Gonorrhea remains a pressing global health challenge, with rising antibiotic resistance and asymptomatic cases driving the need for advanced diagnostic solutions. This resource explores the full spectrum of gonorrhea testing, from conventional methods to next-generation technologies, while highlighting key biomarkers and future directions.
Introduction to Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is a globally prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) with an estimated 87 million new cases annually (WHO). Often asymptomatic, particularly in women, it can lead to severe complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, and increased HIV susceptibility. The rise of antibiotic-resistant strains underscores the critical need for accurate, rapid diagnostics.
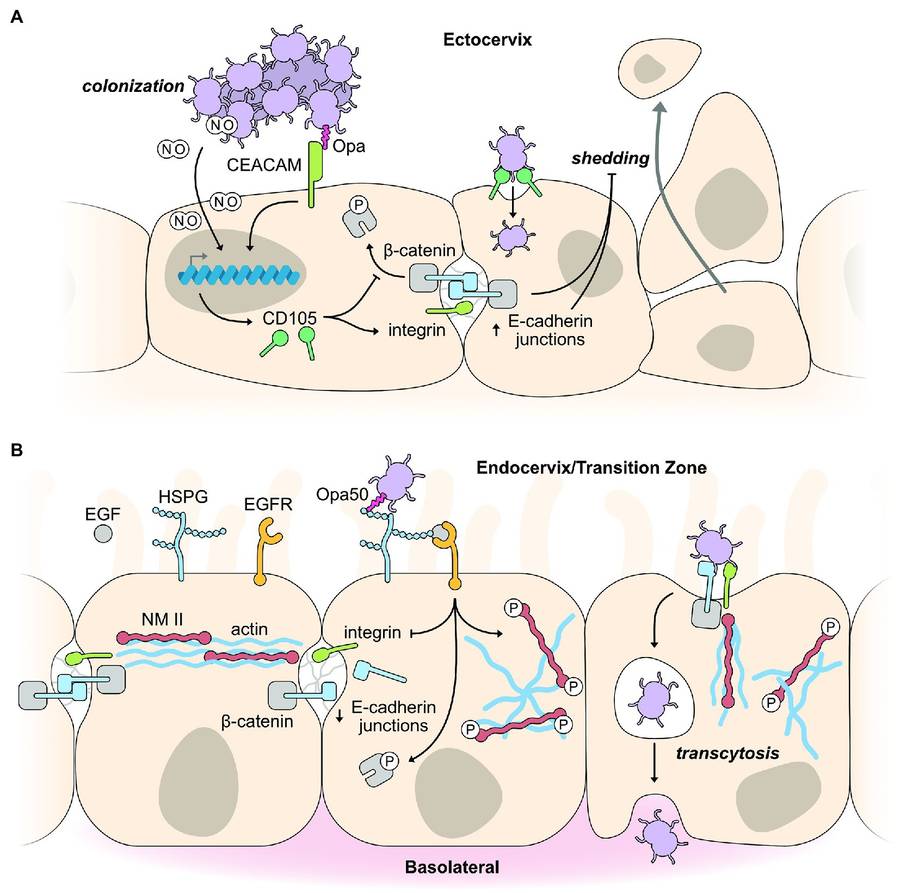 Fig.1 Exploitation of host epithelial cell signaling pathways for colonization and infection. (Walker E, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Exploitation of host epithelial cell signaling pathways for colonization and infection. (Walker E, et al., 2023)
Current Diagnostic Landscape of Gonorrhea
The diagnosis of gonorrhea relies primarily on nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), the gold standard due to their high sensitivity (>95%) and ability to detect asymptomatic infections from non-invasive samples like urine. Traditional methods, such as culture testing, remain critical for antibiotic susceptibility profiling but are limited by slow turnaround times (2-5 days) and stringent transport requirements. While Gram stain microscopy offers rapid results, its low sensitivity (∼50% in cervical samples) restricts utility.
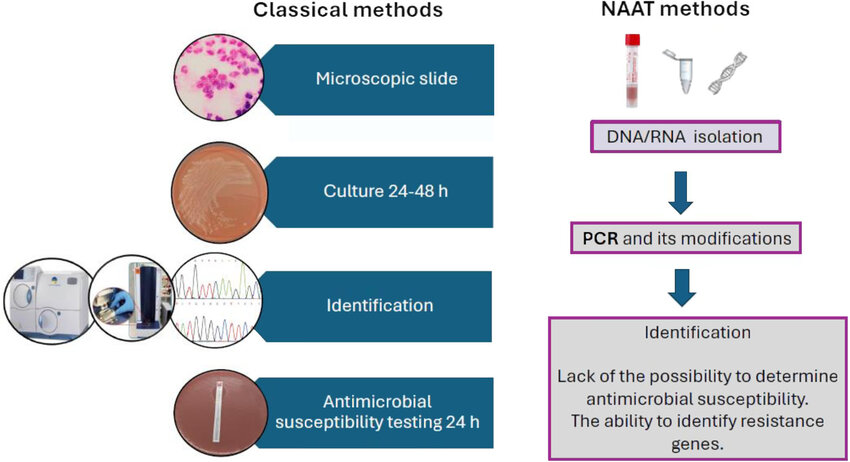 Fig.2 Methods used in the diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. (Białecka J, et al., 2024)
Fig.2 Methods used in the diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. (Białecka J, et al., 2024)
Cutting-Edge Technologies for Gonorrhea Diagnostics
Gonorrhea diagnostics have evolved from traditional culture methods to advanced molecular techniques, driven by the need for rapid, accurate detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and its antibiotic-resistant strains. Conventional methods like microscopy and culture remain relevant but are being supplemented or replaced by nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), point-of-care (POC) platforms, and emerging technologies such as microfluidics.
Conventional Diagnostic Methods
Gram stain microscopy offers rapid, low-cost screening but suffers from low sensitivity (~50–70% for cervical samples). Culture remains the gold standard for antibiotic susceptibility testing but requires 2–5 days and specialized lab conditions. While these methods persist in resource-limited areas, they are increasingly overshadowed by molecular techniques.
Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs)
NAATs (e.g., PCR, TMA) are the current gold standard, with >95% sensitivity for detecting N. gonorrhoeae DNA/RNA. Multiplex NAATs streamline STI panels by testing for gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis simultaneously. Their limitations include cost and lab dependency, spurring development of portable NAAT systems.
Point-of-Care (POC) Technologies
POC platforms deliver NAAT-level accuracy in <90 minutes, enabling same-day treatment. Emerging lateral flow assays target rapid, low-cost screening but currently lag in sensitivity (~80–90%) compared to NAATs.
Emerging Technologies
Microfluidics technologies enable compact, automated lab-on-a-chip devices for decentralized testing. Digital PCR and AI-based analysis are improving sensitivity and drug resistance prediction, although these technologies are still in development or early application stages.
Key Biomarkers for Precision Detection of Gonorrhea
Accurate diagnosis of gonorrhea relies on identifying specific biomarkers of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, including genetic, proteomic, and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) markers. These biomarkers enable precise detection, strain differentiation, and resistance monitoring—critical for effective treatment and public health surveillance.
- Genetic Biomarkers: porA, opa, pilA, cppB, etc.
- Antibiotic Resistance Markers: penA, ponA, gyrA, parC, 23S rRNA, rpsJ, etc.
- Proteomic & Metabolic Biomarkers: PorB, PilQ, TbpA, lactate, polyamines, IL-6, IL-8, etc.
- Emerging Biomarkers: rplL, recA, N-acetylglucosamine, etc.
Future of Gonorrhea Diagnostics
The future of gonorrhea diagnostics lies in integrated, next-generation solutions that combine ultra-sensitive detection, real-time AMR profiling, and AI-driven data analytics to combat silent transmission and antibiotic resistance. Emerging technologies like wearable biosensors, smartphone-connected POC devices, and at-home multiplex NAAT kits will democratize testing, while multi-omics biomarkers (genomic, proteomic, metabolic) enable precision diagnostics.
Alta DiagnoTech provides cutting-edge in vitro diagnostic (IVD) solutions for gonorrhea detection, offering a complete portfolio that includes highly accurate PCR-based genetic test kits, rapid antigen detection kits, and sensitive antibody assay kits. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us for more information or product support.
References
- Walker E, Van Niekerk S, Hanning K, et al. Mechanisms of host manipulation by Neisseria gonorrhoeae[J]. Frontiers in microbiology, 2023, 14: 1119834.
- Białecka J, Rak K, Kiecka A. Gonococci–Pathogens of Growing Importance. Part 1. Current Data on Diagnostics, Genotyping and Therapy[J]. Advancements of Microbiology, 2024, 63(1).
This article is for research use only. Do not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic application.



 Fig.1 Exploitation of host epithelial cell signaling pathways for colonization and infection. (Walker E, et al., 2023)
Fig.1 Exploitation of host epithelial cell signaling pathways for colonization and infection. (Walker E, et al., 2023) Fig.2 Methods used in the diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. (Białecka J, et al., 2024)
Fig.2 Methods used in the diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. (Białecka J, et al., 2024)