Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection remains a significant clinical challenge, particularly in immunocompromised patients and neonates, where delayed diagnosis can lead to serious complications. This resource explores the evolution of CMV diagnostics, from traditional serological methods to today's molecular gold standard and the cutting-edge technologies of the future.
Introduction to Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection
Cytomegalovirus (CMV), a member of the herpesvirus family, is a globally prevalent pathogen that establishes lifelong latency after primary infection. While often asymptomatic in immunocompetent individuals, CMV poses serious risks to immunocompromised patients (transplant recipients, HIV/AIDS cases) and can cause congenital disabilities when acquired during pregnancy. The clinical spectrum ranges from mononucleosis-like symptoms to severe manifestations including retinitis, pneumonitis, and disseminated disease in vulnerable populations. With reactivation occurring in up to 60% of seropositive transplant patients, accurate diagnosis is critical for timely intervention.
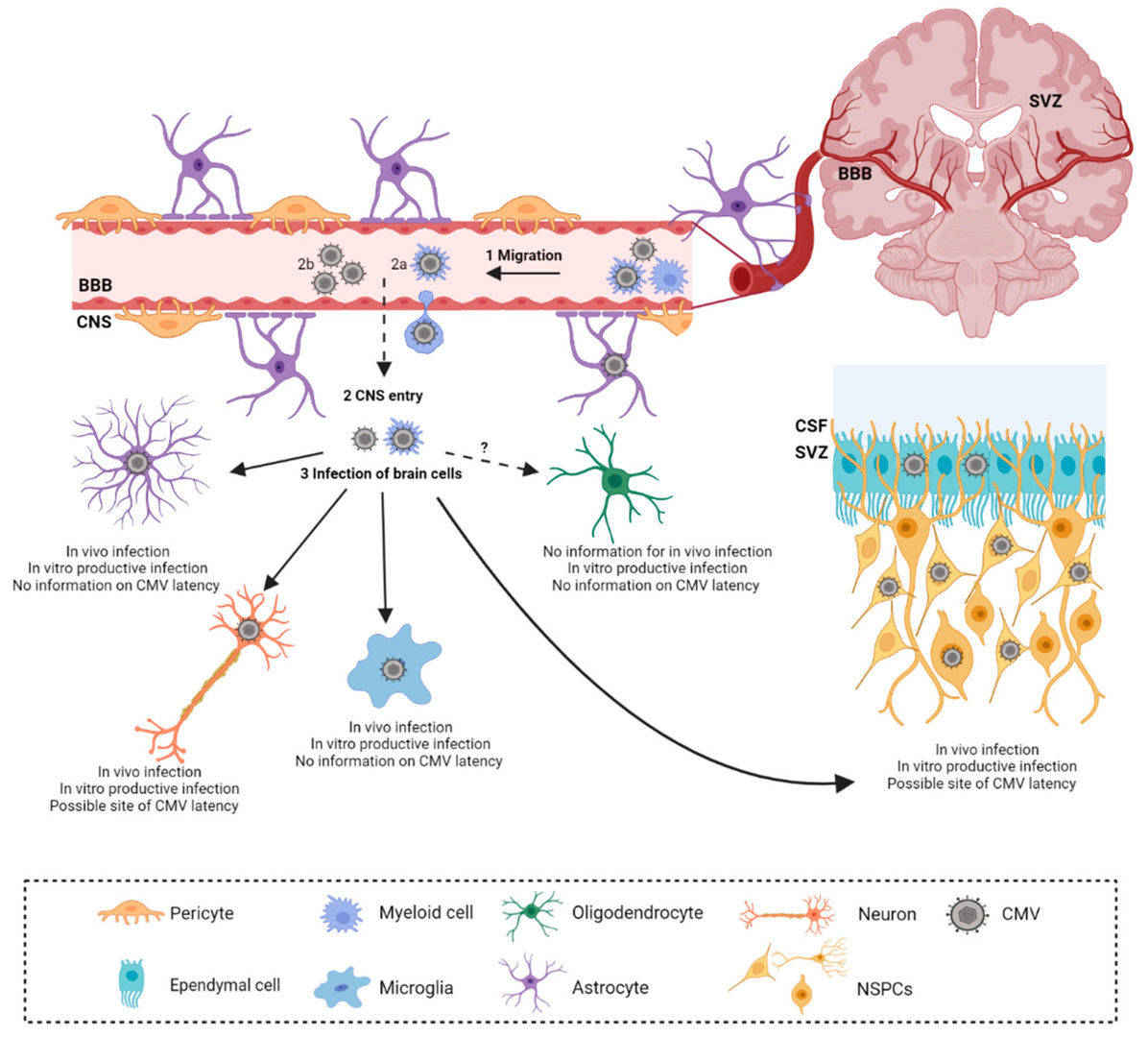 Fig.1 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in developing brain. (Krstanović, Fran, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in developing brain. (Krstanović, Fran, et al., 2021)
Diagnostic Methodologies of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection
Accurate diagnosis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is critical for guiding clinical management, particularly in immunocompromised patients, transplant recipients, and neonates. Due to CMV's ability to establish latency and reactivate, diagnostic strategies must differentiate between active infection, viral shedding, and past exposure. Modern methodologies span traditional techniques (culture, serology) to advanced molecular assays (qPCR, NGS), each with distinct advantages and limitations.
Conventional Methods
Traditional CMV diagnostics include viral culture (slow but specific) and pp65 antigenemia (faster but labor-intensive), primarily used before molecular assays became widespread. Serology (IgG/IgM) helps determine immune status but cannot reliably distinguish active from latent infection. These methods remain relevant for specific scenarios but lack the speed and sensitivity required for modern patient management.
Molecular Diagnostics
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) is now the gold standard, enabling precise viral load measurement (WHO-standardized) for guiding preemptive therapy in transplant patients. Automated real-time PCR platforms offer high throughput and reproducibility, while qualitative PCR aids screening. These tools are critical for detecting early reactivation and monitoring treatment response.
Emerging Technologies
Digital PCR (dPCR) achieves ultra-sensitive detection (<10 IU/mL), ideal for minimal residual disease monitoring. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) identifies resistance mutations (e.g., UL97/UL54) and outbreak strains, while point-of-care isothermal amplification (e.g., LAMP) promises decentralized testing. Future innovations include non-invasive biomarkers (saliva/urine DNA) and AI-driven viral load prediction.
Diagnostic Algorithm for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection
A well-defined diagnostic algorithm for cytomegalovirus (CMV) is critical to ensure timely detection, accurate risk stratification, and appropriate clinical intervention, particularly in high-risk populations like transplant recipients, HIV patients, and neonates. Structured testing pathways help distinguish active infection from latency, guide preemptive vs. prophylactic therapy, and optimize viral load monitoring to prevent CMV disease. By integrating patient-specific factors (immune status, symptoms) with test methodologies (qPCR, antigenemia, serology), these algorithms standardize decision-making, reduce unnecessary treatments, and improve outcomes—especially in settings where rapid turnaround is crucial.
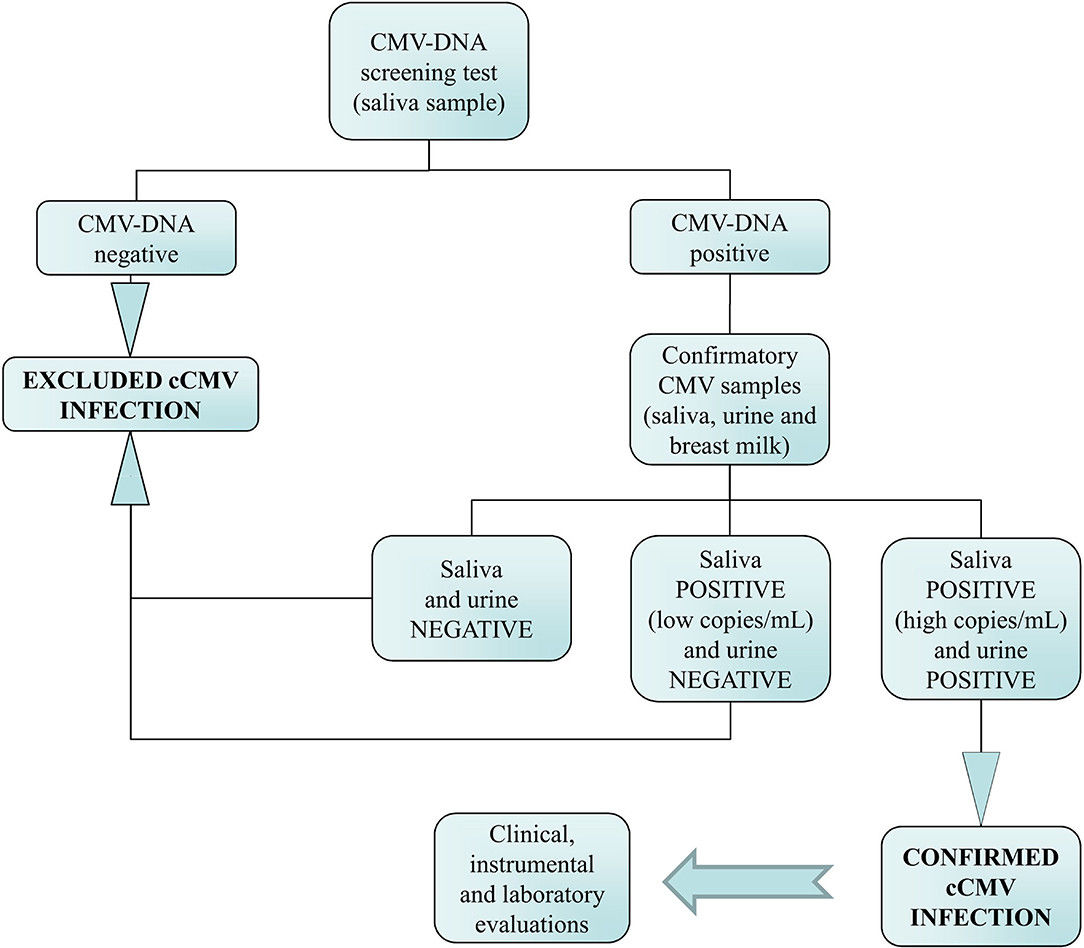 Fig.2 Flowchart of the neonatal congenital CMV (cCMV) screening and the algorithm used for the diagnosis of infection. (Chiereghin, Angela, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Flowchart of the neonatal congenital CMV (cCMV) screening and the algorithm used for the diagnosis of infection. (Chiereghin, Angela, et al., 2022)
Future Directions of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diagnostics
The future of cytomegalovirus (CMV) diagnostics is advancing toward faster, more precise, and accessible solutions, driven by innovations like ultra-sensitive digital PCR (detecting <5 IU/mL), portable next-generation sequencing for real-time resistance profiling, and non-invasive saliva/urine-based assays for congenital screening. Emerging AI-powered predictive models will analyze viral kinetics to forecast reactivation risks in transplant patients, while multiplex syndromic panels integrating CMV with other opportunistic pathogens will optimize immunocompromised care. These developments, combined with global standardization efforts, aim to deliver personalized, actionable insights, bridging gaps in early detection, resistance management, and point-of-care testing for high-burden settings.
Alta DiagnoTech delivers precision IVD solutions for cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, including routine testing products as well as qPCR assays, rapid POC tests, and comprehensive viral load monitoring systems, empowering early detection and optimized treatment decisions for immunocompromised patients worldwide. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
References
- Krstanović, Fran, et al. "Cytomegalovirus infection and inflammation in developing brain." Viruses 13.6 (2021): 1078.
- Chiereghin, Angela, et al. "Universal newborn screening for congenital cytomegalovirus infection–from infant to maternal infection: a prospective multicenter study." Frontiers in pediatrics 10 (2022): 909646.
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.



 Fig.1 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in developing brain. (Krstanović, Fran, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in developing brain. (Krstanović, Fran, et al., 2021)


 Fig.2 Flowchart of the neonatal congenital CMV (cCMV) screening and the algorithm used for the diagnosis of infection. (Chiereghin, Angela, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Flowchart of the neonatal congenital CMV (cCMV) screening and the algorithm used for the diagnosis of infection. (Chiereghin, Angela, et al., 2022)