- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- Quantum Dots Revolutionize Rapid Detection of Heart Inflammation Biomarkers: A Breakthrough in CRP and PCT Testing
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases represent the leading cause of mortality among middle-aged and elderly populations in China, with inflammation identified as a significant driving factor. Within this context, two biomarkers have emerged as pivotal for clinical diagnosis: C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT).
CRP, an acute-phase protein synthesized in the liver, exhibits a remarkable ability to reflect systemic inflammation. Under normal physiological conditions, its concentration in blood remains below 10 μg/mL, but during episodes of infection, trauma, surgery, tissue necrosis, or acute inflammation, this value can surge dramatically. Beyond its role as a general inflammation marker, CRP serves as a strong predictor of cardiovascular disease and a critical indicator for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Its rapid quantitative detection can significantly improve the timeliness of intervention in myocardial injury cases.
PCT, a 116-amino-acid glycoprotein and propeptide of calcitonin, demonstrates unique value in distinguishing bacterial infections from other inflammatory conditions. Unlike CRP, PCT levels rise specifically in response to bacterial stimulation, particularly during sepsis, with various tissues and cell types releasing it into the circulatory system. Clinically, PCT exhibits higher specificity than CRP in identifying bacterial infections, while the combined detection of both biomarkers yields significantly higher sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy than either alone. This combination not only enhances diagnostic precision but also guides rational antibiotic use, reducing unnecessary prescriptions and addressing the growing concern of antimicrobial resistance.
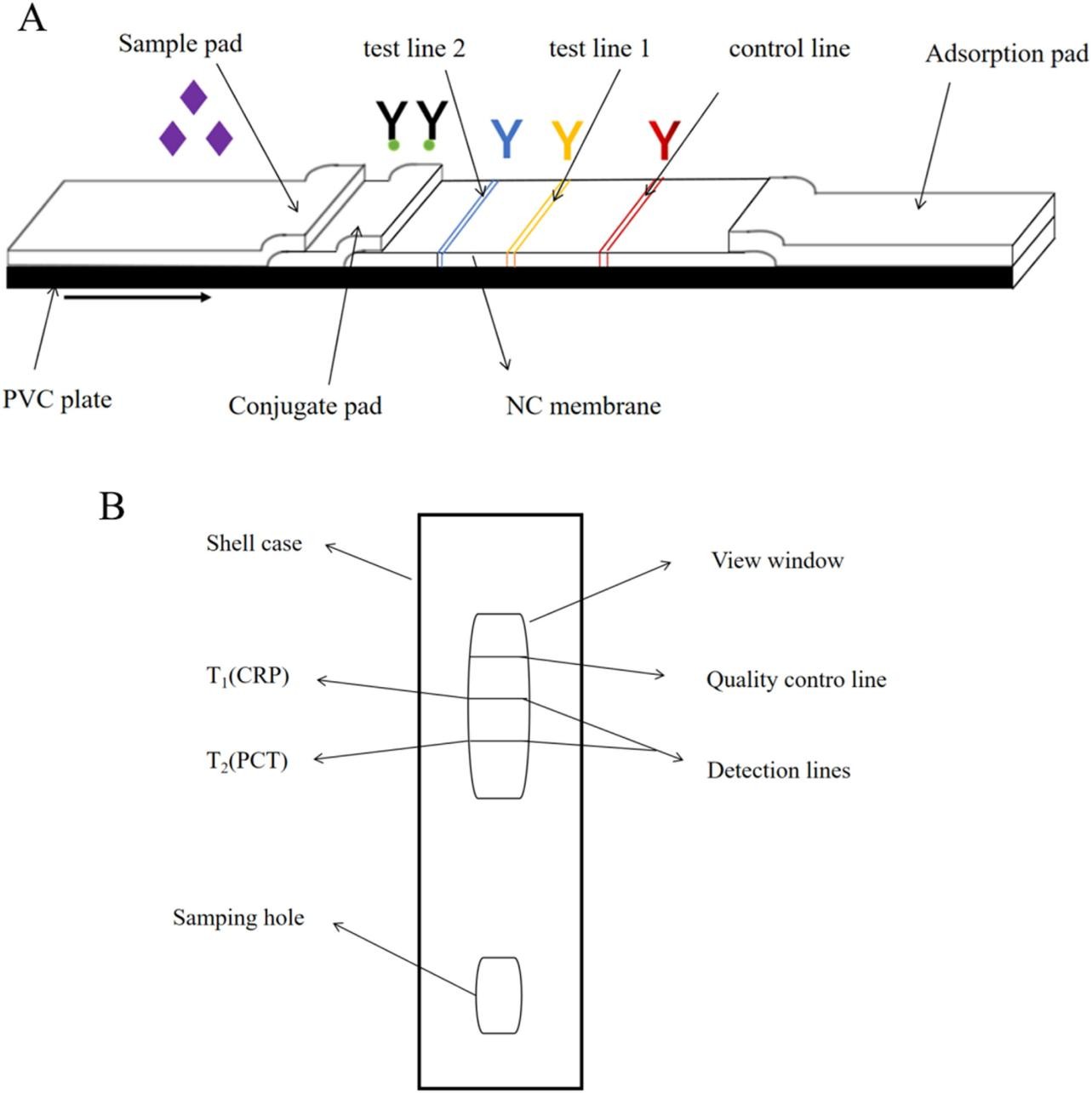 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of (A) the structure of the CRP and PCT QD test strip (Definitions: NC: nitrocellulose; PVC: polyvinyl chloride); (B) the structure of the CRP and PCT QD reagent card. (Yingshu, F. E. N. G., et al., 2024)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of (A) the structure of the CRP and PCT QD test strip (Definitions: NC: nitrocellulose; PVC: polyvinyl chloride); (B) the structure of the CRP and PCT QD reagent card. (Yingshu, F. E. N. G., et al., 2024)

Traditional detection methods for CRP and PCT, including immunodiffusion, latex agglutination, ELISA, colloidal gold, and biosensors, each present limitations, from false results to cumbersome procedures and high equipment demands. Quantum dot (QD) immunochromatography, an emerging point-of-care testing (POCT) technology, addresses these drawbacks through the unique optical properties of quantum dots.
Quantum dots are semiconductor nanocrystals with size-tunable fluorescence emission, exceptional photostability, and high quantum yield—attributes that make them ideal for biosensing applications. However, oil-soluble quantum dots (such as CdSe/ZnS), which typically offer superior optical performance, require modification to function in aqueous biological environments. The breakthrough came through the synthesis of comb amphiphilic poly(octadecyl-alt-polyethylene glycol) via amide reaction, which coats oil-soluble QDs to form water-soluble core-shell QD microbeads.
Characterization via transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed that these microbeads exhibit uniform particle sizes (58–68 nm) and consistent morphology. Fluorescence testing over 10 days demonstrated minimal loss of intensity, confirming excellent stability. Most notably, comparative analysis showed that these custom QD microbeads emit stronger fluorescence than commercial water-soluble QDs at equivalent concentrations, particularly at low levels, directly translating to enhanced detection sensitivity.
The construction of the CRP/PCT dual-detection quantum dot immunochromatographic test strip involved meticulous optimization of each component and reaction parameter, resulting in a robust, user-friendly diagnostic tool.
QD-Antibody Conjugation: Precision Engineering
The conjugation of quantum dots with CRP and PCT antibodies required careful selection of crosslinking agents (1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide [EDC] and N-hydroxysuccinimide [NHS]) to activate carboxyl groups on QD surfaces, facilitating stable amide bond formation with antibody amino groups. Systematic optimization identified optimal conditions:
| Coupling agent dosages | 7.6 μL EDC with 8.7 μL NHS for CRP; 7.6 μL EDC with 43.5 μL NHS for PCT |
| pH | 7.4 (matching physiological conditions) |
| Temperature | 25°C (eliminating the need for temperature control equipment) |
| Reaction time | 90 minutes (balancing efficiency and completeness) |
| Antibody concentrations | 12 μg for CRP; 18 μg for PCT |
UV spectroscopy, fluorescence analysis, and agarose gel electrophoresis confirmed successful conjugation, with complexes retaining over 80% of QD fluorescence intensity and exhibiting reduced electrophoretic mobility due to increased molecular weight—unequivocal evidence of antibody binding.
Test Strip Assembly: Integrating Components for Optimal Performance
The final test strip architecture comprises five functional elements laminated on a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) backing:
| Sample pad | Treated with a formulation containing Tween-20, BSA, and specific buffers to optimize sample flow and reduce nonspecific binding. |
| Conjugate pad | Contains pre-immobilized QD-CRP and QD-PCT antibody complexes, released upon sample application. |
| Nitrocellulose membrane | Features two test lines (T1 for CRP, T2 for PCT) coated with capture antibodies and a control line with goat anti-mouse IgG to validate test integrity. |
| Absorbent pad | Facilitates capillary flow through the strip via wicking action. |
Critical optimization of coating concentrations (0.5 mg/mL for CRP capture antibody, 1.5 mg/mL for PCT) and conjugate deposition rates (0.5 μL/cm for CRP, 6 μL/cm for PCT) balanced signal intensity and signal-to-noise ratio, ensuring reliable detection across clinically relevant concentration ranges.
Rigorous evaluation of the dual-detection test strip confirmed its suitability for clinical application through comprehensive performance testing.

Sensitivity and Linear Range
The test strip demonstrated exceptional sensitivity, with limits of detection (LOD) at 0.197 mg/L for CRP and 0.04 ng/mL for PCT—both below physiological levels, enabling early inflammation detection. Calibration curves showed strong linear relationships between concentration and optical density (R² = 0.9966 for CRP, 0.9957 for PCT) across broad ranges: 0.39–100 mg/L for CRP and 0.195–200 ng/mL for PCT, covering the full spectrum of clinical relevance.

Precision and Stability
Intra-batch and inter-batch precision testing revealed coefficient of variation (CV) values below 15% for both biomarkers, confirming consistent performance. Stability trials demonstrated reliable results after one week of storage at 4°C and 25°C, with minimal degradation even at 37°C, supporting practical storage and transportation requirements.

Specificity and Interference Resistance
Cross-reactivity testing confirmed no interference between CRP and PCT detection, with distinct signals at their respective test lines. Evaluation of potential interferents (Na+, K+, EDTA) showed minimal impact on results (CV < 5%), ensuring accuracy in diverse clinical samples.

Clinical Validation
Comparison with commercial immunofluorescence kits using 40 clinical samples (20 positive, 20 negative for each biomarker) yielded 100% agreement. Correlation analysis with hospital laboratory results demonstrated exceptional concordance (R² = 0.9972 for CRP, 0.9981 for PCT), validating the test strip’s clinical utility.
The CRP/PCT dual-detection quantum dot immunochromatographic test strip offers transformative benefits for clinical practice:
Compared to colloidal gold strips, the quantum dot-based system eliminates false negatives at low concentrations through superior sensitivity. Relative to ELISA, it reduces processing time from hours to minutes while maintaining comparable accuracy. These advantages position the test strip as a valuable tool for early diagnosis of myocardial inflammation, guiding therapeutic interventions, and monitoring patient responses.
The development of a quantum dot immunochromatographic test strip for simultaneous CRP and PCT detection represents a significant advancement in cardiovascular and infectious disease diagnostics. By leveraging the unique properties of quantum dots and meticulous optimization of assay components, this technology addresses critical limitations of existing methods, combining speed, sensitivity, and convenience in a single platform.
Clinical validation confirms its potential to improve early detection of myocardial inflammation, guide antibiotic stewardship, and enhance patient outcomes through timely intervention. As quantum dot-based diagnostics continue to evolve, their application in multiplexed biomarker detection holds promise for revolutionizing point-of-care testing across diverse medical fields, ultimately contributing to more precise, personalized healthcare.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00203
Rotavirus Antigen Group A and Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00206
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00207
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00211
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00212
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. IP-00189
Influenza A Rapid Assay Kit

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00200
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00201
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00202
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00208
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00209
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit(Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00210
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0001
hCG Pregnancy Test Strip
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0002
hCG Pregnancy Test Cassette
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0003
hCG Pregnancy Test Midstream

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0001
Cocaine (COC) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0002
Marijuana (THC) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0003
Morphine (MOP300) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0004
Methamphetamine (MET) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0005
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine ecstasy (MDMA) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0006
Amphetamine (AMP) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0007
Barbiturates (BAR) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0008
Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0009
Methadone (MTD) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0011
Opiate (OPI) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0002
Multi-Drug Test L-Cup, (5-16 Para)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0005
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) with Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0006
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) without Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0007
Multi-Drug 2~14 Drugs Rapid Test (Dipstick & Dipcard & Cup)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0008
Fentanyl (FYL) Rapid Test (For Prescription Use)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0009
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (CLIA Waived)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0010
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (Home Use)
|
There is no product in your cart. |