Precision in Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) Diagnosis: The Role of Cardiac Biomarkers and Risk Stratification
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) represents a spectrum of life-threatening cardiac conditions caused by abrupt coronary artery occlusion, requiring immediate diagnosis and intervention to prevent irreversible myocardial damage. This resource provides a comprehensive guide to the precision diagnosis of ACS, detailing the integrated clinical pathway from electrocardiographic evaluation and advanced cardiac biomarker testing to risk stratification. Additionally, it introduces relevant products available for ACS diagnosis.
Introduction to Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) encompasses a spectrum of life-threatening cardiac conditions caused by abrupt reduction in coronary blood flow, most commonly due to atherosclerotic plaque rupture and thrombosis. This critical condition ranges from unstable angina (UA) to myocardial infarction, categorized as non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) or ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) based on electrocardiographic findings. Diagnosis relies on the integration of clinical presentation, characteristic ECG changes, and serial measurement of cardiac biomarkers, particularly cardiac troponins, to guide urgent reperfusion therapy and risk stratification.
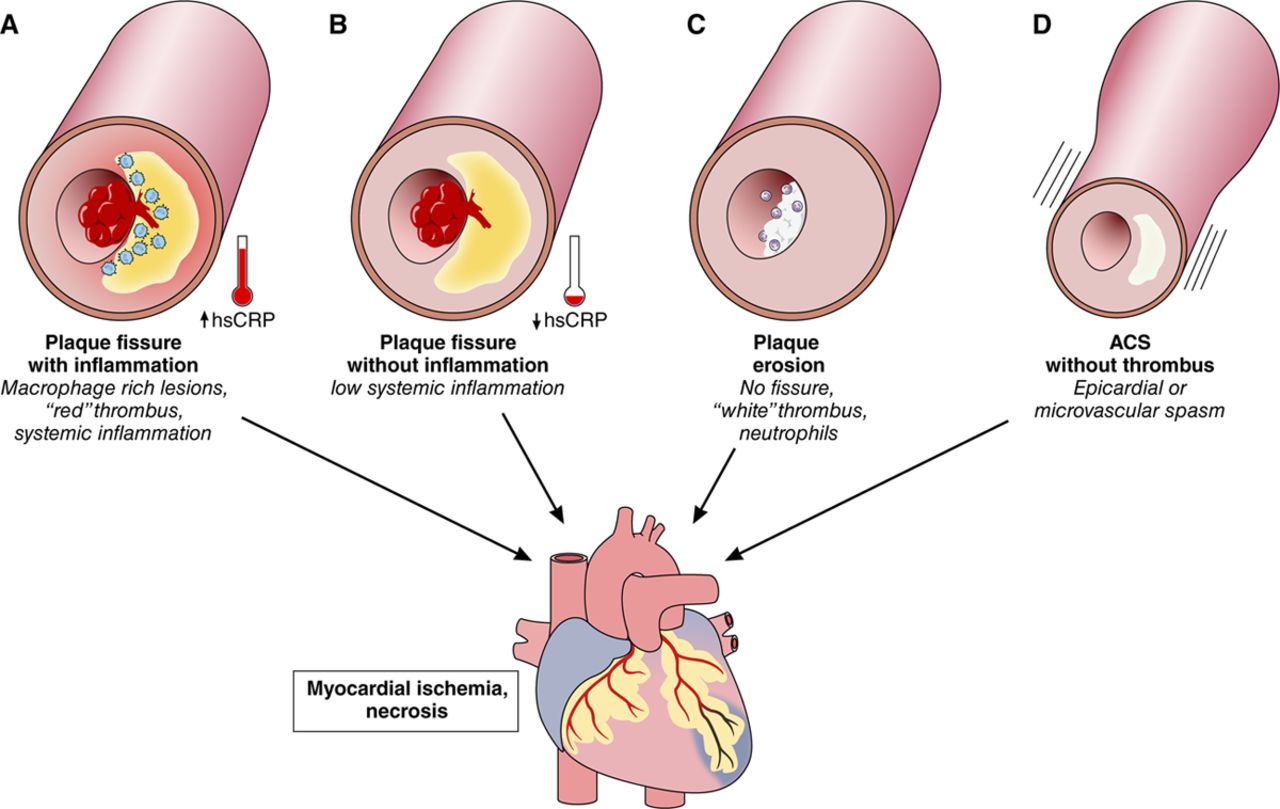 Fig.1 Four diverse mechanisms cause acute coronary syndromes (ACS). (Crea F, Libby P., 2017)
Fig.1 Four diverse mechanisms cause acute coronary syndromes (ACS). (Crea F, Libby P., 2017)
Electrocardiographic Evaluation of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is an essential initial diagnostic tool for acute coronary syndrome (ACS), providing immediate evidence of myocardial ischemia through characteristic patterns of ST-segment elevation or depression, T-wave inversion, and other dynamic changes. These findings are critical for rapidly differentiating between STEMI, NSTEMI, and unstable angina, guiding urgent reperfusion decisions, and facilitating early risk stratification to optimize patient outcomes.
Cardiac Biomarkers for Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) Diagnostics
Cardiac biomarkers play a pivotal role in the diagnosis, risk stratification, and management of acute coronary syndrome (ACS), providing critical objective evidence of myocardial injury to guide therapeutic decisions. These laboratory parameters have evolved to offer increasingly sensitive and specific detection of cardiac damage, forming an essential component alongside clinical assessment and electrocardiographic findings in the diagnostic workflow.
High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin (hs-cTn)
High-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays represent the cornerstone of modern ACS diagnostics, providing exceptional sensitivity for detecting myocardial injury. These tests can measure very low troponin concentrations, enabling earlier rule-out of myocardial infarction and more accurate risk stratification. Their high negative predictive value allows for safe discharge of low-risk patients while identifying subtle cardiac damage that conventional assays might miss.
Additional Biomarkers
Beyond troponin, several established biomarkers contribute valuable diagnostic and prognostic information in ACS. CK-MB remains useful for detecting reinfarction, while BNP and NT-proBNP help assess ventricular strain and predict mortality risk. Myoglobin, though less specific, offers rapid early detection capabilities that can complement troponin testing in acute settings.
Emerging Biomarkers
Novel biomarkers are expanding the diagnostic horizon for ACS evaluation. Copeptin shows promise in early rule-out strategies when combined with troponin, particularly in the hyperacute phase. Other investigational markers including pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A), heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP), and various microRNAs may provide additional insights into plaque instability and ischemic processes, potentially enabling more personalized risk assessment.
Risk Stratification Models and Clinical Scores
Risk stratification is a critical component in the management of acute coronary syndrome (ACS), enabling clinicians to rapidly identify high-risk patients requiring urgent intervention while safely directing low-risk individuals to appropriate conservative management. These validated tools integrate clinical, electrocardiographic, and biochemical parameters to predict mortality and ischemic events, thereby guiding treatment intensity and site-of-care decisions. Key risk stratification tools include:
- TIMI Risk Score: Estimates mortality risk in NSTEMI/UA patients using 7 clinical variables (age ≥65 years, ≥3 CAD risk factors, known CAD, aspirin use in past 7 days, recent severe angina, ST-segment deviation, elevated cardiac markers). Scores range from 0-7, with higher scores indicating greater risk and benefit from aggressive therapy.
- GRACE Risk Score: More comprehensive than TIMI, incorporating 8 parameters including heart rate, blood pressure, creatinine level, and Killip class to predict in-hospital and 6-month mortality. Recommended for both STEMI and NSTEMI patients to guide discharge planning and long-term management.
- HEART Score: Particularly valuable in emergency department settings, evaluating History, ECG, Age, Risk factors, and Troponin to identify patients suitable for early discharge (scores 0-3) versus those requiring admission and intensive management (scores 4-10).
Featured Products for Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) Diagnostics
With our specialized expertise in cardiovascular diagnostics, Alta DiagnoTech delivers comprehensive testing solutions for acute coronary syndrome (ACS) that support both clinical decision-making and research applications. Our product portfolio encompasses advanced biomarker assays and integrated testing platforms designed to enable rapid diagnosis, accurate risk stratification, and improved patient outcomes across diverse healthcare settings. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name |
Technology |
Application |
| High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I Assay |
Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) |
Early detection and monitoring of myocardial injury |
| CK-MB Mass Detection Kit |
Immunoassay |
Complementary marker for myocardial infarction diagnosis |
| NT-proBNP Quantitative Test |
Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay |
Heart failure assessment and risk stratification |
| Copeptin Rapid Detection Assay |
Lateral Flow Immunochromatography |
Early rule-out of myocardial infarction |
| Point-of-Care Cardiac Panel |
Fluorescent Immunoassay |
Rapid triage and initial assessment in emergency settings |
| Myoglobin Quantitative Test |
Chemiluminescent Immunoassay |
Early marker for acute myocardial infarction |
Reference
- Crea F, Libby P. Acute coronary syndromes: the way forward from mechanisms to precision treatment[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(12): 1155-1166.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.



 Fig.1 Four diverse mechanisms cause acute coronary syndromes (ACS). (Crea F, Libby P., 2017)
Fig.1 Four diverse mechanisms cause acute coronary syndromes (ACS). (Crea F, Libby P., 2017)