- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- Navigating the Global Regulatory Maze: Challenges and Innovations in the Medical Device Industry
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
The global medical device market is vast and ever-evolving, comprising everything from simple tools like thermometers to advanced technologies such as robotic surgical systems. As these devices become increasingly sophisticated, so too do the regulatory frameworks governing their safety and efficacy. Understanding these regulations is crucial for ensuring that medical devices not only meet safety standards but also reach the market efficiently and remain accessible to patients. However, navigating the global regulatory maze presents substantial challenges for manufacturers and regulatory bodies alike.
This article explores the regulatory processes across key global markets, particularly the European Union, the United States, and Japan, focusing on the complexities, the regulatory challenges, and the innovative solutions driving change. By examining these regions' distinct regulatory landscapes and highlighting the emerging trends, this article sheds light on how innovation and harmonization efforts can streamline market access and improve patient safety.
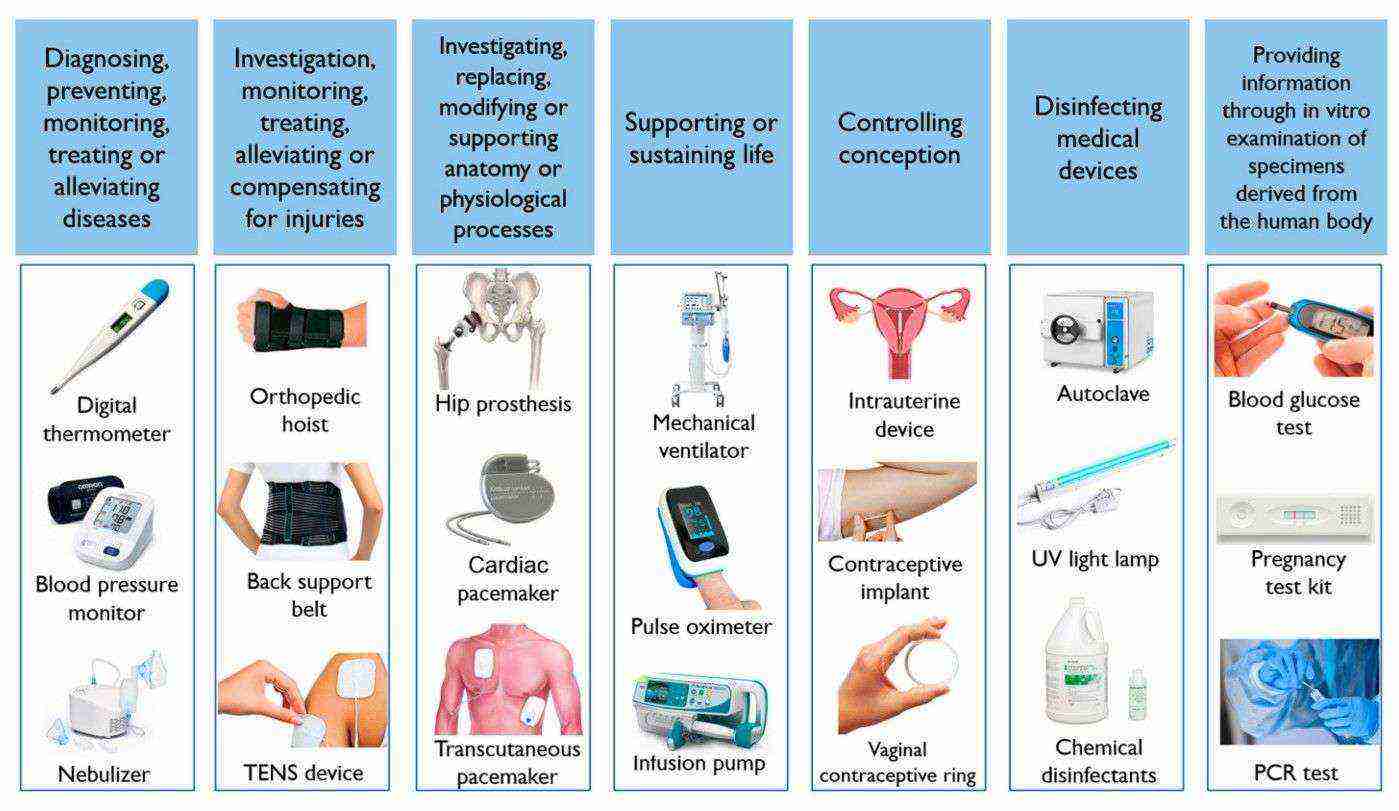 Fig.1 Medical device examples according to their respective purpose. (Amaral C., et al., 2024)
Fig.1 Medical device examples according to their respective purpose. (Amaral C., et al., 2024)
In the European Union, medical devices are governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (Regulation (EU) 2017/745), which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD). The MDR is one of the most stringent regulatory frameworks globally, ensuring that devices meet high safety and performance standards. The regulation focuses on several key areas:

Once a device passes the conformity assessment, it is granted the CE Mark, which allows it to be sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). This certification indicates that the device complies with EU regulations regarding safety, efficacy, and quality.
Despite the common regulatory framework, the European Union's decentralized nature can lead to variations in how regulations are interpreted and enforced across different member states. EUDAMED, the European Database on Medical Devices, helps mitigate this challenge by providing a unified database that enhances transparency, traceability, and coordination of medical device regulation within the EU. However, the complexity of harmonizing regulations across multiple jurisdictions remains an ongoing challenge for both manufacturers and regulators.
In the United States, the regulation of medical devices falls under the jurisdiction of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA uses a risk-based classification system, similar to the EU's approach, but with distinct pathways for approval depending on the risk level of the device. Medical devices are categorized into three classes:

The 510(k) pathway is the most commonly used process for moderate-risk devices. Manufacturers submit data demonstrating that their new device is substantially equivalent to an existing, legally marketed device. If no equivalent device exists, manufacturers may use the de novo classification process to introduce innovative devices that do not fit into existing categories.
For high-risk devices, PMA is required. This process entails a detailed evaluation of the device's safety and efficacy based on clinical data and scientific evidence. The PMA process is far more involved than the 510(k) process, reflecting the higher stakes associated with life-sustaining or critical health-related devices.

Once a device is approved and enters the market, the FDA mandates ongoing post-market surveillance to monitor its performance. This includes adverse event reporting and mandatory clinical studies, especially for devices approved under PMA. The Unique Device Identification (UDI) system also plays a critical role in tracking devices throughout their lifecycle, ensuring traceability and facilitating recalls when necessary.
Japan's medical device regulatory framework is overseen by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), operating under the PMD Act. Devices in Japan are classified into four categories based on their risk profile:
Despite having a robust regulatory framework, Japan faces a significant medical device lag, which refers to the delays in the approval and adoption of new medical technologies. This lag is primarily driven by several factors, including the complexity of regulatory requirements, the need for extensive local clinical data, and a slower approval process compared to the EU and the US. This delay in access can hinder the competitiveness of the Japanese market and limit patient access to innovative treatments.
To address this, Japan has made gradual improvements, such as accelerating the approval process for certain high-priority devices and expanding the use of international clinical data. However, overcoming the medical device lag remains a critical challenge.
The lack of global harmonization in medical device regulations has led to inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs for manufacturers. As medical technologies become more advanced, the need for a unified global regulatory framework has never been more critical. Efforts to harmonize regulations are aimed at reducing these barriers and ensuring faster and more consistent market access for innovative medical devices.
The Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF), established in 1992, was one of the first major international efforts to align medical device regulations. Although the GHTF was dissolved in 2012, its guidelines continue to influence global regulatory practices. The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), which succeeded the GHTF, was formed in 2011 to continue these harmonization efforts. The IMDRF focuses on promoting the sharing of best practices, aligning technical standards, and simplifying the approval process across borders.
The future of medical device regulation lies in adapting to the increasing complexity of medical technologies. Devices incorporating artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and wearables are poised to revolutionize healthcare. However, the regulatory systems in place must evolve to handle the unique challenges posed by these technologies, including ensuring their safety, efficacy, and integration into existing healthcare infrastructures.
As wearable medical devices and remote monitoring technologies become more commonplace, regulators will need to consider how these devices are continuously used and updated. The internet of medical things (IoMT) is expanding rapidly, offering new opportunities for disease prevention, monitoring, and management. Regulatory frameworks must incorporate real-time data collection and analysis, ensuring that devices remain compliant throughout their lifecycle.
The growth of personalized medicine is driving demand for more customized medical devices. Devices that can be tailored to individual patients' needs, based on genetic information or other health data, are becoming more common. Regulatory bodies will need to develop frameworks that allow for these personalized devices while ensuring they meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
The regulatory landscape for medical devices is complex, with each region imposing unique challenges and requirements. However, the growing trend toward global harmonization, driven by initiatives like the IMDRF, offers a promising path forward. As medical technologies continue to evolve, regulatory bodies must adapt to new innovations, ensuring that devices are both safe and accessible. By addressing the regulatory gaps and streamlining approval processes, we can ensure that the next generation of medical devices reaches patients faster, improving outcomes and advancing global healthcare.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00203
Rotavirus Antigen Group A and Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00206
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00207
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00211
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00212
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. IP-00189
Influenza A Rapid Assay Kit

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00200
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00201
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00202
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00208
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00209
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit(Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00210
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0001
hCG Pregnancy Test Strip
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0002
hCG Pregnancy Test Cassette
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0003
hCG Pregnancy Test Midstream

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0001
Cocaine (COC) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0002
Marijuana (THC) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0003
Morphine (MOP300) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0004
Methamphetamine (MET) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0005
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine ecstasy (MDMA) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0006
Amphetamine (AMP) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0007
Barbiturates (BAR) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0008
Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0009
Methadone (MTD) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0011
Opiate (OPI) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0002
Multi-Drug Test L-Cup, (5-16 Para)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0005
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) with Fentanyl
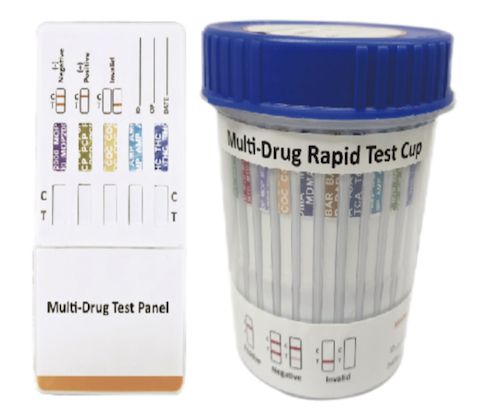
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0006
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) without Fentanyl
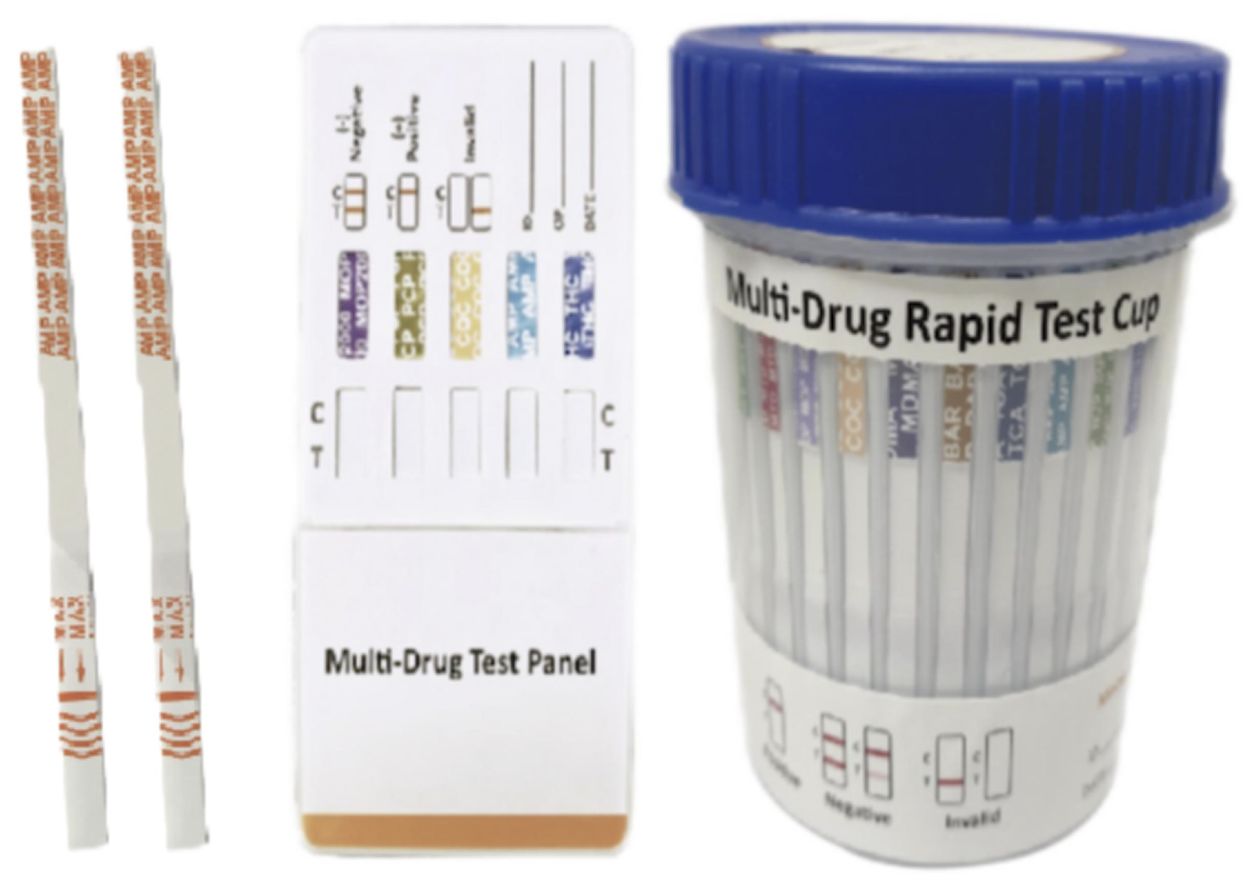
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0007
Multi-Drug 2~14 Drugs Rapid Test (Dipstick & Dipcard & Cup)
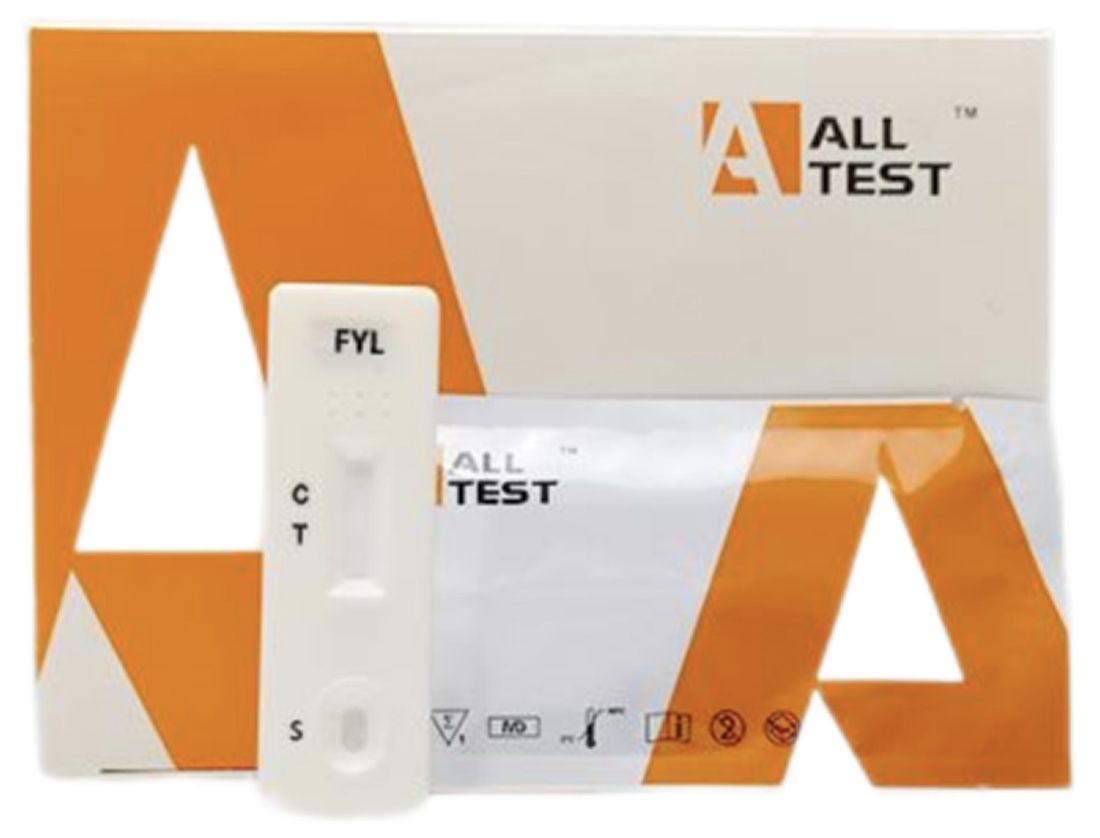
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0008
Fentanyl (FYL) Rapid Test (For Prescription Use)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0009
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (CLIA Waived)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0010
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (Home Use)
|
There is no product in your cart. |