- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Infectious Diseases
- Breaking Down COVID-19 Diagnostics: PCR, Antigen, Antibody & Beyond
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Accurate and timely diagnosis is fundamental to controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of current diagnostic methodologies, including molecular (PCR), antigen, and antibody testing, alongside emerging innovations shaping the future of detection.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious illness caused by SARS-CoV-2, a novel beta-coronavirus first identified in Wuhan, China, in late 2019. The disease primarily spreads via respiratory droplets and aerosols, leading to a wide spectrum of symptoms—from mild fever and cough to severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multi-organ failure. Due to its high transmissibility and global impact, COVID-19 was declared a pandemic by the WHO in March 2020, accelerating the development of diagnostic tools, vaccines, and therapeutics.
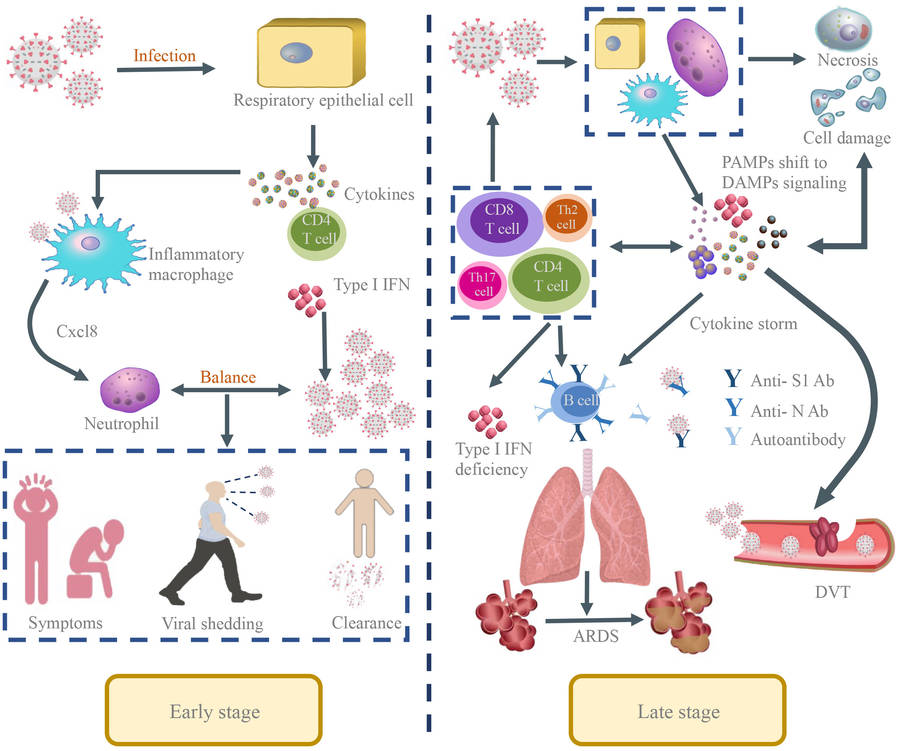 Fig.1 The pathological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the human body. (Zhu Y, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 The pathological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the human body. (Zhu Y, et al., 2023)
Timely and accurate COVID-19 diagnosis is critical for effective patient management, outbreak containment, and mitigating the pandemic's global impact. The diagnostic landscape for COVID-19 encompasses a range of molecular, antigen, and antibody-based tests, each serving distinct clinical and public health needs. RT-PCR remains the gold standard for acute infection due to its high sensitivity, while rapid antigen tests enable scalable, point-of-care screening despite lower sensitivity. Serological assays detect past infections or vaccine-induced immunity by measuring antibodies (IgM/IgG), though they lack utility in early diagnosis.
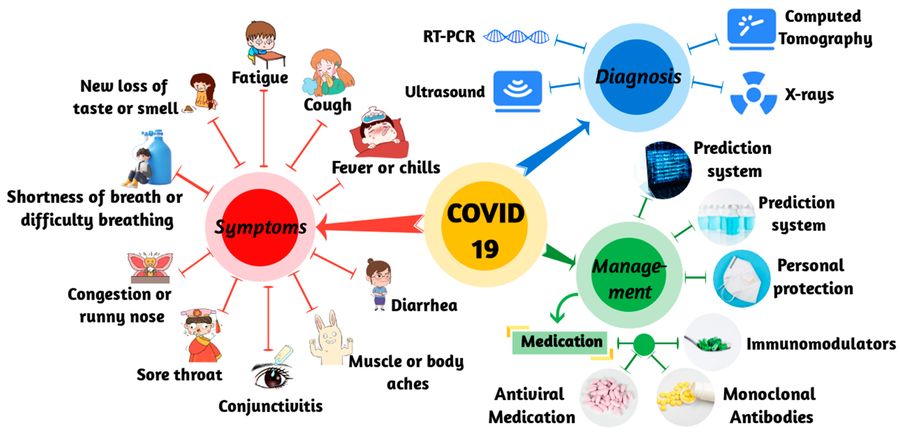 Fig.2 The symptoms, diagnosis, and management of COVID-19. (Jin S, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 The symptoms, diagnosis, and management of COVID-19. (Jin S, et al., 2023)
Diagnosis of COVID-19 relies on three primary testing approaches: molecular diagnostics for direct viral detection, antigen tests for rapid screening, and serology tests for immune response analysis. Each method serves distinct clinical purposes, balancing sensitivity, speed, and practicality to address different stages of infection and public health needs.

Molecular Diagnostics
Molecular tests, such as real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA with high sensitivity (>95%) and specificity. As the gold standard for acute infection, they are ideal for early diagnosis (even pre-symptomatic phases) and confirmatory testing. However, they require specialized lab equipment, trained personnel, and typically deliver results within 4–8 hours. Innovations like point-of-care PCR systems and multiplex assays have expanded their utility.

Antigen Tests
Antigen tests identify viral proteins (e.g., nucleocapsid) via lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs), providing results in 15–30 minutes without lab infrastructure. While less sensitive (~70–90%) than PCR, their speed and scalability make them valuable for mass screening, outbreak control, and home testing. They are most effective during peak viral load (first week of symptoms) but may yield false negatives in low-viral-load cases.
Serology Tests
Serology tests measure IgM/IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in blood/serum, indicating past infection or vaccine-induced immunity. Techniques include ELISA, chemiluminescence, and rapid LFIA devices. These tests are not for acute diagnosis (antibodies develop 1–3 weeks post-infection) but aid in seroprevalence studies, immunity monitoring, and convalescent plasma screening.
The rapid evolution of COVID-19 diagnostics has driven breakthroughs in speed, accuracy, and accessibility, addressing gaps in traditional testing methods. Key innovations include:

NGS enables comprehensive genomic analysis of SARS-CoV-2, providing critical insights into variant evolution, transmission patterns, and drug/vaccine escape mutations. While not routine for diagnosis due to high cost and complexity, it serves as a powerful tool for public health surveillance and research, particularly in tracking emerging variants and detecting co-infections.
These tests simultaneously detect SARS-CoV-2, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and other respiratory pathogens in a single sample, streamlining differential diagnosis during seasonal outbreaks. Available in PCR-based and rapid antigen formats, they optimize lab efficiency and clinical decision-making, especially in "tripledemic" scenarios. Their adoption reduces testing burden and accelerates targeted treatment.
While significant progress has been made in COVID-19 diagnostics, challenges such as variant-driven test evasion, resource disparities in low-income settings, and result interpretation complexities persist. Future efforts must focus on developing variant-proof assays, expanding affordable point-of-care solutions, and integrating diagnostics with digital health systems for real-time surveillance. Innovations in AI-driven analysis, multiplex testing, and novel biomarkers will be crucial to building resilient global testing networks capable of addressing both current and emerging pandemic threats.
Alta DiagnoTech provides comprehensive COVID-19 testing solutions, including high-accuracy RT-PCR kits, rapid antigen test kits, and reliable antibody detection kits, supporting precise diagnosis and effective pandemic control. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
References
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |