Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the leading cause of hypothyroidism globally, requires a multifaceted diagnostic approach integrating serological evidence of autoimmunity with functional assessment of thyroid impairment. This resource details the essential role of key biomarkers and thyroid function tests in confirming disease etiology and evaluating its clinical severity. Beyond established methods, we explore emerging technologies such as refined ultrasound elastography and multiplex assays that promise to enhance diagnostic precision and personalized management.
Introduction to Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying the thyroid gland. This leads to progressive inflammation, impaired thyroid function, and ultimately hypothyroidism. Diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical presentation, serological detection of specific autoantibodies, and assessment of thyroid function through hormone level measurements.
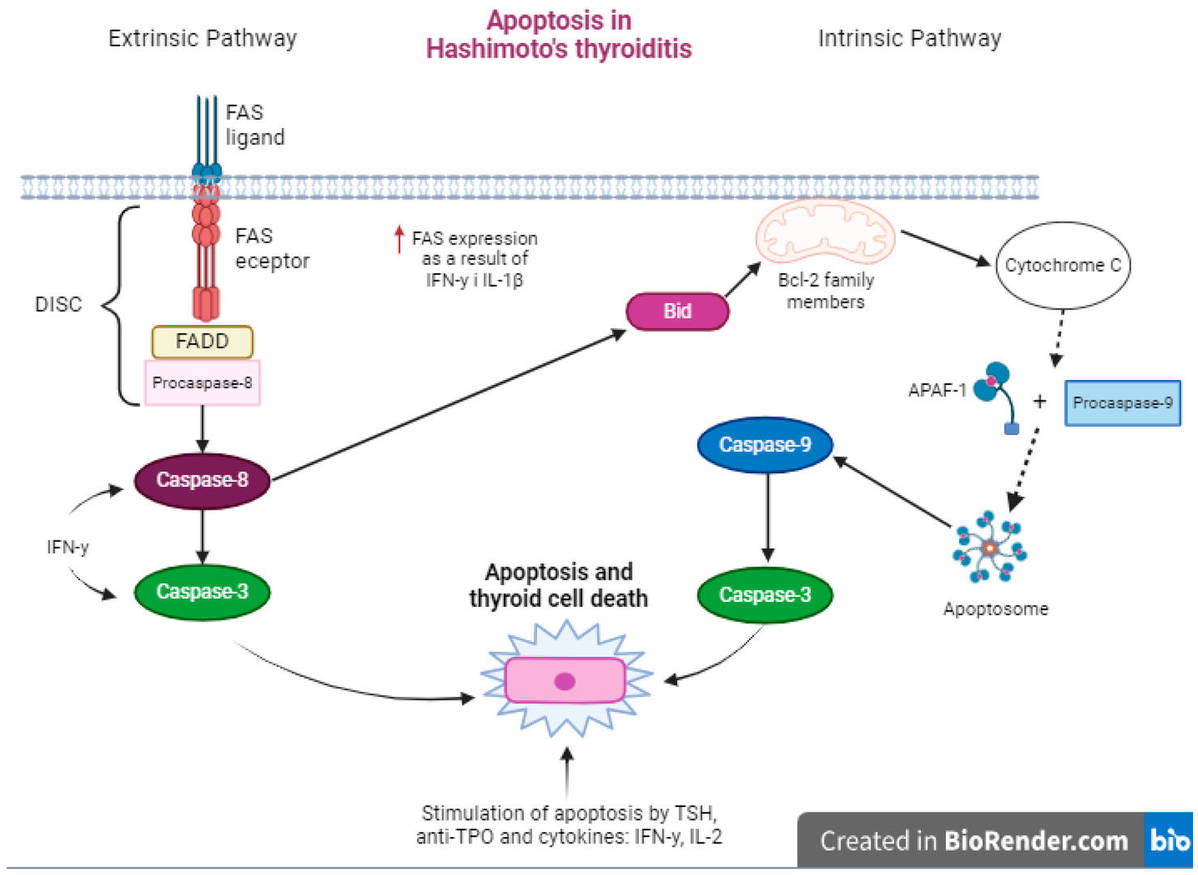 Fig.1 The course of apoptosis in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. (Wrońska K, et al., 2024)
Fig.1 The course of apoptosis in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. (Wrońska K, et al., 2024)
Serological Biomarkers of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Diagnostics
The serological diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis hinges on detecting specific autoantibodies that target thyroid antigens, providing direct evidence of autoimmune activity against the gland. These biomarkers are not only critical for confirming the autoimmune etiology of hypothyroidism but also help differentiate Hashimoto's from other thyroid disorders. Their detection, particularly in combination, offers high diagnostic specificity and sensitivity, forming the cornerstone of a modern and accurate diagnostic workflow for this common autoimmune condition.
Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb)
Anti-TPO antibodies are the most sensitive and clinically paramount serological marker for Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, present in over 90% of patients. They target thyroid peroxidase, a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Due to their exceptionally high disease specificity, TPOAb testing is universally recommended as the first-line serological test to confirm an autoimmune origin of thyroid dysfunction.
Anti-Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TgAb)
Anti-Tg antibodies are another classic marker of autoimmune thyroiditis, though they are generally considered less sensitive and specific than TPOAb. They are directed against thyroglobulin, the precursor protein used in thyroid hormone synthesis. TgAb are often tested alongside TPOAb to increase diagnostic confidence, as their simultaneous presence reinforces the autoimmune diagnosis.
Thyroid Function Tests (TFTs) for Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) are fundamental to assessing the physiological impact of Hashimoto's thyroiditis on hormone production, providing a critical complement to serological biomarkers. While autoantibodies confirm the autoimmune etiology, TFTs quantify the resulting functional impairment of the thyroid gland, ranging from subclinical to overt hypothyroidism. Monitoring TSH and FT4 levels is essential not only for initial diagnosis but also for evaluating disease progression and guiding hormone replacement therapy. The integration of TFTs with serological data forms the cornerstone of effective diagnostic and management strategies for Hashimoto's patients.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): TSH serves as the most sensitive and primary screening test for thyroid dysfunction in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Produced by the pituitary gland, TSH levels rise in response to declining thyroid hormone production, making it an early indicator of hypothyroidism. In Hashimoto's, an elevated TSH level is often the first biochemical sign of functional impairment, even before FT4 levels fall outside the reference range.
- Free Thyroxine (FT4): FT4 measures the biologically active, unbound fraction of thyroxine circulating in the bloodstream and is critical for confirming the severity of hypothyroidism. In Hashimoto's, as thyroid destruction advances, FT4 levels decline, reflecting the gland's diminishing capacity to produce hormones. FT4 can differentiate between subclinical and overt hypothyroidism, a distinction crucial for clinical decision-making.
Emerging Tools for Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Diagnostics
The diagnostic landscape for Hashimoto's thyroiditis is evolving beyond traditional antibody and thyroid function testing, driven by advances in technology and a deeper understanding of the disease's complexity. Emerging tools aim to address limitations in current methods, such as seronegative cases, variable antibody expression, and the need for earlier detection or prognostic stratification. These innovations focus on enhancing sensitivity, providing mechanistic insights, and enabling a more personalized approach to diagnosis and management.
Refined Imaging and Ultrasound Technologies
Emerging imaging tools are significantly enhancing the diagnostic and monitoring capabilities for Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Beyond standard ultrasound, technologies like shear-wave elastography quantitatively measure tissue stiffness, reflecting fibrosis and inflammatory activity, while contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) evaluates microvascular perfusion patterns to detect early functional changes.
Novel Biomarkers and Multiplex Assays
Emerging biomarker strategies extend beyond traditional antibodies to refine diagnosis and prognostic evaluation. These include antibody isotyping (e.g., IgG subclasses of TPOAb) to assess disease severity, cytokine profiles (e.g., IL-17, IFN-γ) to dynamically monitor immune activity, and autoantibody panels against broader antigens (e.g., Na+/I- symporter). Multiplex assays enable simultaneous detection of these biomarkers from a single sample, providing a comprehensive immune signature.
Conclusion
The diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis relies on a synergistic integration of serological biomarkers (TPOAb/TgAb) and thyroid function tests (TSH/FT4), which together confirm autoimmune etiology and assess functional impact. While current approaches remain fundamental, emerging tools, ranging from sophisticated ultrasound elastography and novel cytokine assays to artificial intelligence-driven data integration, promise to revolutionize diagnostic approaches by enabling earlier detection, precise prognostic stratification, and personalized treatment strategies. This evolution toward multimodal, precision medicine ensures more effective and individualized patient care.
As a leading provider of IVD solutions for Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Alta DiagnoTech offers a comprehensive diagnostic product portfolio, including TPOAb and TgAb immunoassay kits, TSH and FT4 assay kits, designed to improve diagnostic accuracy, support early detection and enable personalized patient management. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Wrońska K, Hałasa M, Szczuko M. The role of the immune system in the course of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: the current state of knowledge[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(13): 6883.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.



 Fig.1 The course of apoptosis in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. (Wrońska K, et al., 2024)
Fig.1 The course of apoptosis in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. (Wrońska K, et al., 2024)