment decisions. Many existing methods also suffer from low throughput, meaning they cannot process large numbers of samples quickly. This limitation is particularly problematic in high-demand settings such as emergency departments or large-scale screening programs.
Furthermore, many detection methods require lengthy assay times and specialized instruments, which restrict their use to laboratory settings. These requirements make them impractical for point-of-care (POC) applications, where rapid results are crucial for timely intervention. Additionally, the need for trained personnel to interpret results further complicates widespread adoption, as it limits the accessibility of these tests in resource-limited or remote areas.
Specimen Compatibility
The diverse range of biological specimens used for drug detection, such as urine, serum, and whole blood, each pose unique challenges that complicate the development of a universal detection platform. Urine is a commonly used specimen due to its ease of collection and the relatively long detection windows for many drugs. However, it may not be suitable for detecting substances with short half-lives or for individuals who cannot provide a urine sample.
Serum and whole blood offer more immediate detection windows, making them valuable for identifying recent drug use. However, these specimens require more complex handling and preparation. For instance, whole blood analysis often necessitates centrifugation to separate plasma, a process that is not easily adaptable to POC environments due to the need for specialized equipment and trained personnel. Additionally, blood collection itself can be more invasive and may not be feasible in all settings.
Each matrix also has different stability and storage requirements, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of test results. For example, some drugs and their metabolites may degrade more rapidly in blood compared to urine, requiring immediate processing or specific preservation methods. These differences in specimen handling and preparation make it difficult to develop a single platform that can efficiently and accurately detect drugs across all specimen types.
Introducing the Integrated CV-Chip Platform
Concept and Design
The Integrated Competitive Volumetric-bar-chart Chip (CV-Chip) represents a groundbreaking advancement in POC drug abuse detection. It integrates microfluidic technology with competitive ELISA principles to provide a sensitive, accurate, and rapid platform. The CV-Chip's design allows for the simultaneous detection of multiple drug targets, addressing the need for comprehensive drug screening.
Working Principle
The CV-Chip operates on the principle of competitive binding between sample drugs and preloaded drug-BSA-PtNP (platinum nanoparticle) conjugates for antibody binding sites. The assay involves four main steps: sample loading, competitive binding, washing, and gas generation for bar-chart readout. Oxygen gas produced by the reaction between PtNPs and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) pushes red ink to generate a visual bar-chart, indicating the presence and concentration of target drugs.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
The CV-Chip overcomes several limitations of traditional drug detection methods. Its quantitative readout, rapid assay time (under 10 minutes), and compatibility with diverse specimens make it highly suitable for POC applications. The platform eliminates the need for external instruments, providing a portable and user-friendly solution.
Validation and Performance
- Clinical Sensitivity and Specificity
The performance of the CV-Chip was rigorously validated using a comprehensive set of 38 patient urine and serum samples. To ensure the highest level of accuracy, results were compared against those obtained from LC-MS/MS, which is widely recognized as the gold standard for drug quantification. This validation process revealed that the CV-Chip demonstrated an impressive clinical sensitivity of 0.94 and a specificity of 1.00. These metrics indicate that the platform is highly accurate and reliable, capable of detecting the presence of drugs with minimal false negatives and no false positives.
- Multiplexed Detection
One of the standout strengths of the CV-Chip is its ability to detect multiple drugs simultaneously, addressing the need for comprehensive and efficient drug screening. In a multiplex assay, the platform was tested with six drugs—cocaine, amphetamine, methamphetamine, benzodiazepine, opiate, and tetrahydrocannabinol—in eight patient samples. The CV-Chip successfully distinguished between positive and negative samples for each drug, showcasing its wide dynamic range and analytical specificity. This capability is particularly valuable in clinical settings where patients may use multiple substances, allowing for a more complete assessment of drug use patterns.
- Whole Blood Analysis
To further enhance its applicability in point-of-care (POC) settings, the CV-Chip was integrated with an on-chip blood separator, enabling direct analysis of finger-prick whole blood samples. This innovative approach significantly simplifies blood handling and processing, making it ideal for use in environments where laboratory equipment is unavailable or impractical. Tests conducted on spiked whole blood samples demonstrated good recovery rates for cocaine and amphetamine, confirming the platform's accuracy and reliability in detecting drugs directly from whole blood. This advancement not only streamlines the testing process but also ensures that the CV-Chip can provide rapid and accurate results in real-world POC scenarios.
Technological Innovations
- Surface Modification for Enhanced Antibody Immobilization
The CV-Chip platform introduces a significant technological advancement through the use of aldehyde-modified surfaces for antibody coating. This innovative approach significantly improves the efficiency of antibody immobilization compared to traditional epoxy-based methods. Aldehyde-modified surfaces offer a more stable and uniform binding environment for antibodies, ensuring that a higher proportion of antibodies are correctly oriented and active. This enhanced immobilization efficiency directly contributes to the platform's high analytical sensitivity, allowing for more accurate and reliable detection of target substances.
The use of aldehyde-modified surfaces also provides greater flexibility in the types of antibodies that can be effectively immobilized. This versatility is crucial for the development of multiplex assays, where multiple antibodies are required to detect a range of different drugs. By optimizing the surface chemistry, the CV-Chip ensures that each antibody maintains its full binding capacity, thereby maximizing the overall performance of the detection system.
- Platinum Nanoparticle Probes
Another key technological innovation in the CV-Chip is the substitution of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) with platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) as ELISA probes. This advancement marks a significant leap forward in the field of immunoassay technology. PtNPs exhibit superior catalytic activity for oxygen gas generation at room temperature, which is a critical factor in enhancing the platform's sensitivity and reliability.
Unlike HRP, which requires incubation at 37°C to achieve optimal catalytic activity, PtNPs operate efficiently at room temperature. This eliminates the need for temperature-controlled environments, making the CV-Chip more practical for use in a variety of settings, including point-of-care (POC) environments where laboratory-grade equipment may not be available. The enhanced catalytic activity of PtNPs also leads to a faster and more pronounced gas generation reaction, which translates into quicker and more accurate detection of target drugs.
The use of PtNPs as probes not only improves the sensitivity of the CV-Chip but also enhances its robustness and ease of use. By simplifying the assay process and reducing the time required for reactions to occur, PtNPs make the CV-Chip a highly efficient and user-friendly platform for drug detection. This innovation underscores the platform's commitment to delivering rapid, accurate, and reliable results in diverse testing scenarios.
Future Prospects and Applications
- Expanding Drug Panels
The modular design of the CV-Chip offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing for easy expansion of detectable drug panels. This feature is crucial for adapting to the evolving landscape of drug abuse, where new substances and combinations continually emerge. Future iterations of the CV-Chip could incorporate a broader range of substances, including emerging designer drugs and synthetic compounds, thereby enhancing its utility in diverse clinical and forensic scenarios. By expanding the drug panels, the CV-Chip can provide a more comprehensive and up-to-date screening solution, ensuring that healthcare providers and law enforcement agencies stay ahead of emerging drug trends.
- Integration with Wireless Technology
The integration of the CV-Chip with wireless connectivity represents a significant leap forward in real-time diagnostics. By enabling real-time data transmission and remote monitoring, this advancement would facilitate continuous patient management and improve treatment outcomes. Healthcare providers could receive immediate alerts and detailed reports on patients' drug use, allowing for timely interventions and personalized treatment plans. This feature is particularly valuable in settings where patients require ongoing monitoring, such as rehabilitation centers, correctional facilities, and community-based treatment programs.
Moreover, wireless integration could enhance the efficiency of data management and analysis, allowing for seamless integration with electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare information systems. This would streamline the workflow for healthcare providers and researchers, ensuring that critical information is readily available when needed.
- Global Accessibility
Ensuring the global accessibility of the CV-Chip is a critical goal for its widespread adoption and impact. Efforts to streamline manufacturing processes and reduce costs are essential for making this advanced technology affordable and accessible in resource-limited settings. By developing cost-effective and easy-to-use point-of-care (POC) solutions, the CV-Chip can significantly enhance drug abuse detection and management in regions where traditional laboratory testing is impractical or unavailable.
Affordable and user-friendly POC solutions can empower local healthcare providers and community organizations to conduct regular and reliable drug screening, thereby improving public health outcomes. Additionally, reducing the cost of manufacturing can make the CV-Chip a viable option for large-scale screening programs, such as those in schools, workplaces, and community health initiatives. This broader accessibility can contribute to a more comprehensive and effective global response to drug abuse.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Li, Ying, et al. "Fast, sensitive, and quantitative point-of-care platform for the assessment of drugs of abuse in urine, serum, and whole blood." Analytical chemistry 89.16 (2017): 8273-8281.
Drug Abuse Test Kits (ICT)
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
 Fig.1 Working principle of the integrated CV-Chip. (Li Y., et al., 2017)
Fig.1 Working principle of the integrated CV-Chip. (Li Y., et al., 2017)