Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Malaria Control and Elimination
Malaria, caused by Plasmodium parasites, remains one of the most significant global health challenges. Despite substantial progress in malaria control and elimination efforts, the disease continues to afflict millions, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Accurate and timely diagnosis is critical for effective case management and transmission control. Traditional diagnostic methods, such as microscopy and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), have been instrumental but face limitations, especially in detecting low-density infections. This gap necessitates the exploration of more sensitive and reliable diagnostic technologies, such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP).
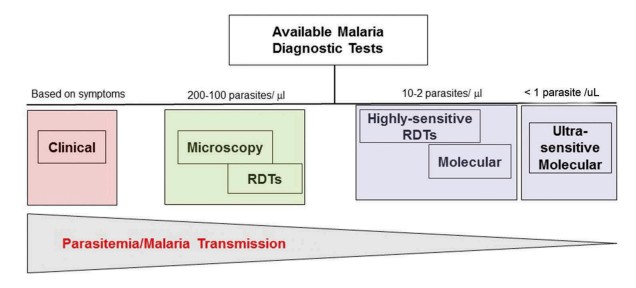 Fig.1 Diagnostic tools for malaria with changing transmission intensity. (Lucchi N. W., et al., 2018)
Fig.1 Diagnostic tools for malaria with changing transmission intensity. (Lucchi N. W., et al., 2018)
Overview of LAMP Technology
- The Science Behind LAMP
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is a nucleic acid amplification technique that operates at a constant temperature, typically around 60-65°C. Unlike polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which requires thermal cycling to denature DNA, anneal primers, and extend strands, LAMP utilizes a set of four to six primers that recognize six distinct regions on the target DNA. This design enables rapid and efficient amplification, producing large amounts of DNA in a short period. The isothermal nature of LAMP makes it highly suitable for point-of-care testing and field applications, where access to sophisticated laboratory equipment is limited.
- Evolution and Development of Malaria LAMP Assays
Since its inception over a decade ago, LAMP technology has undergone significant evolution, particularly in the context of malaria diagnosis. Researchers have developed numerous malaria-specific LAMP assays, targeting various Plasmodium species. These assays have been optimized for sensitivity, specificity, and ease of use. Notably, more than 26 malaria LAMP assays have been documented, with several achieving the World Health Organization (WHO)-recommended limit of detection of two parasites per microliter. The commercial availability of kits such as the Loopamp MALARIA kit (Eiken Chemical Co) and the Illumigene malaria LAMP (Meridian Bioscience) underscores the maturation and acceptance of LAMP technology in the diagnostic market.
Advantages of LAMP in Malaria Diagnosis

High Sensitivity and Specificity
One of the most compelling advantages of LAMP technology is its high sensitivity and specificity. Studies have demonstrated that LAMP assays can detect parasite densities as low as 0.02 parasites/µL, surpassing the detection limits of conventional RDTs and microscopy. This capability is particularly crucial for identifying asymptomatic carriers and low-density infections, which are often missed by traditional methods but contribute significantly to ongoing transmission. The specificity of LAMP assays is also noteworthy, with minimal cross-reactivity observed with non-malarial pathogens.

Simplified Sample Preparation
Traditional nucleic acid amplification techniques, such as PCR, require complex sample preparation steps, including DNA extraction and purification. In contrast, LAMP assays have been optimized to simplify these processes. Innovations such as vacuum-driven setups, boil-and-spin methods, and gravitation-based systems have reduced the need for specialized equipment and trained personnel. Furthermore, the use of unprocessed whole blood in some LAMP assays has been evaluated with promising results, further streamlining the diagnostic workflow.
Ready-to-Use Kits and Room Temperature Stability
The development of ready-to-use LAMP kits has been a game-changer in the field of malaria diagnostics. These kits come with premixed, lyophilized reagents that are stable at room temperature, eliminating the need for cold chains and reducing assay setup steps. The Loopamp Malaria Pan/Pf kit and the Illumigene Malaria LAMP assays are prime examples of such innovations. Their ease of use and portability make them ideal for resource-limited settings, where access to reliable electricity and refrigeration is often a challenge.

Non-Subjective Results Readout
Another significant advantage of LAMP technology is the availability of non-subjective results readout methods. Turbidity, colorimetric, and fluorescence-based assays have been developed to provide clear and unambiguous results. Colorimetric assays, in particular, offer visual inspection capabilities without the need for specialized equipment. Dyes such as malachite green and hydroxy-naphthol-blue have been successfully used to indicate positive LAMP reactions, enhancing the user-friendliness of these assays.
Applications of LAMP in Specific Contexts
- Detection of Imported Malaria Cases
Globalization and increased international travel have led to a rise in imported malaria cases in non-endemic countries. Accurate and rapid diagnosis of these cases is crucial for prompt treatment and prevention of local transmission. Molecular tests, including LAMP, offer high sensitivity and specificity, making them suitable alternatives to microscopy and RDTs in non-endemic settings. The Eiken Loopamp Pan/Pf LAMP assay and the Illumigene malaria LAMP tests have demonstrated excellent performance in diagnosing imported malaria cases in the UK and Canada, respectively.
- Detect and Treat Studies
Detect-and-treat approaches, such as active case detection (ACD), mass testing and treatment (MTaT), and reactive case detection (RCD), rely on highly sensitive diagnostic tests to identify and treat infected individuals. Traditional methods like RDTs and microscopy are inadequate for detecting low-density infections, which are critical reservoirs of transmission. LAMP assays, with their high sensitivity, offer viable alternatives for these studies. High-throughput LAMP platforms, capable of processing large numbers of samples simultaneously, further enhance their utility in large-scale epidemiological studies.
- Special Situations: HRP2 Deletions and Quality Microscopy Limitations
In regions where the use of HRP2-based RDTs is compromised due to HRP2 and HRP3 deletions, or where quality microscopy is lacking, LAMP assays provide reliable and easy-to-perform diagnostic options. Their simplicity and high sensitivity make them suitable for case management in facilities with limited resources. For instance, in areas with a high prevalence of HRP2 deletions, LAMP assays can serve as a valuable tool for confirming malaria infections and guiding appropriate treatment.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Addressing Key Challenges
Despite their promise, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of LAMP assays in malaria control programs. These include the need for further simplification of sample preparation, enhancement of reagent stability, and reduction of costs. While significant progress has been made in these areas, continued research and development are necessary to address these challenges comprehensively.
- Cost Considerations
The cost of LAMP assays remains a significant barrier to their routine use in malaria-endemic countries. While some LAMP tests, like the NINA-LAMP, offer competitive costs, the overall expense of LAMP-based diagnostics is higher than that of microscopy and RDTs. Balancing cost with sensitivity and ease of use will be crucial for their widespread adoption. Innovations in reagent production, assay optimization, and economies of scale could help reduce costs and make LAMP assays more accessible.
- Future Innovations
Continued research and development are needed to enhance the field applicability of LAMP assays. Innovations in sample preparation, reagent stability, and results readout will further streamline LAMP-based diagnostics. Additionally, the development of non-HRP2-based RDTs and highly sensitive RDTs will complement molecular diagnostics in malaria control and elimination efforts. The integration of LAMP technology with digital health platforms and telemedicine could also enhance its utility in remote and underserved areas.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
- Lucchi, Naomi W., et al. "Expanding the malaria molecular diagnostic options: opportunities and challenges for loop-mediated isothermal amplification tests for malaria control and elimination." Expert review of molecular diagnostics 18.2 (2018): 195-203.
We provide molecular diagnostic kits, which are efficient tools designed for molecular biology research and clinical diagnosis and can accurately detect changes in nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) sequences, structures, or expression levels in biological samples, which help medical research such as disease diagnosis, pathogen detection, and genetic disease screening. Specifically covering the following types:
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
 Fig.1 Diagnostic tools for malaria with changing transmission intensity. (Lucchi N. W., et al., 2018)
Fig.1 Diagnostic tools for malaria with changing transmission intensity. (Lucchi N. W., et al., 2018)



