- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- Advancing Pancreatic Cancer Detection: Modern IVD Strategies and Solutions
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most challenging malignancies due to its late diagnosis and aggressive nature. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of modern diagnostic strategies, focusing specifically on the critical role of in vitro diagnostics (IVD) in transforming patient outcomes. We will explore the evolving landscape of biomarkers and examine the technologies that enable their detection, demonstrating how integrated diagnostic approaches are advancing early detection and personalized management.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most formidable malignancies, characterized by an often insidious onset, aggressive biology, and a persistently high mortality rate. It typically presents at an advanced stage due to non-specific early symptoms and the lack of effective, widely-adopted screening tools for the general population. The disease most commonly arises as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), which is notorious for its dense tumor microenvironment and rapid progression. This challenging landscape underscores the critical and urgent need for advancements in diagnostic strategies, particularly in the realm of minimally invasive testing, to enable earlier detection and improve patient outcomes.
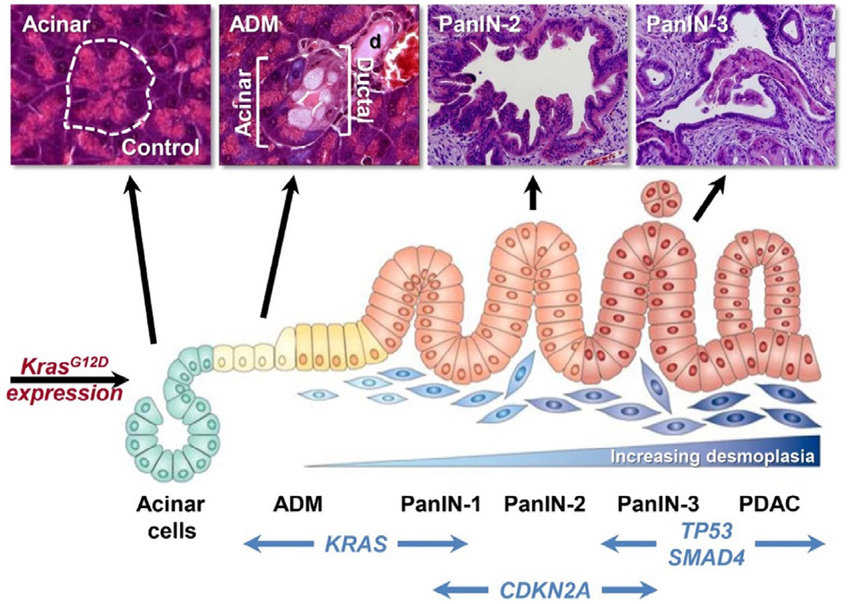 Fig.1 Pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. (Choi S R, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 Pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. (Choi S R, et al., 2020)
Modern in vitro diagnostics (IVD) are revolutionizing the approach to pancreatic cancer by providing critical, minimally invasive tools that address the critical challenge of late-stage detection. Moving beyond the limited utility of the traditional biomarker CA19-9 for early diagnosis, contemporary IVD strategies leverage advanced liquid biopsy techniques. These include detecting circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) for genetic mutations, analyzing microRNA signatures, and utilizing multi-marker protein panels. Integrated with high-sensitivity technologies like next-generation sequencing and automated immunoassays, these IVD solutions empower a new paradigm for risk stratification in high-risk individuals, aiding in the differential diagnosis of suspicious lesions, and enabling real-time monitoring of treatment response and disease recurrence.
The accurate diagnosis of pancreatic cancer relies heavily on the detection of specific biomarkers, which provide critical insights for early detection, differential diagnosis, and treatment monitoring. The biomarker landscape spans established serum proteins, novel molecular markers, and innovative liquid biopsy applications, collectively enabling a more precise and minimally invasive diagnostic approach.

Established Biomarkers
Emerging Biomarkers
Liquid Biopsy and Molecular Biomarkers
The accurate detection of pancreatic cancer biomarkers relies on a sophisticated suite of core in vitro diagnostic (IVD) technologies. These platforms are the essential engines that translate a simple blood sample into a precise, clinically actionable result, enabling the shift towards earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
This category represents the technological evolution of traditional protein detection, forming the backbone for quantifying established serum biomarkers like CA19-9 and CEA. Modern platforms, such as CLIA and ECLIA, provide superior sensitivity, wide dynamic range, and full automation. This allows for the reliable measurement of even low levels of biomarkers, which is critical for detecting early-stage disease and monitoring subtle changes in tumor burden.

Molecular techniques are paramount for analyzing the genetic and epigenetic signatures of pancreatic cancer through liquid biopsy. These technologies target nucleic acids, detecting mutations in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or specific microRNA (miRNA) expression patterns. Key platforms include digital PCR (dPCR) and qPCR for the ultra-sensitive detection of known, low-abundance mutations, and NGS, which offers a comprehensive, hypothesis-free profile of the tumor's genomic landscape from a single blood draw.

Beyond immunoassays and standard molecular methods, the field is being advanced by novel platforms that enhance sensitivity and multiplexing capabilities. This includes technologies like mass spectrometry-based proteomics for the discovery and simultaneous quantification of novel multi-protein biomarker panels, and advanced digital cell-free DNA isolation and enrichment techniques that improve the yield and quality of ctDNA, thereby increasing the success rate of downstream molecular analyses for early detection.
At Alta DiagnoTech, we are dedicated to advancing the early and accurate diagnosis of pancreatic cancer through our comprehensive portfolio of high-performance in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions. Our products leverage cutting-edge technologies to detect key biomarkers, empowering clinicians with critical insights for risk assessment, differential diagnosis, and treatment monitoring. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| CA19-9 Quantitative Assay | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) | Measurement of CA19-9 levels for treatment monitoring and recurrence detection |
| CEA Immunoassay | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA)/ELISA | Quantification of carcinoembryonic antigen as an adjunct biomarker in diagnosis |
| KRAS Mutation Detection Kit | Digital PCR/Next-Generation Sequencing | Identification of specific KRAS mutations in tissue or liquid biopsy samples |
| Pancreatic Cancer miRNA Panel | Quantitative PCR (qPCR) | Analysis of microRNA signatures for early detection and diagnostic support |
| Liquid Biopsy NGS Panel | Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | Comprehensive genomic profiling of circulating tumor DNA |
| THBS2 Immunoassay | ELISA/Chemiluminescent Assay | Detection of Thrombospondin-2 for early detection applications |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |