- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- Beyond Imaging: The Role of IVD in Kidney Cancer Diagnosis
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Kidney cancer, particularly renal cell carcinoma, presents significant diagnostic challenges that often lead to delayed detection and suboptimal treatment outcomes. This comprehensive resource examines how modern in vitro diagnostics (IVD) are transforming kidney cancer management by moving beyond traditional imaging approaches. We will explore the complete landscape of blood and urine biomarkers, from established proteins to cutting-edge liquid biopsy applications, and detail the innovative technologies that enable their detection.
Kidney cancer, with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) being the most prevalent type in adults, represents a significant urological malignancy characterized by its often asymptomatic nature in early stages. While frequently discovered incidentally during abdominal imaging for unrelated reasons, its clinical behavior can range from indolent to highly aggressive. Known risk factors include smoking, obesity, hypertension, and specific genetic syndromes such as von Hippel-Lindau disease. The diagnosis and management of kidney cancer have evolved beyond anatomical imaging alone, with growing emphasis on molecular characterization through tissue and liquid biopsies to enable more precise prognostication and treatment selection, particularly in advanced disease settings.
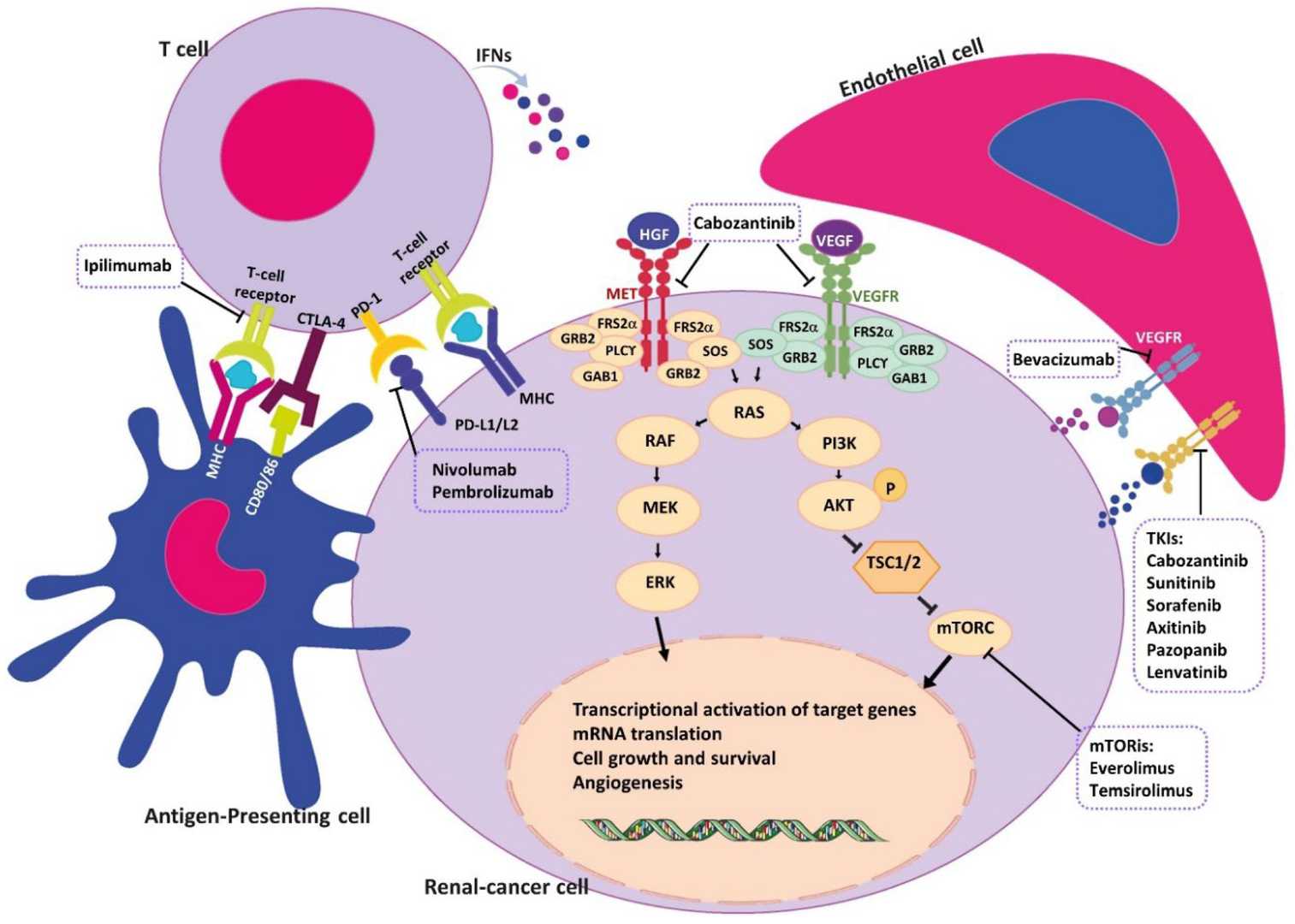 Fig.1 Schematic representation of major signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas (nccRCC) and therapeutic agents. (Khoshdel Rad N, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of major signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas (nccRCC) and therapeutic agents. (Khoshdel Rad N, et al., 2022)
While imaging remains fundamental for detecting renal masses, modern in vitro diagnostics (IVD) have become an indispensable complement by addressing critical limitations of anatomical assessment alone. Through the analysis of blood and urine biomarkers - including circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), specific proteins like CAIX, and urinary AQP1 - IVD provides unique insights into tumor biology that imaging cannot. These minimally invasive tools are revolutionizing kidney cancer care by enabling more accurate differentiation of benign and malignant masses, detecting molecular recurrence post-surgery earlier than radiographic changes, and monitoring real-time treatment response, ultimately guiding more personalized clinical decisions beyond what imaging alone can offer.
The evolving landscape of kidney cancer diagnostics is increasingly guided by specific biomarkers that provide crucial biological insights beyond anatomical imaging. These markers, detectable in blood and urine, are revolutionizing clinical management by enabling non-invasive detection, risk stratification, and treatment monitoring.

Blood-Based Protein Biomarkers
Urine-Based Biomarkers
Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers
The accurate detection and quantification of kidney cancer biomarkers rely on sophisticated in vitro diagnostic (IVD) platforms that transform biological samples into clinically actionable data. These technologies form the essential foundation for modern, non-invasive diagnostic strategies in renal cell carcinoma.

Immunoassays serve as the workhorse technology for detecting protein biomarkers in blood and urine samples, utilizing the specific binding between antibodies and antigens. Through platforms like enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and automated chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLIA), these tests enable precise quantification of key kidney cancer markers including CAIX, NGAL, and VEGF with high sensitivity and reproducibility, supporting both diagnostic and monitoring applications.

Molecular diagnostics target nucleic acid biomarkers through advanced amplification and sequencing technologies that provide unprecedented genetic insights. Techniques including quantitative PCR (qPCR) and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) allow ultra-sensitive detection of specific mutations in circulating tumor DNA, while next-generation sequencing (NGS) panels enable comprehensive genomic profiling that captures mutation patterns, copy number variations, and other molecular signatures from liquid biopsy samples.

Novel technology platforms are continuously expanding the capabilities of kidney cancer diagnostics through enhanced multiplexing and analytical performance. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics facilitates simultaneous quantification of multiple protein biomarkers in discovery and validation phases, while advanced biosensor platforms and single-cell analysis technologies are pushing the boundaries of sensitivity for detecting rare circulating tumor cells and characterizing tumor heterogeneity at unprecedented resolution.
At Alta DiagnoTech, we are committed to advancing kidney cancer care through our comprehensive portfolio of innovative in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions. Our products leverage cutting-edge technologies to enable precise detection of key biomarkers across blood, urine, and liquid biopsy samples, supporting clinicians in early detection, accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment monitoring for renal cell carcinoma. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| CAIX Immunoassay Kit | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) | Quantitative detection of Carbonic Anhydrase IX in serum for clear cell RCC identification |
| NGAL Detection Assay | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | Measurement of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in plasma for renal mass differentiation |
| AQP1/PLIN2 Urine Test | Multiplex Immunoassay | Simultaneous detection of Aquaporin-1 and Perilipin-2 in urine for non-invasive RCC screening |
| RCC Liquid Biopsy Panel | Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | Comprehensive genomic profiling of ctDNA for mutation detection and treatment guidance |
| CTC Enumeration Kit | Immunomagnetic Separation | Isolation and counting of circulating tumor cells for metastatic risk assessment |
| VEGF Signaling Panel | Electrochemiluminescence Assay | Multiplex quantification of VEGF pathway biomarkers for therapy monitoring |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |