- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- Navigating Mesothelioma Diagnosis: Key Biomarkers and Imaging Modalities
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive malignancy primarily associated with asbestos exposure, characterized by diagnostic challenges and poor prognosis. This resource provides a comprehensive guide to its modern diagnostic workup, detailing the integrated clinical pathway from initial imaging and histopathological examination to advanced biomarker analysis.
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive malignancy primarily arising from the mesothelial lining of the pleura, peritoneum, or other serous membranes, with strong etiological links to asbestos exposure. Characterized by a long latency period and non-specific early symptoms, it often presents at advanced stages, posing significant diagnostic challenges. Pathological confirmation remains the gold standard, requiring integration of histopathological features with immunohistochemical staining patterns to distinguish it from morphologically similar carcinomas. Current diagnostic paradigms increasingly incorporate advanced imaging modalities and molecular biomarkers to achieve accurate classification and guide therapeutic decisions.
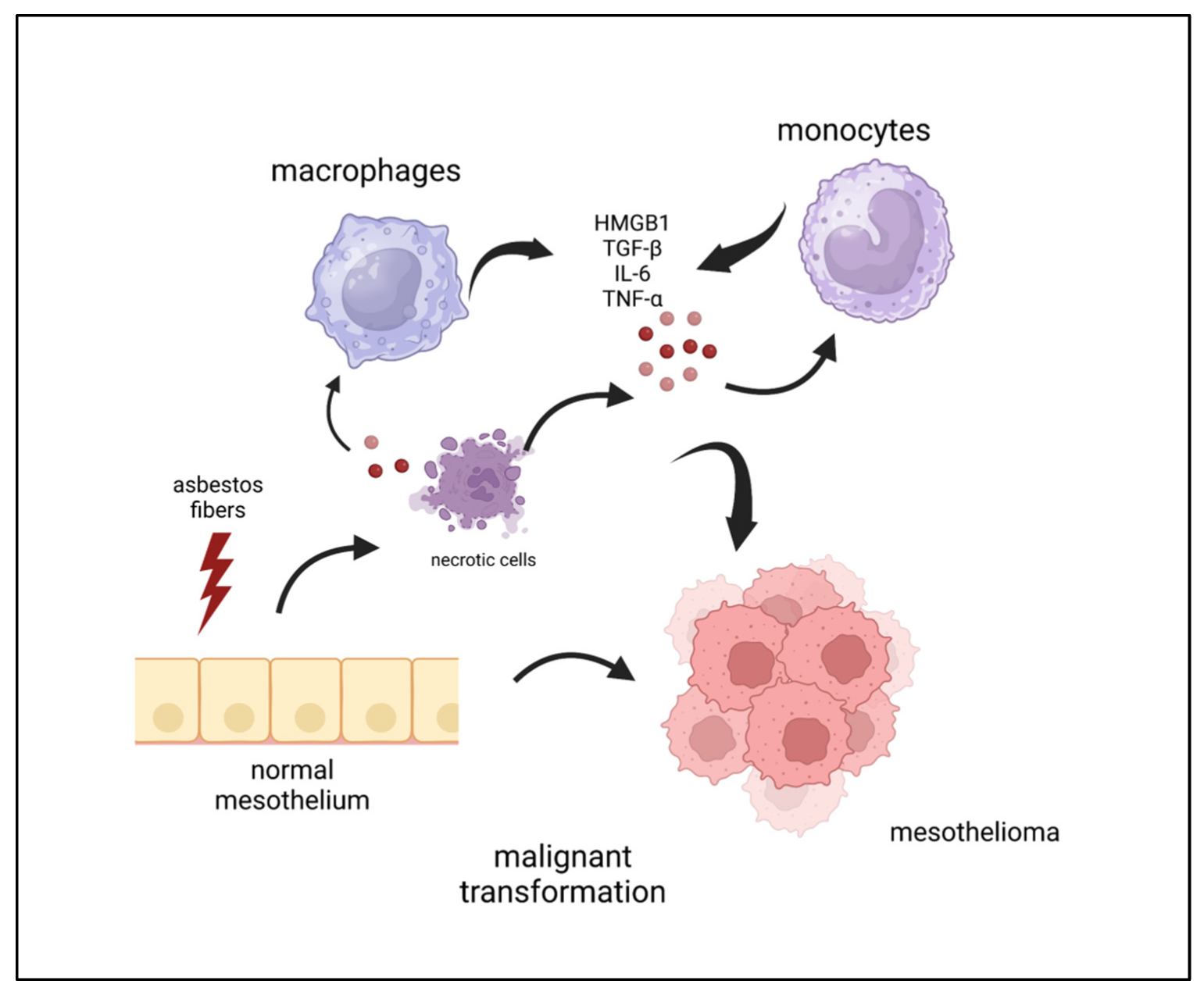 Fig.1 Cellular and soluble factors involved in asbestos-induced mesothelial cell transformation. (Fiorilla I, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Cellular and soluble factors involved in asbestos-induced mesothelial cell transformation. (Fiorilla I, et al., 2023)
Imaging plays a fundamental role in the diagnosis, staging, and monitoring of mesothelioma, providing essential information about tumor location, extent, and characteristics. These non-invasive techniques guide biopsy planning, assess resectability, and help evaluate treatment response, forming a critical component of the multidisciplinary management approach.
CT is the primary initial imaging modality for evaluating mesothelioma. It provides detailed cross-sectional images that effectively demonstrate pleural thickening, pleural effusions, and involvement of the fissures. While excellent for assessing calcifications and lung parenchyma, its limitation lies in distinguishing benign from malignant pleural disease and accurately evaluating chest wall invasion.
MRI offers superior soft tissue contrast compared to CT, making it particularly valuable for evaluating local tumor invasion into the diaphragm, chest wall, and other adjacent structures. Its multiplanar capability and advanced sequences provide crucial information for surgical planning, especially in cases where resectability is being determined.

PET-CT combines metabolic and anatomical information, serving as an essential tool for staging and restaging. The increased FDG uptake in malignant tissues helps distinguish benign from malignant processes, identifies occult metastatic disease, monitors treatment response, and provides prognostic information based on metabolic activity levels.
Histopathological evaluation forms the cornerstone of mesothelioma diagnosis, providing definitive morphological confirmation that distinguishes this malignancy from other thoracic and abdominal tumors. This microscopic analysis requires careful integration of architectural patterns, cytological features, and ancillary immunohistochemical studies to achieve an accurate classification. Key diagnostic features include:
Biomarkers play an indispensable role in the accurate diagnosis and management of mesothelioma, providing critical tools for differential diagnosis, prognostic stratification, and treatment monitoring. The integration of immunohistochemical, serum, and molecular biomarkers has significantly improved diagnostic accuracy and personalized patient management in this challenging malignancy.
Immunohistochemical Markers
Serum Biomarkers
Molecular Biomarkers
As a leading IVD provider, Alta DiagnoTech delivers specialized diagnostic solutions for mesothelioma through integrated testing platforms. Our product portfolio encompasses immunohistochemical, molecular, and serological assays that provide reliable diagnostic data for clinical decision-making. These standardized test systems support pathologists and oncologists in achieving accurate diagnosis, prognosis assessment, and treatment monitoring throughout the patient care pathway. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| Mesothelioma IHC Panel | Immunohistochemistry | Differential diagnosis from adenocarcinoma |
| BAP1 Loss Detection Assay | Immunohistochemistry | Diagnostic confirmation and subtyping |
| Serum Mesothelin (SMRP) Quantification Kit | ELISA | Disease monitoring and treatment response assessment |
| CDKN2A Deletion Detection Assay | FISH | Prognostic stratification |
| MSLN Expression Assay | RNA in situ hybridization | Patient selection for targeted therapies |
| PD-L1 Expression Assay | Immunohistochemistry | Immunotherapy eligibility assessment |
| Liquid Biopsy ctDNA Panel | NGS | Comprehensive molecular profiling and monitoring |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |