- Home
- Resource
- Explore & Learn
- Approaches Rooted in DNA Nanotechnology for Diagnosing and Treating Gastric Cancer
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Gastric cancer (GC) remains a global health concern, ranking fifth among all malignancies. Its late detection and high mortality rates are attributed to non-specific early symptoms and the inefficiency of current screening methods. Traditional diagnostic tools such as endoscopy and histology are invasive and often miss early-stage tumors. DNA nanotechnology, with its unique properties of biocompatibility and programmability, offers a ray of hope in the fight against GC. This article delves into how DNA nanomaterials are transforming the landscape of GC management, from precise diagnosis to targeted treatment.
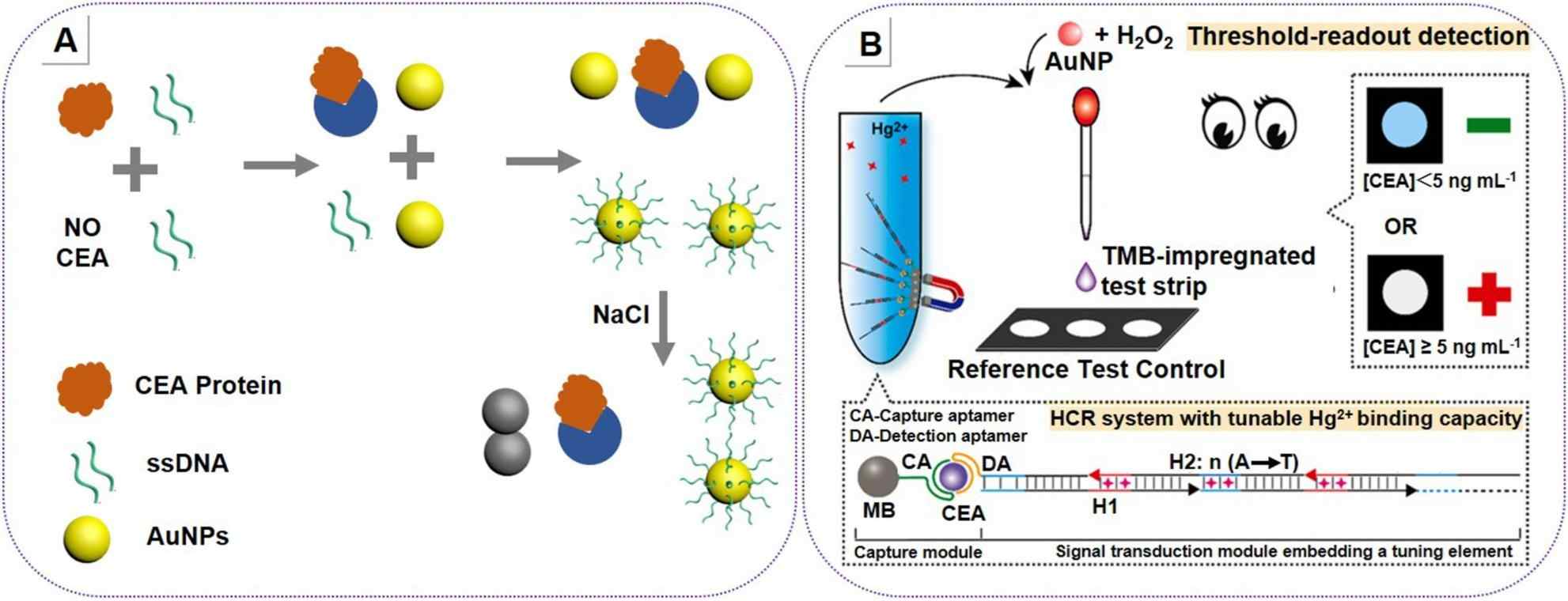 Fig.1 Colorimetric-based DNA biosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) detection. (Fonseca W. T., et al., 2025)
Fig.1 Colorimetric-based DNA biosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) detection. (Fonseca W. T., et al., 2025)
Biomarkers Detection

CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen)
CEA, a well-known tumor marker, is crucial for GC monitoring, despite its low specificity. DNA nanotechnology-based biosensors have significantly enhanced CEA detection. For example, aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticle (AuNP) systems can change color in the presence of CEA. When CEA binds to the aptamer on the AuNP surface, it causes the AuNPs to aggregate, leading to a color change from red to blue. This visual detection method can achieve a detection limit of 3 ng/mL. Electrochemical sensors, on the other hand, using 3D DNA nanotweezers, can detect CEA at an ultra-low concentration of 4.88 fg/mL. The 3D structure of the nanotweezers provides more binding sites for CEA, enhancing the sensor's sensitivity.

miRNA
Dysregulated miRNAs like miRNA-21 and miRNA-135b are potential biomarkers for GC. Isothermal amplification-based lateral flow biosensors (IA-LFB) combine rolling circle amplification (RCA) with a lateral flow strip for visual detection. In the presence of miRNA-135b or miRNA-21, the RCA reaction is triggered, and the amplified products can be detected on the lateral flow strip, allowing for the differentiation of GC patients from healthy individuals. Fluorescence-based biosensors, such as those using carbon dots (CDs) and T7 exonuclease amplification, can perform ratiometric detection of miRNA-21. The CDs emit fluorescence, and when miRNA-21 hybridizes with the probe, the T7 exonuclease cleaves the probe, changing the fluorescence signal, which can accurately detect miRNA-21 levels.
Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) and Exosomes
CTCs, although rare, play a crucial role in GC metastasis. DNA aptamers targeting epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), a protein overexpressed on CTCs, can be used for their capture. Dual-aptamer (EpCAM/PTK7)-modified magnetic nanoparticles improve the capture efficiency of CTCs. The number of captured CTCs has been correlated with the chemosensitivity of GC patients, providing valuable information for treatment planning. Exosomes, small vesicles released by cells, carry GC-specific markers. Electrochemical sensors using hemin/G-quadruplex systems can detect exosomes. The hemin/G-quadruplex complex acts as an electrochemical signal generator, and when exosomes bind to the sensor surface, the RCA-amplified signal is enhanced, enabling sensitive exosome detection.
Colorimetric Sensors
Colorimetric sensors based on DNA nanotechnology offer a simple and cost-effective way for GC biomarker detection. AuNPs and DNAzymes are commonly used components. For instance, a test strip assay uses Hg2+-assisted AuNP peroxidase-like activity. In the presence of a target biomarker (e.g., CEA), the DNA probe on the AuNP surface changes its conformation, allowing Hg2+ to bind and activate the peroxidase-like activity of AuNPs. This leads to the oxidation of a chromogenic substrate, turning the test strip blue. The threshold for biomarker detection can be adjusted by modifying the DNA probe sequence.
Fluorescence Sensors
Fluorescence sensors utilize the fluorescence properties of various nanomaterials combined with DNA-based recognition elements. DNA walkers and hybridization chain reaction (HCR) are often employed for signal amplification. A DNA nanomachine composed of exonuclease III and a DNA walker cascade can detect CEA at 1.2 pg/mL. The exonuclease III cleaves the DNA substrate, releasing the DNA walker, which then moves along the track, triggering a series of fluorescence-generating reactions. HCR, on the other hand, can create a branched DNA structure, greatly amplifying the fluorescence signal in the presence of the target biomarker.
Electrochemical Sensors
Electrochemical sensors provide highly sensitive and label-free detection of GC biomarkers. 3D DNA nanotweezers and catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) are key techniques. An enzyme-free biosensor using DNA tetrahedrons (TDNs) and CHA can detect CEA at 0.04567 pg/mL. The TDNs provide a stable 3D structure, and the CHA reaction generates an electrochemical signal in the presence of CEA. The signal is proportional to the concentration of CEA, allowing for accurate quantification.
SERS Sensors
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) sensors offer ultrasensitive detection of GC-related biomarkers. Combining CRISPR/Cas13a with branched HCR on silver nanorod chips can achieve extremely low detection limits for miRNAs. The CRISPR/Cas13a system specifically cleaves the target miRNA, and the branched HCR amplifies the Raman signal. The silver nanorod chips provide a high-enhancement factor for Raman scattering, enabling the detection of minute amounts of miRNAs.
Chemotherapy with Precision
Gene Therapy
Phototherapy
Despite the significant progress in DNA nanotechnology for GC diagnosis and treatment, several challenges remain. The stability of DNA nanomaterials in the bloodstream is a concern, as nucleases can degrade them. Chemical modifications, such as phosphorothioate linkages in DNA, can improve stability. Developing multiplex detection methods that can simultaneously detect multiple biomarkers (CEA, miRNA, ctDNA, etc.) is also crucial for more accurate diagnosis. In terms of clinical translation, the complexity of manufacturing non-nucleic acid components in some DNA-based systems and the differences between pre-clinical models and human patients need to be addressed. Pure nucleic acid-based nanomedicines may offer a more straightforward and cost-effective solution for future clinical applications.
DNA nanotechnology has shown great potential in revolutionizing the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer. From ultrasensitive biomarker detection to targeted therapies and integrated diagnosis-treatment platforms, DNA nanomaterials provide unprecedented opportunities. Although challenges exist, continued interdisciplinary research and technological advancements will likely lead to the widespread adoption of DNA-based nanomedicines in GC precision medicine, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00203
Rotavirus Antigen Group A and Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00206
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00207
Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00211
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. GP-DQL-00212
Rotavirus Antigen Group A Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Card Type

Cat.No. IP-00189
Influenza A Rapid Assay Kit

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00200
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00201
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00202
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold)

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00208
Follicle-stimulating Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. GH-DQL-00209
Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Rapid Test Kit(Colloidal Gold), Strip Style

Cat.No. GH-DQL-00210
Luteinizing Hormone Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold), Strip Style
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0001
hCG Pregnancy Test Strip
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0002
hCG Pregnancy Test Cassette
Cat.No. IH-HYW-0003
hCG Pregnancy Test Midstream

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0001
Cocaine (COC) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0002
Marijuana (THC) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0003
Morphine (MOP300) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0004
Methamphetamine (MET) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0005
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine ecstasy (MDMA) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0006
Amphetamine (AMP) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0007
Barbiturates (BAR) Rapid Test Kit

Cat.No. GD-QCY-0008
Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0009
Methadone (MTD) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. GD-QCY-0011
Opiate (OPI) Rapid Test Kit
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0002
Multi-Drug Test L-Cup, (5-16 Para)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0005
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) with Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0006
Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Dipcard & Cup) without Fentanyl
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0007
Multi-Drug 2~14 Drugs Rapid Test (Dipstick & Dipcard & Cup)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0008
Fentanyl (FYL) Rapid Test (For Prescription Use)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0009
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (CLIA Waived)
Cat.No. ID-HYW-0010
Fentanyl Urine Test Cassette (Home Use)
|
There is no product in your cart. |