- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Beyond the Murmur: Integrating Imaging and Biomarkers in Valvular Heart Disease Diagnosis
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Valvular heart disease involves structural or functional disorders of the heart valves that disrupt normal blood flow, potentially leading to severe cardiovascular complications. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the modern diagnostic approach for valve disorders, detailing how to effectively integrate imaging technologies with advanced biomarker strategies. This integrated methodology enables more accurate disease characterization, supports timely clinical decision-making, and ultimately contributes to improved patient management outcomes.
Valvular heart disease (VHD) encompasses a group of conditions characterized by damage or defects in one or more of the heart's four valves—aortic, mitral, tricuspid, or pulmonary—impairing their ability to open (stenosis) or close (regurgitation) properly. This dysfunction disrupts normal blood flow, leading to pressure overload or volume overload on the heart chambers, which can ultimately result in symptoms such as breathlessness, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure if left undiagnosed and unmanaged. Modern diagnosis extends beyond detecting a heart murmur to integrating advanced imaging for precise anatomical and functional evaluation with biomarker analysis to assess the resulting myocardial impact, forming a comprehensive approach essential for effective treatment planning.
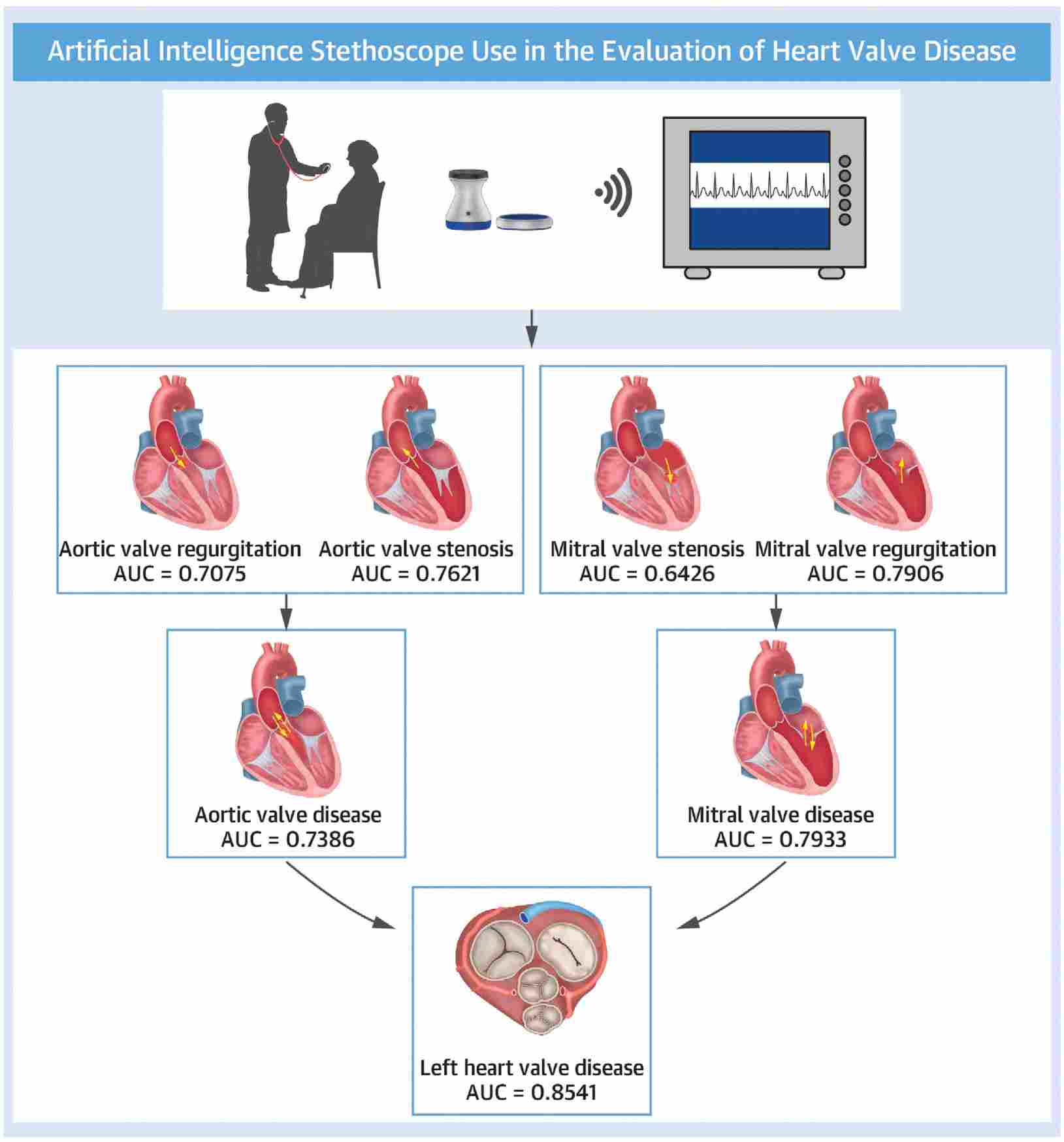 Fig.1 Automatic diagnosis of left valvular heart disease based on artificial intelligence stethoscope. (Zhou Z, et al., 2025)
Fig.1 Automatic diagnosis of left valvular heart disease based on artificial intelligence stethoscope. (Zhou Z, et al., 2025)
Imaging forms the foundational pillar for diagnosing valvular heart disease (VHD), providing critical insights into valve morphology, function, and hemodynamic consequences that guide clinical decision-making. This comprehensive assessment enables precise characterization of valve pathology severity and its impact on cardiac chambers, establishing the baseline for determining appropriate treatment strategies. The evaluation relies primarily on transthoracic echocardiography, supplemented by advanced imaging modalities for complex clinical scenarios.

Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) serves as the primary, first-line imaging modality for initial diagnosis and serial monitoring of VHD. Using ultrasound technology, TTE provides real-time assessment of valve structure and motion, accurately quantifies stenosis severity through Doppler measurements, evaluates regurgitation severity, and assesses secondary effects on cardiac chamber size and function. Its non-invasive nature, wide availability, and comprehensive diagnostic capability make it indispensable in routine clinical practice.

Advanced and Supportive Imaging
Advanced and supportive imaging modalities provide crucial supplemental information when echocardiography yields inconclusive results or requires anatomical correlation. Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) offers superior visualization of posterior cardiac structures, particularly the mitral valve, while cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) provides exact quantitation of ventricular volumes and regurgitant fractions. Cardiac CT plays an essential role in procedural planning for transcatheter interventions and in assessing coronary anatomy, creating a comprehensive multimodality imaging framework for complex cases.
While imaging defines the structural pathology of valve disease, biomarkers provide crucial insight into its functional consequences on the heart muscle. These circulating molecular signals objectively quantify the myocardial response to pressure or volume overload, offering invaluable data for assessing hemodynamic significance, guiding management decisions, and refining prognostic stratification. The clinical utility of biomarkers in valvular heart disease (VHD) is anchored in established assays and augmented by promising research tools, primarily encompassing natriuretic peptides, cardiac troponins, and novel markers of remodeling.

Natriuretic peptides (BNP/NT-proBNP) are hormones released by cardiac myocytes in response to chamber wall stress and volume overload. They serve as the cornerstone biomarkers for identifying and monitoring hemodynamic cardiac compromise in VHD. Elevated levels provide an objective measure of the severity of the ventricular burden, helping to corroborate symptomatic status and guide the optimal timing for valve intervention, especially in ambiguous clinical scenarios.
Cardiac troponins (cTnI/cTnT) are specific proteins released upon myocyte injury and necrosis. In chronic, severe VHD, the persistent mechanical strain can lead to low-grade, ongoing myocardial damage. Detection of elevated high-sensitivity troponin levels identifies this subclinical injury, which is associated with worse outcomes and can help inform risk stratification and the urgency of treatment.

Emerging biomarkers such as soluble ST2 (sST2) and Galectin-3 are focused on the process of myocardial fibrosis and maladaptive remodeling. These markers, currently utilized in a research context (RUO), show promise in providing a more nuanced understanding of the fibrotic response to long-standing valve disease, potentially offering additional prognostic information beyond the established natriuretic peptides and troponins.
The modern diagnosis of valvular heart disease (VHD) relies on a structured, stepwise algorithm that synergistically integrates clinical evaluation, imaging findings, and biomarker data to guide management from initial detection through to treatment planning. This systematic approach ensures no critical diagnostic element is overlooked, facilitating timely and patient-specific clinical decisions.
Alta DiagnoTech is committed to advancing valvular heart disease assessment through our comprehensive suite of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions. Our integrated product portfolio delivers essential biochemical insights that work synergistically with imaging modalities, enabling precise evaluation of myocardial impact across the entire diagnostic continuum, from initial detection to ongoing therapeutic monitoring. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| NT-proBNP Quantitative Assay Kit | Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay (ECLIA) | Assessment of ventricular wall stress in valvularheart disease |
| High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I Assay Kit | Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA) | Detection of myocardial injury in valvular heartdisease |
| BNP Rapid Quantitative Test Kit | Fluorescence Immunoassay (FIA) | Point-of-care assessment of heart failure in valvedisease |
| Cardiac Function Panel Assay | Multiplex Immunoassay | Comprehensive evaluation of myocardial stress andinjury |
| sST2 Quantitative Detection Kit | Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA) | Myocardial fibrosis risk assessment in chronic valvedisease |
| Galectin-3 CLIA Test Kit | Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA) | Evaluation of cardiac remodeling in progressivevalve disease |
| Heart Failure Biomarker Panel | Multiplex Immunoassay | Multi-parameter assessment of disease progressionand prognosis |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |