Antibody Purification Using MNPs
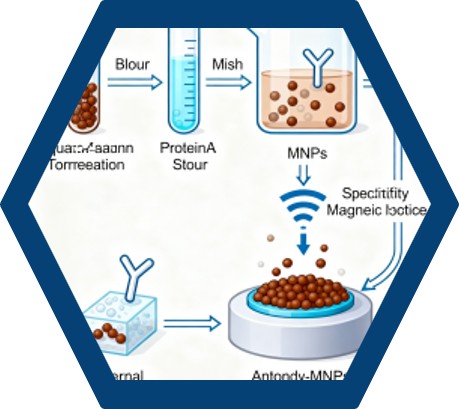
The purification of antibodies from serum samples involves a series of steps. Initially, the serum is subjected to ammonium sulfate precipitation to concentrate the immunoglobulins. The precipitated sample is then dialyzed and applied to an immunoaffinity spin column containing protein A, which selectively binds to the antibodies. The eluted fractions, enriched with purified antibodies, are combined and concentrated for further use.
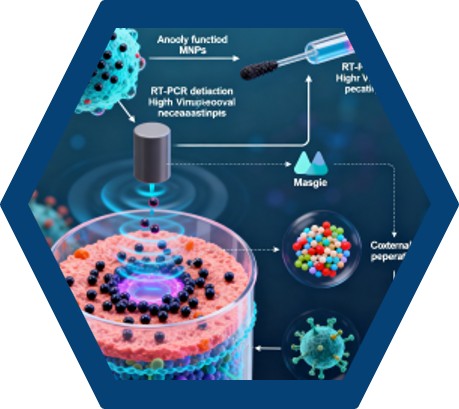
To enhance the purification process, MNPs functionalized with protein A can be employed. These MNPs provide a larger surface area for antibody binding, increasing the yield and purity of the isolated antibodies. The functionalized MNPs are mixed with the serum sample, allowing the antibodies to bind to the protein A on the MNP surface. An external magnetic field is then applied to separate the MNPs-antibody complex from the rest of the sample, followed by elution of the purified antibodies.



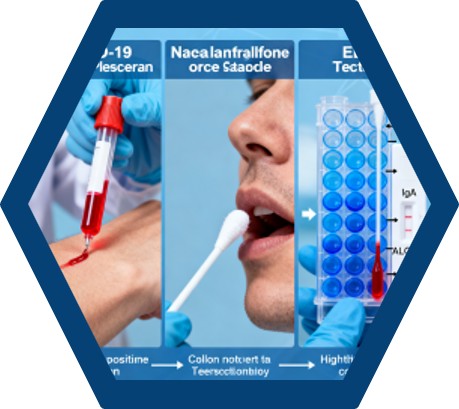
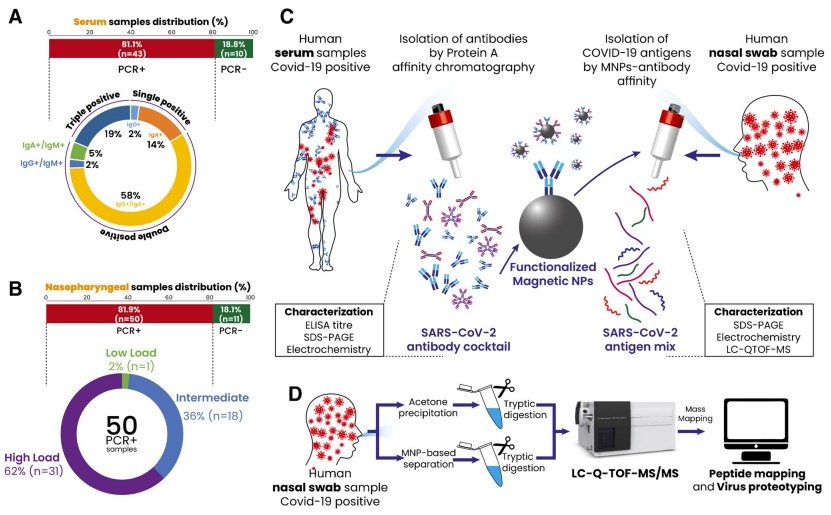 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the current study design. (Tok K., et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the current study design. (Tok K., et al., 2021)