- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Cancers
- Advances in Adrenocortical Carcinoma Diagnosis: From Radiology to Molecular Assays
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is a rare and aggressive endocrine malignancy that poses significant diagnostic challenges due to its heterogeneous presentation and clinical behavior. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the modern diagnostic landscape for ACC, detailing the integrated clinical pathway from initial imaging to definitive histopathological assessment and molecular profiling.
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is a rare and aggressive malignancy originating from the adrenal cortex, characterized by heterogeneous clinical behavior ranging from indolent growth to rapid metastasis. It may present with hormonal hypersecretion syndromes (such as Cushing's syndrome or virilization) or as a non-functioning mass discovered incidentally. Diagnosis requires a multimodal approach integrating radiological imaging, detailed hormonal profiling, histopathological evaluation using established criteria like the Weiss system, and emerging molecular biomarkers to distinguish ACC from benign adenomas and guide therapeutic decisions.
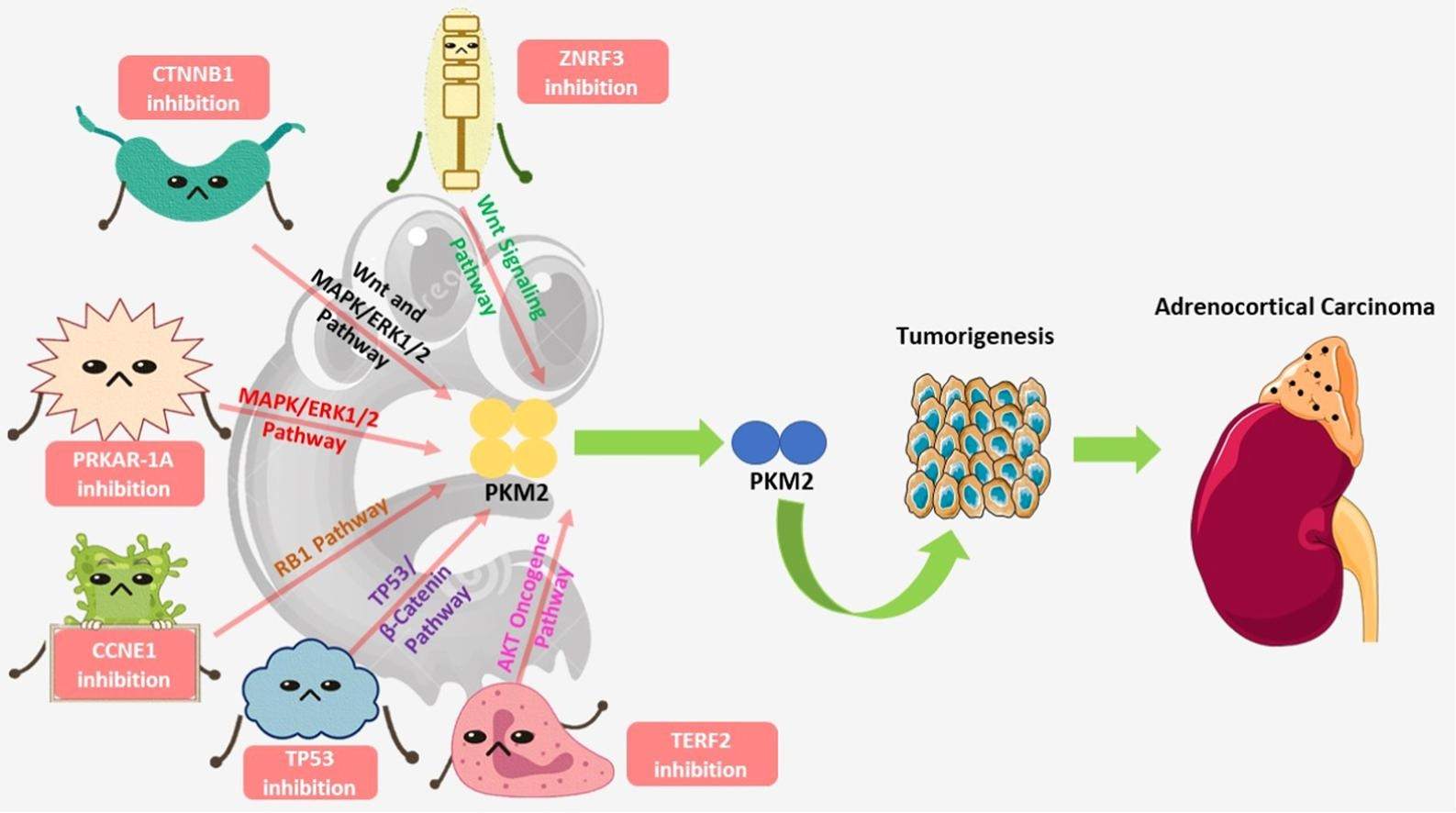 Fig.1 Driver genes in adrenocortical carcinoma and their correlation with tumor pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). (Das R, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Driver genes in adrenocortical carcinoma and their correlation with tumor pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). (Das R, et al., 2022)
Imaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis, staging, and management of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), providing essential information about tumor characteristics, local invasion, and distant metastasis. These advanced modalities are crucial for differentiating ACC from benign adrenal lesions and guiding treatment decisions.

CT and MRI
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) serve as the primary imaging tools for initial characterization of adrenal masses. CT excells in demonstrating tumor size, density, and calcifications, while MRI provides superior soft tissue contrast for evaluating local invasion and detecting intracellular lipid content. Both modalities utilize contrast enhancement patterns, particularly the absolute and relative washout characteristics, to help distinguish ACC from adenomas.

PET-CT
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) with 18F-FDG provides functional metabolic information that complements anatomical imaging. ACC typically demonstrates significantly increased FDG avidity due to its high glycolytic activity, making PET-CT particularly valuable for detecting distant metastases, evaluating treatment response, and monitoring disease recurrence. This modality enhances staging accuracy and helps identify occult metastatic disease not apparent on conventional imaging.
Histopathological examination is essential for confirming the diagnosis of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) and distinguishing it from benign adrenal tumors. This process involves meticulous microscopic evaluation using established criteria to assess malignant potential, complemented by immunohistochemical staining to support the diagnosis and provide prognostic information. Key diagnostic components include:

The most widely used diagnostic criteria, which evaluates nine histological features including high nuclear grade, mitotic rate, atypical mitoses, clear cells comprising ≤25% of the tumor, diffuse architecture, necrosis, venous invasion, sinusoidal invasion, and capsular invasion. The presence of three or more of these features indicates malignancy.

A critical biomarker for grading and prognosis, with higher proliferation indices (typically >10-20%) strongly associated with aggressive behavior and poor outcomes in ACC.

Utilizes a panel of markers including SF-1 (steroidogenic factor 1), Melan-A, Inhibin-alpha, and Synaptophysin to confirm adrenocortical origin and differentiate ACC from other malignancies such as renal cell carcinoma or pheochromocytoma.
Molecular diagnostics have revolutionized the understanding and management of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) by uncovering the genomic alterations driving tumorigenesis, enabling refined prognostic stratification, and identifying potential therapeutic targets beyond conventional histopathological assessment. Key biomarkers include:

Leveraging deep expertise in cancer diagnostics and diverse product development capabilities, Alta DiagnoTech delivers comprehensive solutions for adrenocortical carcinoma diagnosis and management, covering a complete product spectrum from basic pathology to cutting-edge molecular testing. Our product portfolio includes standardized IVD-compliant detection kits and advanced analytical tools for research use, providing reliable support for both clinical diagnosis and scientific exploration. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
| Product Name | Technology | Application |
| Weiss Criteria Assessment Kit | Histochemical Staining | Standardized histological evaluation for malignancy detection |
| Ki-67 Proliferation Index Detection Kit | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Tumor grading and prognostic assessment |
| Adrenal Lineage Confirmation IHC Panel | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Differential diagnosis using SF-1 and Melan-A markers |
| IGF-2 Expression Assay | RNA In Situ Hybridization | Detection of IGF-2 overexpression for diagnostic confirmation |
| TP53 Mutation Detection Kit | Next-Generation Sequencing | Identification of TP53 mutations for prognostic stratification |
| CTNNB1 Mutation Analysis Panel | Next-Generation Sequencing | Detection of β-catenin pathway alterations |
| Circulating Tumor DNA Monitoring Panel | Digital PCR | Minimally invasive disease monitoring and treatment response assessment |
Reference
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |