Revolutionizing Hormone Detection: The Rise of Lateral Flow Assays
Hormone detection is absolutely essential for diagnosing and managing a wide range of endocrine disorders, including diabetes, thyroid diseases, fertility issues, and stress-related conditions. Traditionally, hormone measurement has heavily relied on sophisticated laboratory techniques such as radioimmunoassay (RIA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Although these methods are known for their high sensitivity and specificity, they come with significant drawbacks—they are often time-consuming, expensive, and require specialized training and equipment. As a result, there has been a growing demand for rapid, cost-effective, and user-friendly diagnostic tools that can be easily deployed at the point of care (POC). This shift towards POC diagnostics aims to provide quicker results, reduce costs, and make hormone testing more accessible, especially in settings where resources are limited.
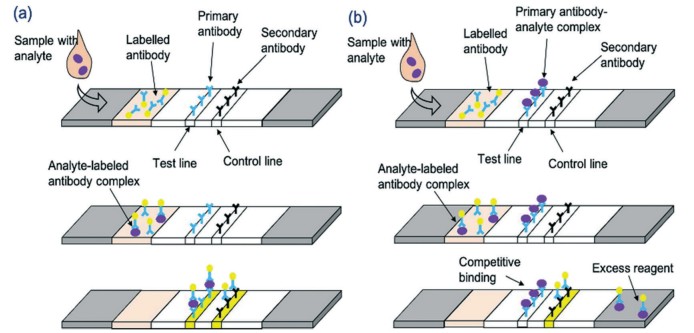 Fig.1 Schematic representation of LFA detection process utilising antibodies and nanoparticle conjugates for (a) sandwich LFA and (b) competitive LFA. (Khelifa L., et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of LFA detection process utilising antibodies and nanoparticle conjugates for (a) sandwich LFA and (b) competitive LFA. (Khelifa L., et al., 2022)
The Emergence of Lateral Flow Assays (LFAs)
Lateral flow assays (LFAs) have emerged as a groundbreaking solution to the challenges associated with traditional hormone detection methods. LFAs are paper-based diagnostic devices that utilize the principles of immunochromatography to detect specific analytes, including hormones, in various biological samples. They are designed to provide quick, on-site results with minimal sample preparation and no need for specialized training or equipment.
How LFAs Work
LFAs consist of several key components: a sample pad, a conjugate pad, a nitrocellulose membrane, and an absorbent pad. The sample is applied to the sample pad, which ensures optimal characteristics such as viscosity, purity, and pH. The sample then migrates to the conjugate pad, where it rehydrates labeled antibodies specific to the target hormone. These labeled antibodies bind to the hormone in the sample, forming immune complexes.
As the sample continues to flow, the immune complexes reach the test line on the nitrocellulose membrane, where they are captured by immobilized antibodies specific to the hormone. This results in the formation of a visible line, the intensity of which is proportional to the concentration of the hormone in the sample. A control line is also present to ensure proper flow and function of the assay. The absorbent pad at the end of the strip ensures complete flow of the sample through the device.
Advantages of LFAs in Hormone Detection
LFAs offer several significant advantages over traditional hormone detection methods. Firstly, they are rapid, providing results within minutes, which is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment decisions. Secondly, LFAs are cost-effective, making them accessible to a wider range of healthcare settings, including resource-limited areas. Thirdly, LFAs are user-friendly, requiring minimal sample preparation and no specialized training, thus enabling decentralized testing. Finally, LFAs are versatile, capable of detecting a wide range of hormones in various biological samples, including blood, urine, saliva, and sweat.
Innovations in LFA Technology for Hormone Detection
Enhanced Sensitivity and Specificity
Recent advancements in lateral flow assay (LFA) technology have been driven by the need to improve the sensitivity and specificity of hormone detection. Traditional LFAs often rely on colored nanoparticles, such as gold nanoparticles, which are known for their strong optical signals and ease of detection. However, these materials have limitations in terms of signal intensity and background noise.
- Novel Labeling Materials: Innovations in labeling materials have introduced new options that offer higher signal-to-noise ratios. For instance, fluorescent nanoparticles and quantum dots provide enhanced sensitivity due to their superior optical properties. These materials can emit light at specific wavelengths, allowing for more precise detection even at low analyte concentrations. Additionally, superparamagnetic nanoparticles have shown promise in improving sensitivity by enabling more efficient capture and detection of target molecules.
- Superior Detection Capabilities: The implementation of these advanced materials has significantly improved the performance of LFAs. For example, quantum dots can be engineered to emit light at different wavelengths, allowing for multiplexed detection and reducing the risk of cross-reactivity. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles, on the other hand, can be manipulated using magnetic fields, enabling more controlled and efficient detection processes.

Multiplexing Capabilities
A major innovation in LFA technology is the development of multiplexed assays capable of detecting multiple hormones simultaneously. This advancement is particularly valuable in diagnosing complex endocrine disorders, where the interplay of multiple hormones is crucial for accurate assessment.
- Multiplexed LFA Design: Multiplexed LFAs utilize different colored nanoparticles or spatial separation on the nitrocellulose membrane to distinguish between multiple analytes. For example, a single LFA strip can be designed to detect luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and progesterone simultaneously. This capability allows for a comprehensive assessment of fertility status or other endocrine conditions with a single test, reducing the need for multiple assays and improving diagnostic efficiency.
- Clinical Applications: The ability to detect multiple hormones in a single test is particularly beneficial in clinical settings. For instance, in fertility clinics, a multiplexed LFA can provide a detailed hormonal profile, aiding in the diagnosis and management of reproductive health issues. Similarly, in the context of thyroid disorders, a multiplexed LFA could detect thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) simultaneously, offering a more holistic view of thyroid function.

Digitalization and Smartphone Integration
The integration of LFAs with digital technologies, particularly smartphones, has revolutionized point-of-care (POC) hormone detection. This innovation has expanded the capabilities of LFAs, making them more accurate, user-friendly, and connected.
- Smartphone-Based LFA Readers: Smartphone-based LFA readers leverage the device's camera and image processing capabilities to quantify the intensity of the test and control lines. This digital approach provides more accurate and objective results compared to visual interpretation. By analyzing the intensity of the colorimetric or fluorescent signals, these readers can provide quantitative measurements of hormone levels, enhancing the diagnostic value of LFAs.
- Remote Monitoring and Data Sharing: The digitalization of LFAs also enables remote monitoring and data sharing with healthcare providers. Patients can perform tests at home and share the results with their doctors in real-time, facilitating continuous monitoring and personalized care. This is particularly beneficial for chronic conditions that require frequent hormone level checks, such as diabetes or thyroid disorders.
- Smartphone Apps and Real-Time Tracking: The development of smartphone apps linked to LFAs allows for real-time tracking of hormone levels. These apps can store historical data, set reminders for regular testing, and provide insights into hormonal trends. This level of personalization empowers patients to take a more proactive role in managing their health, while also providing healthcare providers with valuable data for more informed decision-making.
Clinical Applications of LFA-Based Hormone Detection
- Pregnancy and Fertility Monitoring
One of the most well-established applications of lateral flow assays (LFAs) in hormone detection is pregnancy testing. Home pregnancy tests, which detect human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine, have become a staple in reproductive healthcare due to their accuracy, convenience, and ease of use. These tests provide women with the ability to confirm pregnancy in the privacy of their own homes, often before a missed menstrual period.
Beyond pregnancy testing, LFAs are increasingly being used to monitor fertility by detecting key hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and estradiol. LH surge detection using LFAs is particularly valuable for predicting ovulation. By identifying the LH surge, which typically occurs 24-36 hours before ovulation, women can time intercourse more effectively for natural family planning or optimize the timing of assisted reproductive technologies such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF). This application not only enhances the chances of successful conception but also empowers individuals to take a more proactive role in their reproductive health.
- Stress and Cortisol Monitoring
Cortisol, often referred to as the "stress hormone," plays a crucial role in the body's response to stress. Elevated cortisol levels are associated with chronic stress, anxiety, and depression, while abnormally low levels may indicate adrenal insufficiency. Monitoring cortisol levels is essential for diagnosing and managing conditions related to stress and adrenal function.
LFAs capable of detecting cortisol in saliva, blood, and sweat have been developed, offering a non-invasive and convenient method for monitoring stress levels. These assays are particularly valuable in various clinical settings:
- Occupational Health: In high-stress work environments, regular cortisol monitoring can help identify individuals at risk of burnout or stress-related health issues, allowing for early intervention and preventive measures.
- Sports Medicine: Athletes often experience high levels of physical and mental stress. Cortisol monitoring can help optimize training regimens, prevent overtraining, and enhance performance by ensuring that stress levels are managed effectively.
- Mental Health: In clinical settings, cortisol assays can aid in the diagnosis and management of anxiety disorders, depression, and other stress-related conditions. By providing objective measures of stress, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans more effectively.
- Thyroid Function Assessment
Thyroid hormones, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), and thyroxine (T4), are essential for regulating metabolism, growth, and development. Dysregulation of thyroid function can lead to a wide range of health problems, from hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism to thyroid cancer. Accurate and timely detection of thyroid hormone levels is crucial for diagnosing and managing these disorders.
- LFAs for thyroid hormone detection offer a rapid and cost-effective alternative to traditional laboratory tests. These assays can provide results within minutes, enabling healthcare providers to make timely clinical decisions. The ability to perform thyroid function tests at the point of care is particularly beneficial in settings where access to laboratory facilities is limited or where immediate results are needed for patient management.
- Primary Care Settings: In primary care clinics, LFAs can facilitate the initial screening and diagnosis of thyroid disorders, allowing for prompt referral to specialists if needed.
- Resource-Limited Areas: In regions with limited healthcare infrastructure, LFAs can provide essential thyroid hormone testing, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care even in the absence of advanced laboratory facilities.
- Chronic Disease Management: For patients with known thyroid disorders, LFAs can be used for regular monitoring of hormone levels, helping to optimize treatment regimens and improve patient outcomes.
Future Perspectives and Challenges
- Expanding the Range of Detectable Hormones
While LFAs have made significant strides in hormone detection, there is still a need to expand the range of detectable hormones. Many hormones, particularly those present at low concentrations or with complex molecular structures, remain challenging to detect using current LFA technology. Future research should focus on developing novel antibodies and labeling materials capable of binding to these elusive hormones with high affinity and specificity.
- Improving Sample Preparation and Pre-Concentration
Sample preparation and pre-concentration are critical steps in LFA-based hormone detection, particularly when dealing with complex biological samples such as blood and saliva. Current methods often require extensive sample processing, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. The development of simplified and automated sample preparation techniques, along with pre-concentration methods that enhance assay sensitivity, will be crucial for the widespread adoption of LFAs in clinical settings.
- Standardization and Regulatory Compliance
As the market for LFA-based hormone detection continues to grow, there is a pressing need for standardization and regulatory compliance. Ensuring that LFAs meet stringent quality and performance standards is essential for their acceptance by healthcare providers and regulatory agencies. Future efforts should focus on developing standardized protocols for LFA development, validation, and manufacturing, as well as establishing clear guidelines for their use in clinical practice.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Khelifa, Leena, et al. "Lateral flow assays for hormone detection." Lab on a Chip 22.13 (2022): 2451-2475.
Hormone Level Test Kits (ICT)
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
 Fig.1 Schematic representation of LFA detection process utilising antibodies and nanoparticle conjugates for (a) sandwich LFA and (b) competitive LFA. (Khelifa L., et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of LFA detection process utilising antibodies and nanoparticle conjugates for (a) sandwich LFA and (b) competitive LFA. (Khelifa L., et al., 2022)