- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach to Esophageal Cancer: From Endoscopy to Biomarker Testing
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Esophageal cancer is a complex malignancy where precise diagnostic profiling is fundamental to effective treatment selection. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the essential in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tools and methodologies for esophageal cancer, detailing the complete diagnostic pathway from endoscopic biopsy through histopathological analysis to critical biomarker testing for HER2, PD-L1, and MSI/dMMR that guide modern targeted and immunotherapy decisions.
Esophageal cancer is a highly aggressive malignancy originating in the esophageal lining, primarily classified into two distinct histological subtypes: esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), often linked to chronic gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett's esophagus, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), strongly associated with tobacco and alcohol use. Characterized by late diagnosis and poor survival rates, its clinical management and treatment strategy are fundamentally dictated by accurate histological subtyping and, increasingly, by the molecular profiling of the tumor to guide targeted and immunotherapeutic approaches.
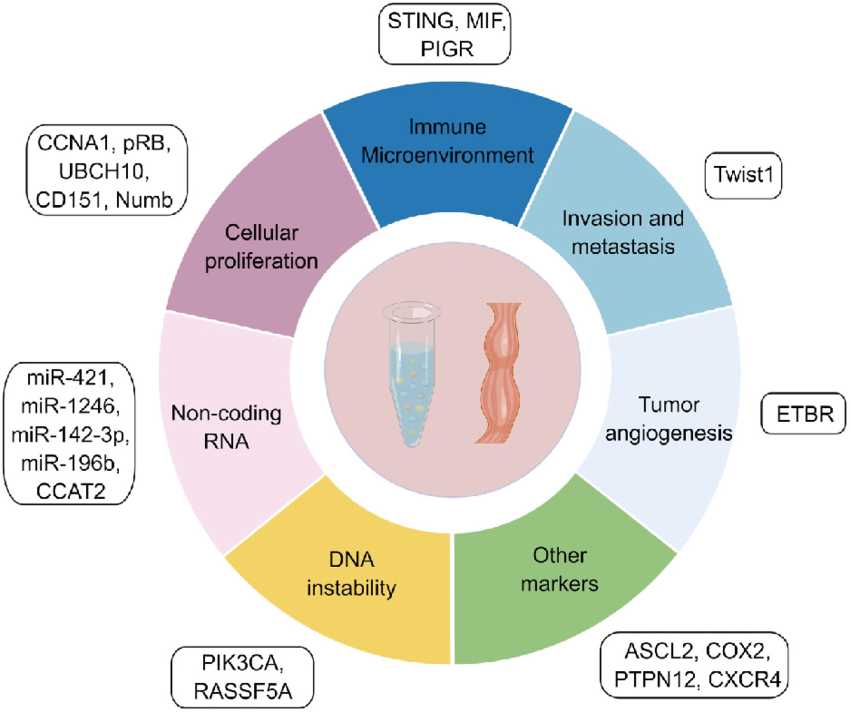 Fig.1 Different types of prognostic molecular markers in esophageal cancer. (Yuan X, et al., 2024)
Fig.1 Different types of prognostic molecular markers in esophageal cancer. (Yuan X, et al., 2024)
Endoscopic examination with biopsy forms the fundamental first step in the diagnosis of esophageal cancer. During esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), a flexible endoscope is used to directly visualize the esophageal mucosa, allowing for the identification of suspicious lesions, assessment of tumor extent, and evaluation of associated conditions such as Barrett's esophagus. The procedure enables precise tissue sampling through biopsy, which provides the essential material for histopathological diagnosis and classification of tumor type.
Advanced endoscopic techniques, including chromoendoscopy with Lugol's solution and narrow-band imaging (NBI), enhance the detection of early neoplasia by highlighting mucosal patterns and vascular changes. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) may be integrated during the procedure to evaluate the depth of tumor invasion and regional lymph node involvement, providing valuable staging information. The quality and quantity of biopsy specimens are crucial for accurate diagnosis and subsequent biomarker testing, making standardized biopsy protocols essential for optimal patient management.
Histopathological analysis is the cornerstone of esophageal cancer diagnosis, providing definitive evidence for the diagnosis and classification of the disease. This microscopic examination accurately distinguishes the two major histological subtypes: esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Beyond diagnosis, pathological evaluation provides crucial prognostic information by assessing tumor grade, depth of invasion, lymphovascular invasion, and resection margin status. A comprehensive histopathology report directly impacts the accuracy of staging and serves as the foundation for all subsequent treatment decisions.
Biomarker testing has fundamentally transformed the management of esophageal cancer, moving treatment strategies from a one-size-fits-all approach to personalized, precision-based care. By identifying specific molecular characteristics of individual tumors, biomarker analysis enables clinicians to select the most effective targeted therapies and immunotherapies, ultimately improving treatment outcomes and reducing unnecessary side effects.
HER2 testing is essential for identifying esophageal adenocarcinoma patients eligible for targeted therapy. Approximately 15-30% of cases show HER2 overexpression/amplification, detectable through immunohistochemistry (IHC) with reflex in situ hybridization (ISH) confirmation. This biomarker directly guides trastuzumab-based treatment decisions, significantly improving survival in HER2-positive metastatic disease.
PD-L1 assessment serves as a key predictor for immunotherapy response in both esophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Using the Combined Positive Score (CPS) system via immunohistochemistry, it helps identify patients most likely to benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors. This testing has become standard in advanced disease management across histological subtypes.

MMR/MSI testing identifies tumors with deficient DNA repair mechanisms through IHC analysis of four mismatch repair proteins or PCR-based molecular detection. While present in only 2-5% of esophageal cancers, dMMR/MSI-H status represents a crucial biomarker for predicting exceptional responses to immunotherapy, regardless of tumor histology or primary location.
Alta DiagnoTech provides a complete portfolio of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions for esophageal cancer, enabling precise diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies. Our advanced products cover the entire diagnostic workflow, from histopathological analysis to comprehensive biomarker testing, ensuring accurate detection of key biomarkers including HER2, PD-L1, and MSI/dMMR. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| HER2 IHC Complete Detection Kit | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Detection of HER2 protein overexpression in esophageal adenocarcinoma tissue |
| HER2 FISH Testing System | Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) | Confirmation of HER2 gene amplification in equivocal IHC cases |
| PD-L1 IHC Assay (22C3) | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | PD-L1 expression analysis using Combined Positive Score (CPS) for immunotherapy guidance |
| dMMR Panel IHC Kit | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Simultaneous detection of four mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2) |
| MSI Analysis System | PCR Fragment Analysis | Molecular detection of microsatellite instability in esophageal tumor tissue |
| Comprehensive Esophageal Cancer NGS Panel | Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | Simultaneous analysis of multiple biomarkers including HER2, MSI, PD-L1 and other relevant mutations |
| Automated Tissue Processing System | Automated Staining | Standardized processing of esophageal tissue specimens for consistent IHC results |
| Digital Pathology Image Analysis Platform | Digital Pathology | Quantitative assessment of HER2 IHC staining and automated PD-L1 CPS scoring |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |