- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Beyond Imaging: The Evolving Role of Laboratory Diagnostics in Cardiac Sarcoidosis
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Cardiac sarcoidosis is a challenging inflammatory condition characterized by granuloma formation in the heart, often presenting with non-specific symptoms that complicate timely diagnosis. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the modern diagnostic approach, detailing how advanced imaging techniques and evolving laboratory diagnostics work in concert to identify this elusive disease, assess disease activity, and guide clinical management.
Cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) is a rare but life-threatening inflammatory condition characterized by the formation of abnormal granulomas—tiny clumps of inflammatory cells—within the heart muscle. It is a manifestation of systemic sarcoidosis, an autoimmune disease of unknown origin, and can lead to serious complications including heart block, ventricular arrhythmias, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death. Diagnosis is particularly challenging as cardiac involvement can be silent or present with non-specific symptoms, often requiring a high index of suspicion and a multi-modality approach for confirmation.
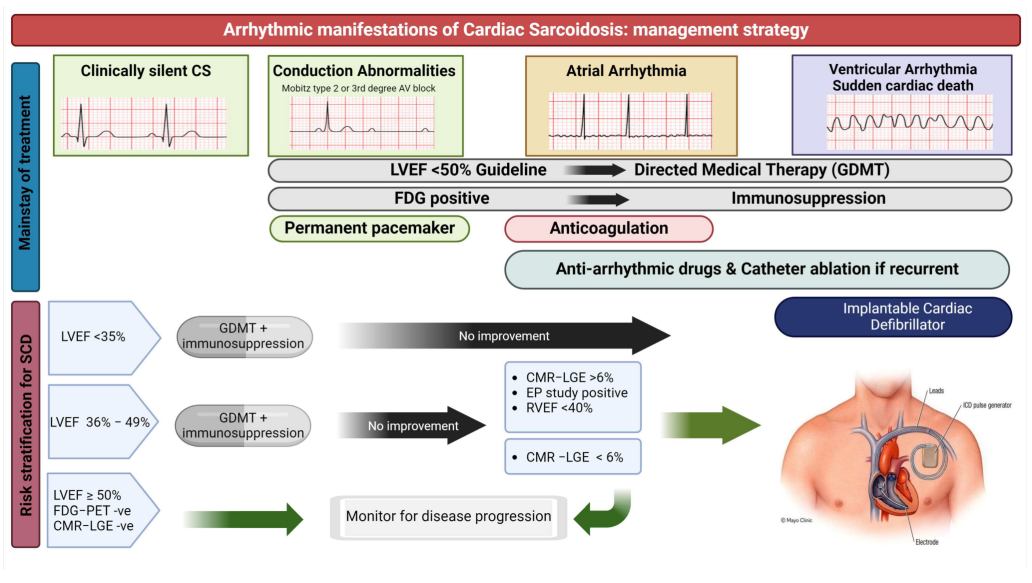 Fig.1 Arrhythmic manifestations and management strategies in cardiac sarcoidosis. (Arunachalam Karikalan S, et al., 2024)
Fig.1 Arrhythmic manifestations and management strategies in cardiac sarcoidosis. (Arunachalam Karikalan S, et al., 2024)
Imaging serves as the cornerstone for diagnosing and managing cardiac sarcoidosis (CS), providing non-invasive methods to detect characteristic inflammatory and fibrotic changes within the heart. Given the patchy nature of the disease and the limitations of endomyocardial biopsy, advanced imaging is essential for establishing a clinical diagnosis, guiding therapy, and monitoring disease activity.

Cardiac MRI (CMR)
Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging offers exceptional tissue characterization without ionizing radiation. Its key strength lies in using late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) to identify focal myocardial fibrosis and scarring, which is a hallmark of established CS. Additionally, T2-weighted imaging and mapping techniques can detect myocardial edema, indicating active inflammation. CMR is highly sensitive for detecting the structural consequences of the disease and provides critical prognostic information.
FDG-PET
Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is the primary modality for assessing active cardiac inflammation. It requires careful patient preparation to suppress normal myocardial glucose uptake. A positive scan shows focal FDG uptake, revealing metabolically active granulomas. FDG-PET is invaluable for diagnosing active CS, guiding biopsy, and most importantly, monitoring response to immunosuppressive therapy by showing a reduction in inflammatory activity.
Laboratory testing provides essential, though non-diagnostic, support in the evaluation of cardiac sarcoidosis (CS). In the current diagnostic paradigm, laboratory analysis serves three critical functions: providing supportive evidence for systemic sarcoidosis, identifying extra-cardiac involvement, and systematically ruling out other conditions that can mimic its clinical presentation. The established approach primarily relies on a combination of non-specific inflammatory markers and biochemical tests to fulfill these roles, forming a foundational component of the multi-disciplinary diagnostic process.

Laboratory biomarkers provide key supportive evidence for cardiac sarcoidosis by detecting systemic inflammation and cardiac involvement. While serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (sACE) remains a classical marker of sarcoidosis activity, its diagnostic utility is limited by variable sensitivity. soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) offers improved sensitivity for monitoring systemic disease activity. For cardiac-specific assessment, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) identifies subclinical myocardial injury, and natriuretic peptides (BNP/NT-proBNP) reflect associated hemodynamic stress and heart failure severity.
A critical function of the laboratory is to systematically exclude conditions that clinically mimic Cardiac Sarcoidosis. This involves targeted biochemical tests to rule out ischemic injury (cardiac troponins), assess thyroid dysfunction (TSH), evaluate for autoimmune rheumatic diseases (e.g., ANA, RF), and screen for hepatic or renal impairment that could contribute to the clinical presentation, thereby helping to narrow the differential diagnosis.
The search for more specific and sensitive biomarkers is crucial to address the significant diagnostic challenges in cardiac sarcoidosis. While current tests provide supportive evidence, emerging biomarkers aim to improve early detection, better differentiate active inflammation from chronic fibrosis, and accurately monitor treatment response. These novel candidates target the unique immunopathological processes of the disease, promising to transform the diagnostic landscape from reliance on indirect evidence to direct, cardiac-specific assessment.

Through innovative biomarker research and specialized assay development, Alta DiagnoTech provides a comprehensive portfolio of advanced testing solutions to address the challenges in the diagnostic evaluation of cardiac sarcoidosis. Our products are engineered to deliver precise and actionable results, enabling clinicians to effectively assess inflammatory activity, detect myocardial injury, and systematically rule out competing diagnoses. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| sIL-2R Quantification Assay Kit | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) | Quantitative measurement of Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor to support assessment of systemic sarcoidosis activity. |
| High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I Assay | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) | Precise detection of low-level myocardial injury to support evaluation of active cardiac involvement. |
| BNP/NT-proBNP Test Kit | Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay (ECLIA) | Measurement of natriuretic peptides for assessment of heart failure stress in suspected or confirmed cases. |
| Cardiac Sarcoidosis Antibody Panel | Multiplex Immunoassay | Simultaneous detection of autoantibodies associated with cardiac inflammation for research use. |
| Automated Inflammatory Marker Panel | Immunoturbidimetric/Chemiluminescent | Integrated testing of CRP, ESR and other inflammatory markers to support disease activity monitoring. |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |