- Home
- Resource
- Disease Diagnosis
- Infectious Diseases
- Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis B Diagnostics: Methods, Challenges, and Future Trends
- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) remains a major global health challenge, with timely and accurate diagnosis critical to reducing transmission, enabling early treatment, and preventing complications like cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. This comprehensive guide explores current diagnostic methods, highlights key challenges and examines emerging innovations poised to transform HBV diagnostics. Whether you're a clinician, researcher, or lab professional, this resource provides actionable insights to navigate HBV detection with confidence.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major global health concern, affecting millions with acute and chronic infections. Transmitted through blood, bodily fluids, and perinatal exposure, HBV can lead to severe liver complications, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Despite effective vaccines, persistent infection remains a significant burden, particularly in endemic regions. Accurate and timely diagnosis is critical for disease management, preventing transmission, and guiding treatment decisions.
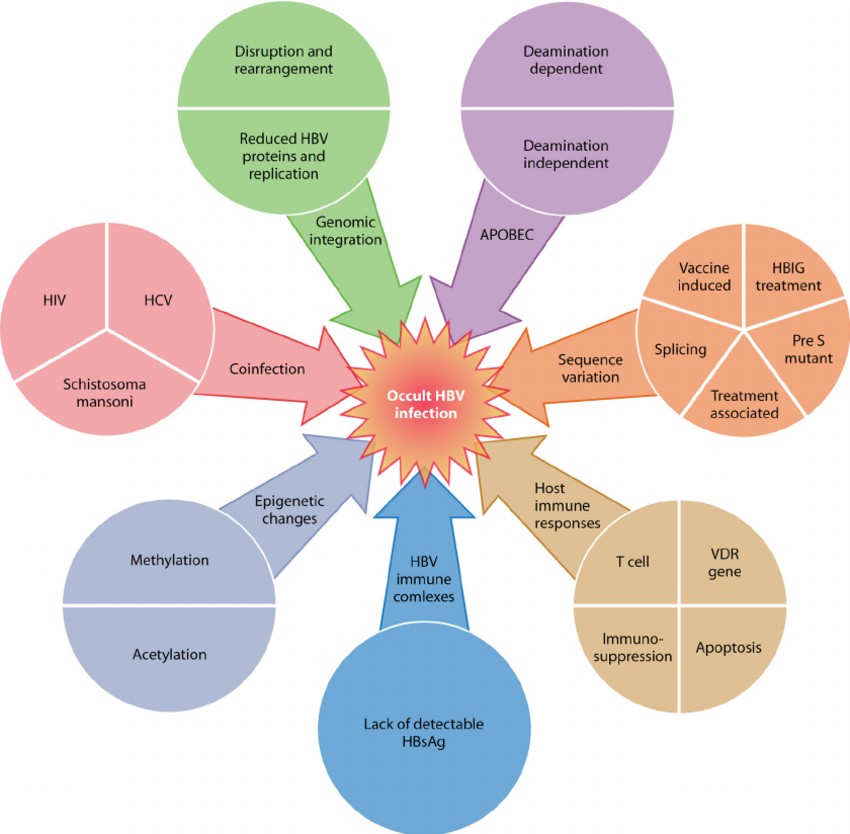 Fig.1 Overview of mechanisms leading to occult hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. (Samal J, et al., 2012)
Fig.1 Overview of mechanisms leading to occult hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. (Samal J, et al., 2012)
The diagnosis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection relies on a combination of serological markers and molecular testing to determine infection status, phase, and liver disease severity. Initial screening typically includes the triple panel (HBsAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc) to differentiate between active infection, immunity, and susceptibility. Further characterization involves HBeAg/anti-HBe to assess viral replication and quantitative HBV DNA PCR to measure viral load. Liver function tests and non-invasive fibrosis assessments or biopsy help evaluate disease progression. This multi-parameter approach ensures accurate staging, guides treatment decisions, and monitors therapeutic response.
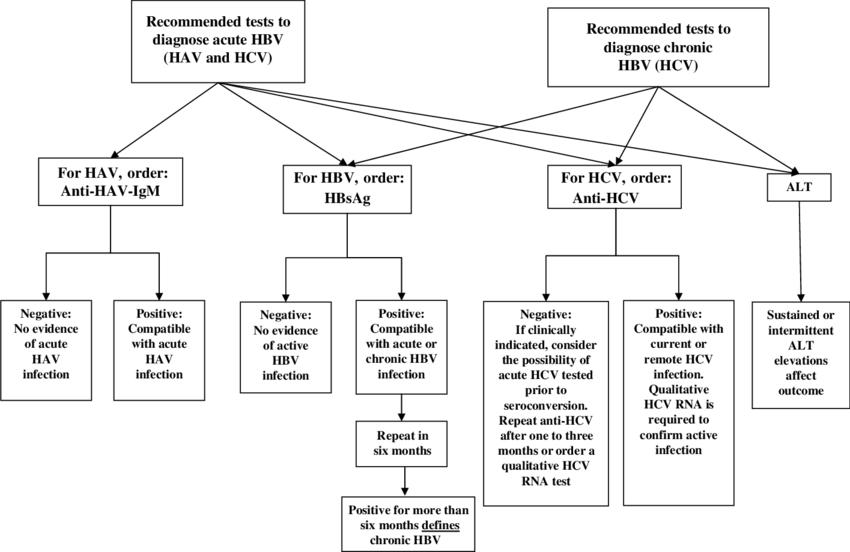 Fig.2 Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. (Krajden M, et al., 2005)
Fig.2 Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. (Krajden M, et al., 2005)
Serological testing is the cornerstone of hepatitis B virus (HBV) diagnosis, providing critical information about infection status, immunity, and disease progression. These tests detect HBV antigens and antibodies in blood samples, helping clinicians determine whether a patient has an acute, chronic, or resolved infection—or immunity from vaccination.
Key Serological Markers
Molecular testing plays a critical role in hepatitis B virus (HBV) diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment decision-making. Unlike serological tests that detect antibodies or antigens, molecular methods directly identify and quantify HBV DNA in blood, providing essential insights into viral replication, infectivity, and drug resistance.
HBV DNA quantification measures viral load using real-time PCR (qPCR), the gold standard for sensitivity (detection limit: 10–20 IU/mL). It assesses disease activity and monitors therapy response. Emerging technologies like digital PCR (dPCR) improve precision for low-level viremia (< IU/mL), critical for detecting occult infections or post-treatment relapse.
HBV genotypes (A–H) influence disease progression and treatment efficacy. Sanger sequencing or next-generation sequencing (NGS) identifies genotypes by analyzing mutations in the viral genome (e.g., pre-core/C regions). Genotyping guides tailored management (e.g., genotype C/D has higher cirrhosis risk) and vaccine escape variant detection.
Resistance testing targets mutations in the HBV polymerase gene (e.g., rtM204V/I for lamivudine resistance) via PCR-based sequencing (Sanger/NGS). It optimizes antiviral therapy (e.g., switching to tenofovir for entecavir resistance) and prevents treatment failure. Commercial assays like line probe assays (LiPA) screen common resistance mutations rapidly.
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) can lead to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, so accurate staging is crucial for prognosis and treatment decisions. Non-invasive methods such as transient elastography (FibroScan) and serum biomarkers such as FIB-4, APRI, ELF testing have become the preferred first-line tools, reducing the reliance on invasive liver biopsy (gold standard). Advanced imaging techniques, including MRI-based elastography (MRE) and shear wave elastography (SWE), have further improved the accuracy of fibrosis assessment. These methods help stratify patients, monitor disease progression, and guide the initiation of antiviral therapy, especially in resource-limited areas where biopsy is not available.

Despite advances, HBV diagnosis faces hurdles including limited access to molecular testing in resource-limited regions, variable assay sensitivity for occult HBV and mutant strains, and lack of standardized cut-offs for viral load/HBsAg quantification. Additionally, non-invasive fibrosis assessment tools (e.g., FibroScan) remain costly, while invasive biopsies pose risks. These gaps delay treatment initiation and complicate global elimination efforts.

Emerging solutions include innovative point-of-care tests (e.g., SHERLOCK) for portable DNA detection, AI-powered imaging to enhance fibrosis staging, and multi-omics biomarkers (e.g., HBV RNA, core-related antigen) to predict disease progression. Affordable paper-based rapid tests integrating serology and nucleic acid detection could revolutionize screening in low-resource settings, aligning with WHO's 2030 elimination goals.
Hepatitis B diagnosis has evolved significantly, yet challenges like accessibility, sensitivity limitations, and standardization gaps persist. The future holds promise with breakthroughs in AI-driven diagnostics and novel biomarkers. At Alta DiagnoTech, we are committed to providing infectious disease in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions and offering comprehensive, high-quality IVD products for hepatitis B, ranging from high-precision serology test kits to cutting-edge molecular testing products, enabling healthcare providers to achieve accurate, timely, and equitable diagnoses. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
References
| Cat.No | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| BDDK-HMM-0001 | Hepatitis B Virus Nucleic Acid Test Kit (Fluorescent PCR Method) | Add To Cart |
| BDDK-HMM-0002 | Hepatitis B Virus Nucleic Acid Test Kit (PCR-Fluorescent Probe Method) | Add To Cart |
| VT-QCY-0035 | Human Hepatitis B Virus e Antigen (HBeAg) ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| VI-QCY-0006 | Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Test Kit | Add To Cart |
| EK-YJL-3649 | Human Anti-hepatitis B Virus Core Antibody, HBcAb ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EK-YJL-3648 | Human Anti-hepatitis B Virus E Antibody, HBeAb ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| EK-YJL-0932 | Human Hepatitis B Virus E Antigen (HBeAg) ELISA Kit | Add To Cart |
| VI-QCY-0006 | Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Test Kit | Add To Cart |
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.
|
There is no product in your cart. |