- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- Diagnosing Ewing Sarcoma: Integrating Imaging, Histopathology, and Molecular Assays
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Ewing sarcoma is a highly aggressive bone and soft tissue tumor characterized by specific chromosomal translocations, most notably the EWSR1- FLI1 fusion gene. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the modern diagnostic approach for Ewing sarcoma, detailing the integrated workflow from clinical presentation through radiological evaluation to pathological confirmation. The following sections will systematically explore the essential roles of imaging techniques, histopathological examination, and crucially, molecular diagnostic assays in establishing an accurate diagnosis and guiding treatment decisions.
Ewing sarcoma is a highly aggressive malignant tumor of bone and soft tissue, representing the second most common primary bone cancer in children and adolescents. It is characterized by a unique and defining molecular hallmark: a specific chromosomal translocation, most commonly t(11;22), which fuses the EWSR1 gene with an ETS-family transcription factor, typically FLI1. Diagnosis relies on a multidisciplinary approach integrating characteristic imaging findings, histopathology revealing a "small round blue cell" morphology, and mandatory molecular confirmation of the pathognomonic gene fusion to differentiate it from other small round cell tumors.
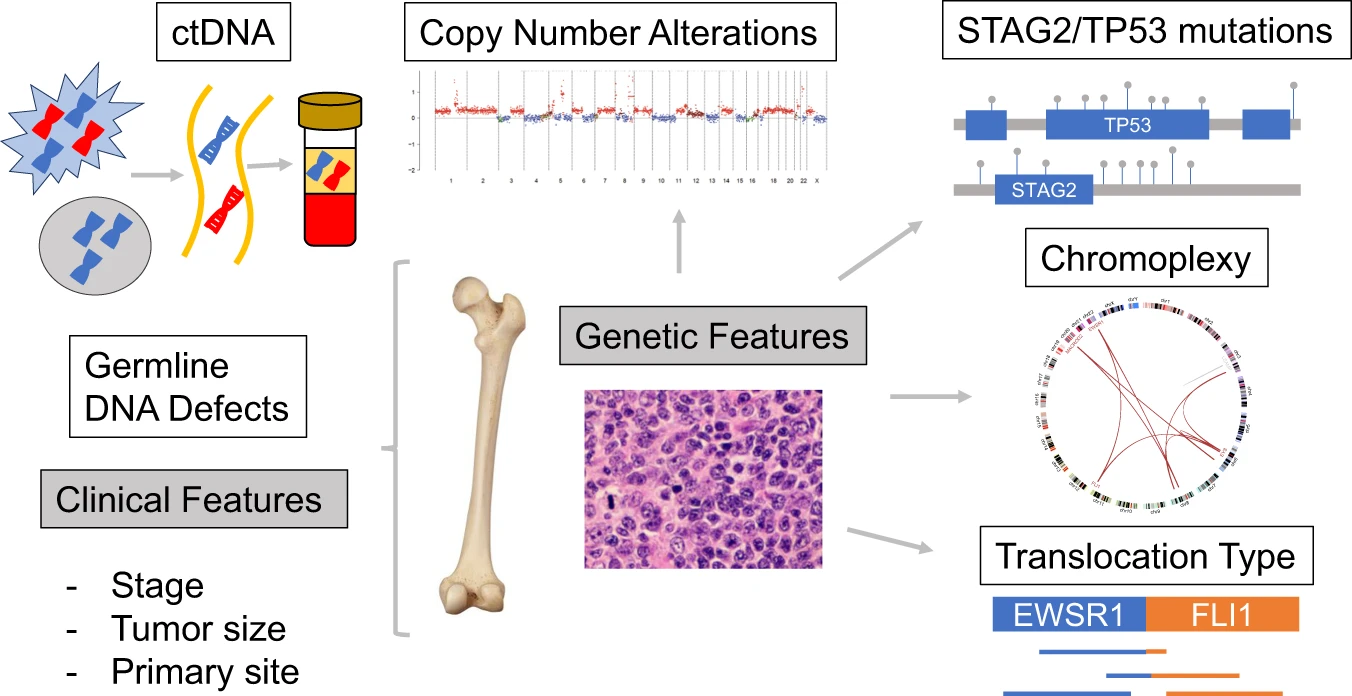 Fig.1 Potential prognostic biomarkers for Ewing sarcoma. (Shulman D S, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Potential prognostic biomarkers for Ewing sarcoma. (Shulman D S, et al., 2022)
Imaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of Ewing sarcoma, providing critical information about the location, extent, and characteristics of the primary tumor and potential metastases. It guides biopsy planning, assesses treatment response, and monitors for disease recurrence, forming an essential component of the multidisciplinary management approach.

Histopathological examination forms the cornerstone of Ewing sarcoma diagnosis, providing the morphological foundation that, when combined with molecular studies, leads to a definitive diagnosis. This microscopic analysis of tissue obtained via biopsy reveals the tumor's characteristic cellular appearance and architecture, serving to narrow the differential diagnosis among small round blue cell tumors. Key histopathological features include:
It is critical to emphasize that the histopathological findings are not pathognomonic on their own. The definitive diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma requires corroboration with molecular genetic testing (such as FISH for EWSR1 rearrangements) to confirm the presence of the characteristic genetic translocation.
The molecular diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma has revolutionized its accurate identification, while emerging biomarkers continue to refine prognostic stratification and therapeutic approaches. This field represents the cornerstone of modern precision medicine for this aggressive malignancy.
Established Molecular Diagnostics
Emerging Biomarkers and Applications
Alta DiagnoTech offers a comprehensive portfolio of molecular diagnostic solutions for Ewing sarcoma, enabling precise detection of characteristic genetic alterations and emerging biomarkers. Our robust reagent kits and integrated testing systems provide standardized, reproducible tools for definitive diagnosis, risk stratification, and therapeutic monitoring. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| EWSR1 Gene Rearrangement Detection Kit | Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) | Primary diagnosis through detection of characteristic gene rearrangements |
| EWS-ETS Fusion Transcript Detection Kit | Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR) | Identification of specific fusion variants for diagnostic confirmation |
| Sarcoma Comprehensive Molecular Profiling Panel | Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | Comprehensive genomic analysis including fusion detection and mutation screening |
| Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) Monitoring Panel | Digital PCR / NGS | Minimal residual disease monitoring and treatment response assessment |
| CD99 Immunohistochemistry Detection Kit | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Diagnostic support through characteristic membranous staining pattern |
| TP53 Mutation Detection Kit | Next-Generation Sequencing | Prognostic stratification and therapy resistance assessment |
| B7-H3 (CD276) Expression Assay | Immunohistochemistry / Flow Cytometry | Identification of potential immunotherapy targets |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |